Device projects holographic images into brain to activate dozens of neurons at once, simulating real patterns of activity that fool the brain into perceiving things that aren’t there.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Bringing woolly mammoths back from extinction might not be such a bad idea — ethicists explain
An excellent article rebutting some of common negative reactions to the idea of de-extinction. I applaud George Church, Ben Lamm, and colleagues for their efforts to leverage the genomics revolution to recreate the wooly mammoth and the Thylacine. These represent exciting steps for repairing damaged ecosystems. Such approaches will also most likely have the side benefit of generating new technologies for biomedical applications. I’d love to see similar de-extinction efforts addressing loss of insect and microorganism biodiversity as well! #biotech #future #crispr #techforgood
When mammoths disappeared from the Arctic some 4,000 years ago, shrubs overtook what was previously grassland. Mammoth-like creatures could help restore this ecosystem by trampling shrubs, knocking over trees, and fertilising grasses with their faeces.
Theoretically, this could help reduce climate change. If the current Siberian permafrost melts, it will release potent greenhouse gases. Compared to tundra, grassland might reflect more light and keep the ground cooler, which Colossal hopes will prevent the permafrost from melting.
While the prospect of reviving extinct species has long been discussed by groups such as Revive and Restore, advances in genome editing have now brought such dreams close to reality. But just because we have the tools to resurrect mammoth-like creatures, does this mean we should?


3D-printed Martian rock and titanium alloy could be used on Mars to make rocket parts
GooKingSword/Pixabay.
Pretty interesting, right? But it could be possible one day with 3D printing technology.



How explainable artificial intelligence can propel the growth of industry 4.0
The very first industrial revolution historically kicked off with the introduction of steam-and water-powered technology. We have come a long way since then, with the current fourth industrial revolution, or Industry 4.0, being focused on utilizing new technology to boost industrial efficiency.
Some of these technologies include the internet of things (IoT), cloud computing, cyber-physical systems, and artificial intelligence (AI). AI is the key driver of Industry 4.0, automating intelligent machines to self-monitor, interpret, diagnose, and analyze all by themselves. AI methods, such as machine learning (ML), deep learning (DL), natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision (CV), help industries forecast their maintenance needs and cut down on downtime.
However, to ensure the smooth, stable deployment and integration of AI-based systems, the actions and results of these systems must be made comprehensible, or, in other words, “explainable” to experts. In this regard, explainable AI (XAI) focuses on developing algorithms that produce human-understandable results made by AI-based systems. Thus, XAI deployment is useful in Industry 4.0.
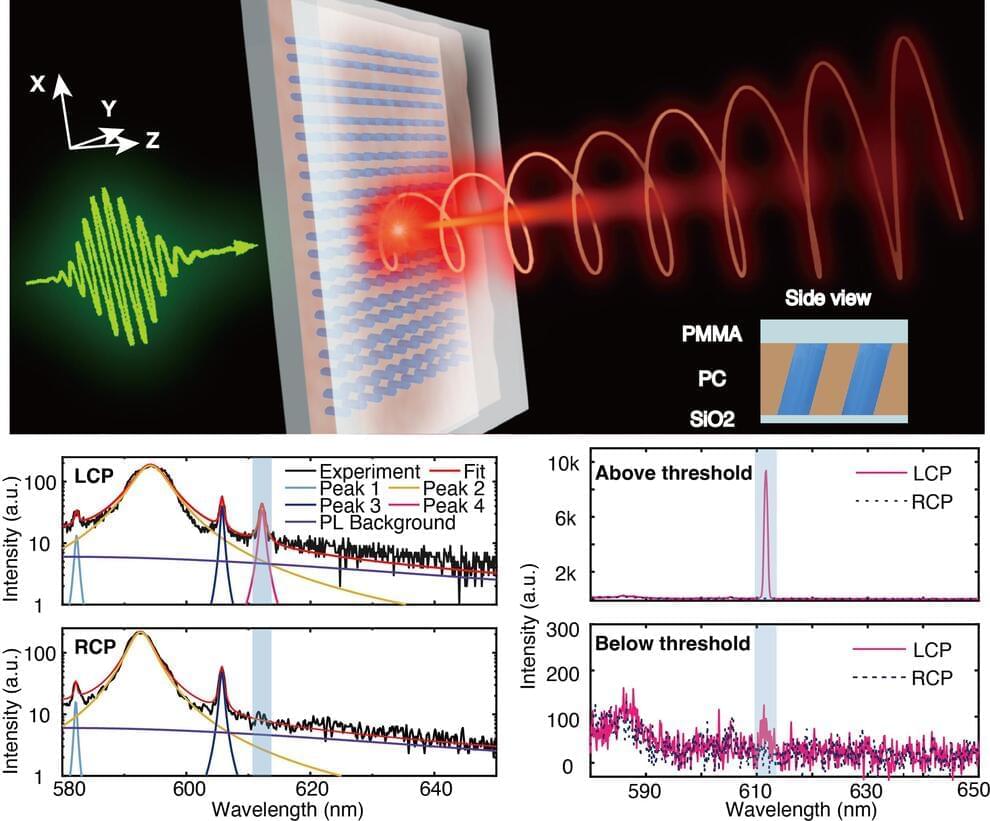
Chiral quasi bound states in the continuum for a high-purity circularly polarized light source
