
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.


The Omnid Mocobots: New mobile robots for safe and effective collaboration
Teams of mobile robots could be highly effective in helping humans to complete straining manual tasks, such as manufacturing processes or the transportation of heavy objects. In recent years, some of these robots have already been tested and introduced in real-world settings, attaining very promising results.
Researchers at Northwestern University’s Center for Robotics and Biosystems have recently developed new collaborative mobile robots, dubbed Omnid Mocobots. These robots, introduced in a paper pre-published on arXiv, are designed to cooperate with each other and with humans to safely pick up, handle, and transport delicate and flexible payloads.
“The Center for Robotics and Biosystems has a long history building robots that collaborate physically with humans,” Matthew Elwin, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told TechXplore. “In fact, the term ‘cobots’ was coined here. The inspiration for the current work was manufacturing, warehouse, and construction tasks involving manipulating large, articulated, or flexible objects, where it is helpful to have several robots supporting the object.”

Space Command moving to Alabama: 4 steps remain; what’s next?
The U.S. Space Command’s proposed move to Huntsville passed a big test July 13 when the Pentagon released a draft environmental assessment finding “no significant impacts on the human or natural environment” if the headquarters is built on the Redstone Arsenal site.
Although there remain four steps ahead of the move, Republican U.S. Sen. Tommy Tuberville of Alabama said the environmental assessment should be the last major hurdle for the plan to move the command from startup headquarters in Colorado to a permanent site. The move would bring 1,800 headquarters staff and their families to north Alabama.
“The Redstone Arsenal site is the (Department of the Air Force’s) Preferred Alternative for implementation of the Proposed Action,” the environmental assessment said. The proposed action is a permanent headquarters.

Huge network of 11,000 fake investment sites targets Europe
Researchers have uncovered a gigantic network of more than 11,000 domains used to promote numerous fake investment schemes to users in Europe.
The platforms show fabricated evidence of enrichment and falsified celebrity endorsements to create an image of legitimacy and lure in a larger number of victims.
The goal of the operation is to trick users into an opportunity for high-return investments and convince them to deposit a minimum amount of 250 EUR ($255) to sign up for the fake services.
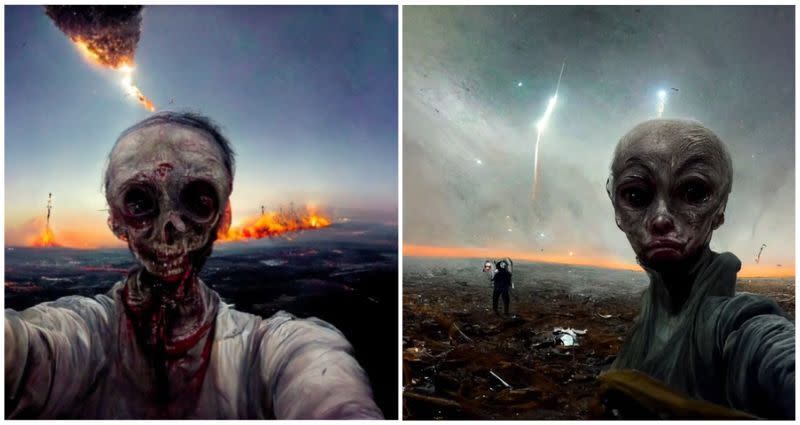


AI’s prediction of what last selfies on Earth would look like are total nightmare fuel
🤔 I certainly hope not!
An artificial intelligence program asked to predict what “the last selfie ever taken” would look like resulted in several nightmarish images.
TikTok account Robot Overloards, which dedicates its page to providing viewers with “daily disturbing AI generated images,” uploaded a video on Sunday where the AI DALL-E was asked to predict what the last selfies on Earth would look like.
The images produced showed bloody, mutilated humans taking selfies amongst apocalyptic scenes. One “selfie” shows a skeleton-like man holding the camera for a selfie with dark hills on fire and smoke in the air behind him.
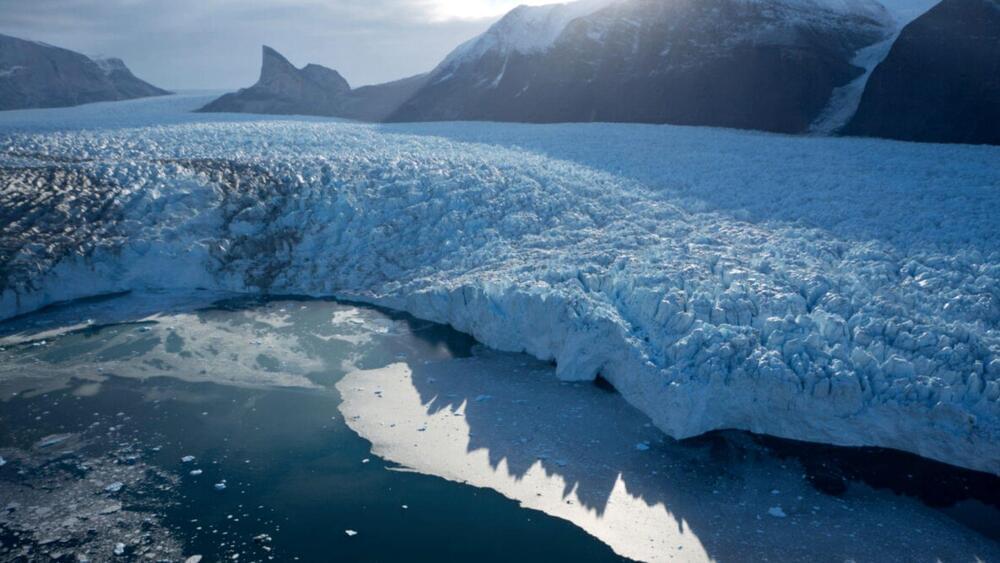


A new robotic submersible could unlock the mysteries of Greenland’s underwater glaciers
You’re in for a surprise.
Picture the ocean, impacted by climate change.
Rising sea levels, ocean acidification, melting of ice sheets, flooded coastlines, and shrinking fish stocks — the image is largely negative. For the longest time, the ocean has been portrayed as a victim of climate change, and rightly so. Ulf Riebesell, Professor of Biological Oceanography at the Geomar Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel, has studied the effects of global warming on the ocean for nearly 15 years, warning the scientific community about the impacts of climate change on ocean life and biochemical cycles. countries aiming to achieve a climate-neutral world by mid-century, experts have decided to include the ocean to tackle climate change.