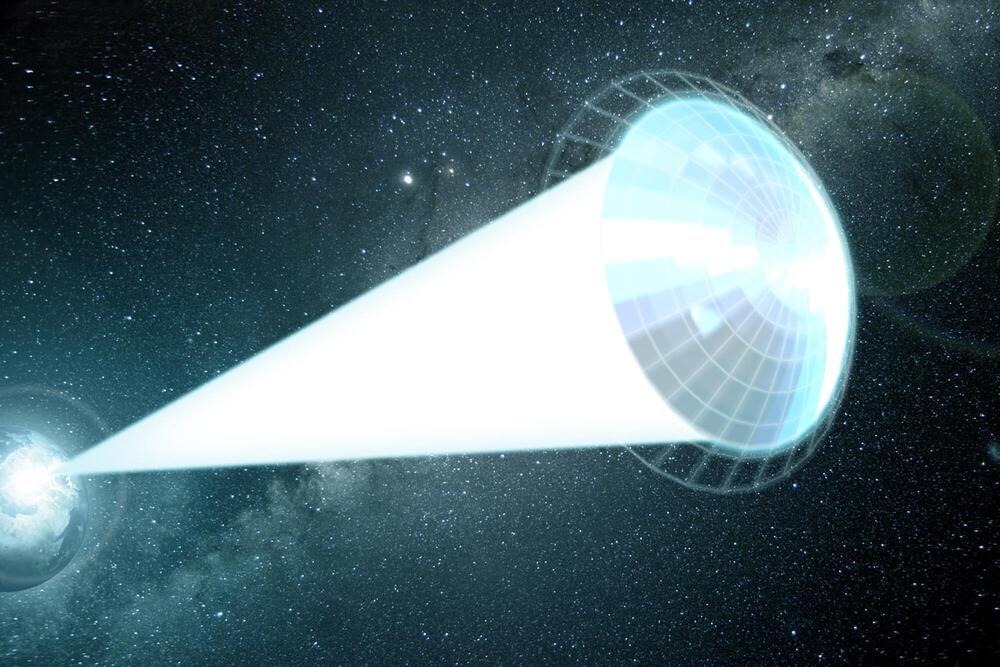
Astronomers have been waiting decades for the launch of the James Webb Space Telescope, which promises to peer farther into space than ever before. But if humans want to actually reach our nearest stellar neighbor, they will need to wait quite a bit longer: a probe sent to Alpha Centauri with a rocket would need roughly 80,000 years to make the trip.
Igor Bargatin, Associate Professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics, is trying to solve this futuristic problem with ideas taken from one of humanity’s oldest transportation technologies: the sail.
As part of the Breakthrough Starshot Initiative, he and his colleagues are designing the size, shape and materials for a sail pushed not by wind, but by light.