An ultracompact circularly polarized light source is a crucial component for the applications of classical and quantum optics information processing. The development of this field relies on the advances of two fields: quantum materials and chiral optical cavities. Conventional approaches for circularly polarized photoluminescence suffer from incoherent broadband emission, limited DOP, and large radiating angles. Their practical applications are constrained by low efficiency and energy waste to undesired handedness and emission directions. The chiral microlasers can have large DOPs and directional output, but only in specific power ranges. Most importantly, their subthreshold performances plummet significantly. Up to now, the strategy for simultaneous control of chiral spontaneous emission and chiral lasing is still absent.
In a new paper published in Science, researchers from Harbin Institute of Technology and Australian National University employ the physics of chiral quasi bound states in the continuum (BICs) and demonstrate the efficient and controllable emission of circularly polarized light from resonant metasurfaces.
BICs with integer topological charge in momentum space and a theoretically infinite Q factor have been explored for many applications including nonlinear optics and lasing. By introducing in-plane asymmetry, BICs turn to be quasi-BICs with finite but still high Q factors. Interestingly, the integer topological charge of BICs mode would split into two half integer charges, which symmetrically distribute in momentum space and correspond to left-and right-handed circular polarization states, also known as C points.
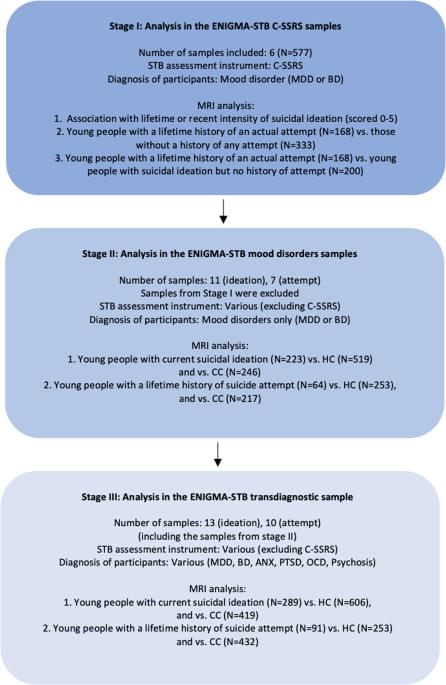
Structural brain alterations associated with suicidal thoughts and behaviors in young people: results from 21 international studies from the ENIGMA Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviours consortium
Suicide is the second leading cause of death for young people aged between 15 and 29 [1]. Suicidal thoughts and behaviors (STBs) typically emerge during adolescence [2]. It has been estimated that between 11 and 29% of adolescents report suicidal ideation (suicidal thoughts), and 2–10% of adolescents attempted suicide in the past year [3]. Unfortunately, the number of suicide attempts among children and adolescents has continued to increase sharply despite national and international prevention efforts [4].
To improve targeting of prevention and intervention efforts and thereby reduce the number of deaths by suicide in this age group, we must increase our understanding of the mechanisms underlying both suicidal thoughts and suicidal behaviors (including suicide attempts) in young people. Neuroimaging, including Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), is a useful tool with which to identify biological risk markers for STBs in vivo and non-invasively. Many neuroimaging studies have been published examining the neural substrates of STBs in the past 20 years, but few have focused on STBs in youth (for a review, see [5]). Although several of these studies support lower regional brain volumes, particularly in ventral and dorsal prefrontal and also in temporal regions [6,7,8,9] in suicide attempters with mood disorders, negative findings have also been reported [10, 11].