DPS Group and Aizon discuss how artificial intelligence is enabling adaptive modeling in process development and integrating activities in biomanufacturing.
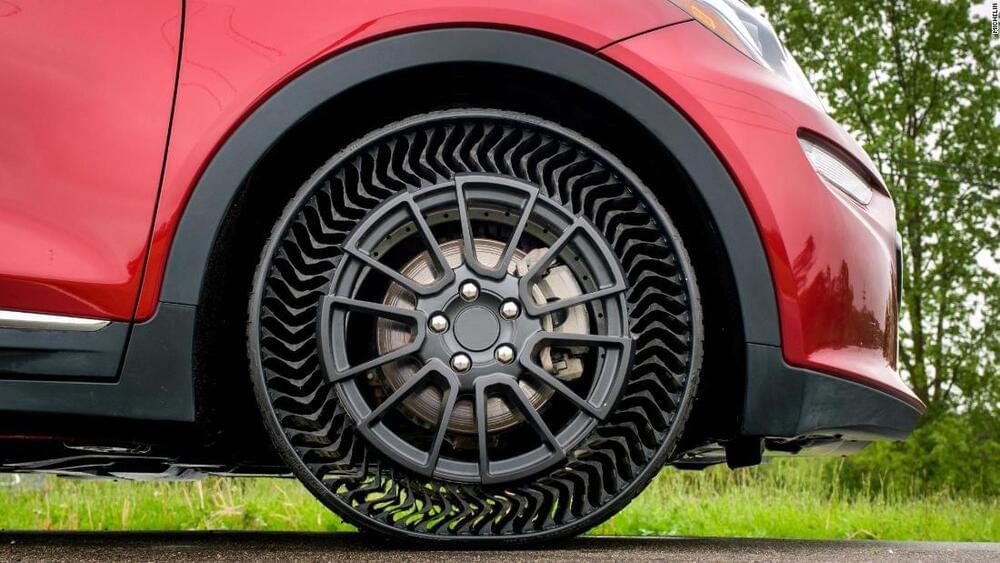



Michelin has been working with General Motors to develop airless tires that will be sold on a next-generation Chevrolet Bolt electric car, expected to go on sale in the next few years, a Michelin executive said. It could mark the decline of over 130 years of tire tradition but also the end of one of the most annoying aspects of car ownership: keeping air in the tires.
“We want to bring the next generation of the Chevrolet Bolt with airless tires,” Alexis Garcin, president of Michelin North America said in an interview with CNN Business, “and it’s going to happen now in the next three to five years.”
New solar panels that don’t need sunlight have been invented and could revolutionize the green energy initiative.
The idea of solar panels that don’t need sunlight might sound crazy, but it’s not completely impossible. As a cornerstone of the revolution to bring more clean energy to people, solar panels have become one of the best options out there. However, these energy conductors have one fatal flaw. They require direct sunlight to create energy. What if we could remove that flaw, though? That was the idea behind AuREUS, a new solar panel that doesn’t rely on direct sunlight to generate energy.
Don’t Miss: Amazon Prime price is going up, here’s how to pay the lower fee
But how do you make solar panels that don’t rely on sunlight? Well, you don’t. At least, not entirely. Instead, you make solar panels that can feed off the ultraviolet rays of the Sun that clouds don’t hinder.

The Martian rover has done the most!
NASA’s Perseverance rover has been on Mars for a full Earth year. During that time, the little robot has gotten pretty familiar with Mars’ terrain and set off a historic mission to find out if life ever existed on the Red Planet.
Perseverance landed on Mars on February 18 with an unprecedented task of collecting samples from the Martian landscape, storing them in tiny tubes, and leaving them on Mars for a future pickup mission.
Here are some of the highlights of that mission so far, and what to look forward to from the Perseverance rover in the future.
Solar panels are a cornerstone of the clean energy revolution. And yet, they have one great flaw: when the clouds roll in their productivity dives.
Now, a new type of solar panel has been developed by an electrical engineering student at Mapua University that harvests the unseen ultraviolet light from the sun that makes it through even dense cloud coverage. Maigue, who won the James Dyson Sustainability Award for his creation, hopes it will soon be used on the windows and walls of large buildings, turning them into constant sources of energy.
The solar panels, developed by student Carvey Maigue, won this year’s Dyson Sustainability Award. Click here to find out more.
Improving Lives Curing Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) — Dr. Sanjoy Dutta, Ph.D. — Chief Scientific Officer, JDRF
Dr. Sanjoy Dutta, PhD, is the Chief Scientific Officer at JDRF International (https://www.jdrf.org/) a nonprofit organization that funds Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) research, provides a broad array of community and activist services to the T1D population, and actively advocates for regulation favorable to medical research and approval of new and improved treatment modalities.
Dr. Dutta oversees all of JDRF’s efforts to cure Type 1 Diabetes and improve the lives of those living with it, which includes beta cell therapies, immunotherapies, glucose control and related disease complications. He is also responsible for international partnerships with world-leading government, non-government, foundation and commercial organizations. Dr. Dutta joined JDRF in 2009.
Prior to coming to JDRF, Dr. Dutta was the Associate Director of Translational Medicine and Clinical Biomarkers at Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Principal Scientist of Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases at Hoffmann-La Roche.
Dr. Dutta obtained his doctorate from the department of biochemistry and molecular biology at the University of Southern California and was a JDRF Postdoctoral Fellow in the department of cell biology and the Joslin Diabetes Center at Harvard Medical School.

Quaise Energy, a startup based in Cambridge, Massachusetts, has announced its intentions to revolutionize how conventional power plants produce electricity. They have developed a new type of drilling technology that they claim will allow virtually any power plant to convert to geothermal as a fuel source.
The new technology uses a gyrotron-powered drilling platform that vaporizes a borehole by emitting millimeter-sized energy waves from the tip of a drill bit. Engineers at Quaise have been working to perfect the technology for the past decade. The energy waves pulverize the rock as the hole is dug, allowing for digging much deeper than conventional drills. The energy waves, notably, are generated on the surface—their frequency is near to that used by microwaves.
Once the hole is excavated, water can be pumped into its depths, where the heat from the Earth will convert it to steam that rises back up out of the hole like a geyser. Also, the well can be used indefinitely to produce electricity using a geothermal source of energy, making it cheaper to produce electricity than conventional methods.
In recent years, scientists have introduced a wide variety of robots of all shapes and sizes. Among these are microswimmers, carefully engineered microstructures that can move in water and other liquids.
Microswimmers could have numerous interesting applications, for instance allowing doctors to deliver drugs to targeted regions inside the human body, or scientists to introduce specific substances in water-based environments. While some of these robotic systems achieved remarkable results, most of them were found to be unable to efficiently move inside the human body.
Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems (MPI-IS) have recently developed new light-driven microswimmers that could be more suited for navigating within biological systems, including body fluids. These microswimmers, introduced in a paper published in Science Robotics, are simple microparticles based on the two-dimensional (2D) carbon nitride poly(heptazine imide) or PHI.
