“Machines Like Us” argues that the artificial intelligence community needs to revisit symbolic reasoning to solve AI’s “common sense” problem.



Physicists love to smash particles together and study the resulting chaos. Therein lies the discovery of new particles and strange physics, generated for tiny fractions of a second and recreating conditions often not seen in our universe for billions of years. But for the magic to happen, two beams of particles must first collide.
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory have announced the first successful demonstration of a new technique that improves particle beams. Future particle accelerators could potentially use the method to create better, denser particle beams, increasing the number of collisions and giving researchers a better chance to explore rare physics phenomena that help us understand our universe. The team published its findings in a recent edition of Nature.


An international collaboration of scientists has created and observed an entirely new class of vortices—the whirling masses of fluid or air.
Led by researchers from Amherst College in the U.S. and the University of East Anglia and Lancaster University in the U.K., their new paper details the first laboratory studies of these “exotic” whirlpools in an ultracold gas of atoms at temperatures as low as tens of billionths of a degree above absolute zero.
The discovery, announced this week in the journal Nature Communications, may have exciting future implications for implementations of quantum information and computing.
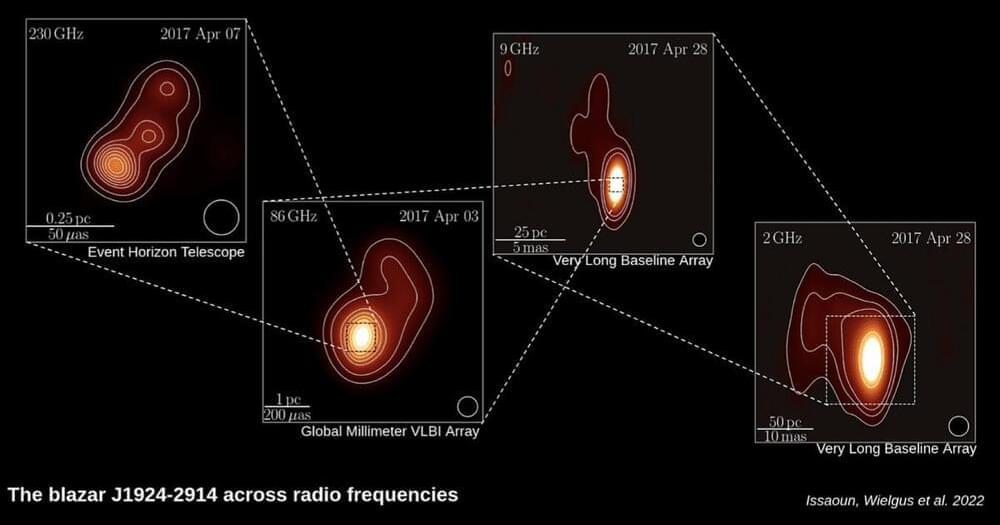
Having a virtual telescope the size of Earth continues to pay off.
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) has released new observations that are once again at the cutting edge of science. The team that gave us the first image of our very own supermassive black hole has now revealed the most detailed radio image of a blazer, J1924-2914.
A blazar, not to be confused with a bright dinner jacket, is an active supermassive black hole whose jet is being shot towards us. The EHT has delivered observations with unprecedented angular resolution: it can resolve structures within 3 light-years of the black hole. Not bad given the host galaxy is located over 4 billion light-years from us.
Published in The Astrophysical Journal, the achievement is based on data conducted during the original observation campaign in April 2017 that gave us the first-ever image of a black hole. The team studied structures just a few light-years in size to hundreds of light-years wide thanks to the combination of multiple observatories around the world acting as one Earth-sized telescope.

SpaceX ignited engines on both the first and second stages of its Starship launch system on Wednesday, signaling that it is getting closer to a test flight of the massive rocket later this year.
On Monday evening at 5:20 pm local time in South Texas, engineers ignited a single Raptor engine on the Super Heavy booster that serves as the rocket’s first stage. This is the first time the company has conducted a static fire test of the booster, which will ultimately be powered by 33 Raptor rocket engines.
About three hours later, on a separate mount at its “Starbase” facility in Texas, SpaceX ignited two engines on the Starship upper stage of the rocket. The company later shared a short video on Twitter of the evidently successful test.
A battle for mainstream GPUs could start later this year.
Intel has released 48 benchmarks that show its upcoming Arc A750 GPU should be able to trade blows with Nvidia’s RTX 3,060 running modern games. While Intel set its expectations low for its Arc GPUs last month, the company has now tested its A750 directly against the RTX 3,060 across 42 DirectX 12 titles and six Vulkan games.
The results look promising for what will likely be Intel’s mainstream GPU later this year. Intel has tested the A750 against popular games like Fortnite, Control, and Call of Duty: Warzone, instead of the cherry picked handful of benchmarks the company released last month.
“These are all titles that we picked because they’re popular,” explains Intel fellow Tom Petersen, in Intel’s benchmark video. “Either reviewers are using them or they’re high on the Steam survey, or new and exciting. These are not cherry picked titles.”

A perovskite solar cell developed by engineers at the University of California San Diego brings researchers closer to breaking the ceiling on solar cell efficiency, suggests a study published Aug. 10 in Nature.
The new solar cell is a lead-free low-dimensional perovskite material with a superlattice crystal structure —a first in the field. What’s special about this material is that it exhibits efficient carrier dynamics in three dimensions, and its device orientation can be perpendicular to the electrodes. Materials in this particular class of perovskites have so far only exhibited such dynamics in two dimensions—a perpendicularly orientated solar cell has never been reported.
Thanks to its specific structure, this new type of superlattice solar cell reaches an efficiency of 12.36%, which is the highest reported for lead-free low-dimensional perovskite solar cells (the previous record holder’s efficiency is 8.82%). The new solar cell also has an unusual open-circuit voltage of 0.967 V, which is higher than the theoretical limit of 0.802 V. Both results have been independently certified.
