Dropbox is a free service that lets you bring your photos, docs, and videos anywhere and share them easily. Never email yourself a file again!



Quantum mechanics, the theory which rules the microworld of atoms and particles, certainly has the X factor. Unlike many other areas of physics, it is bizarre and counter-intuitive, which makes it dazzling and intriguing. When the 2022 Nobel prize in physics was awarded to Alain Aspect, John Clauser and Anton Zeilinger for research shedding light on quantum mechanics, it sparked excitement and discussion.
But debates about quantum mechanics —be they on chat forums, in the media or in science fiction—can often get muddled thanks to a number of persistent myths and misconceptions. Here are four.

ISRIB, a tiny molecule identified by University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) researchers can repair the neural and cognitive effects of concussion in mice weeks after the damage, according to a new study.
ISRIB blocks the integrated stress response (ISR), a quality control process for protein production that, when activated chronically, can be harmful to cells.
The study, which was recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, discovered that ISRIB reverses the effects of traumatic brain injury (TBI) on dendritic spines, an area of neurons vital to cognition. The drug-treated mice also showed sustained improvements in working memory.
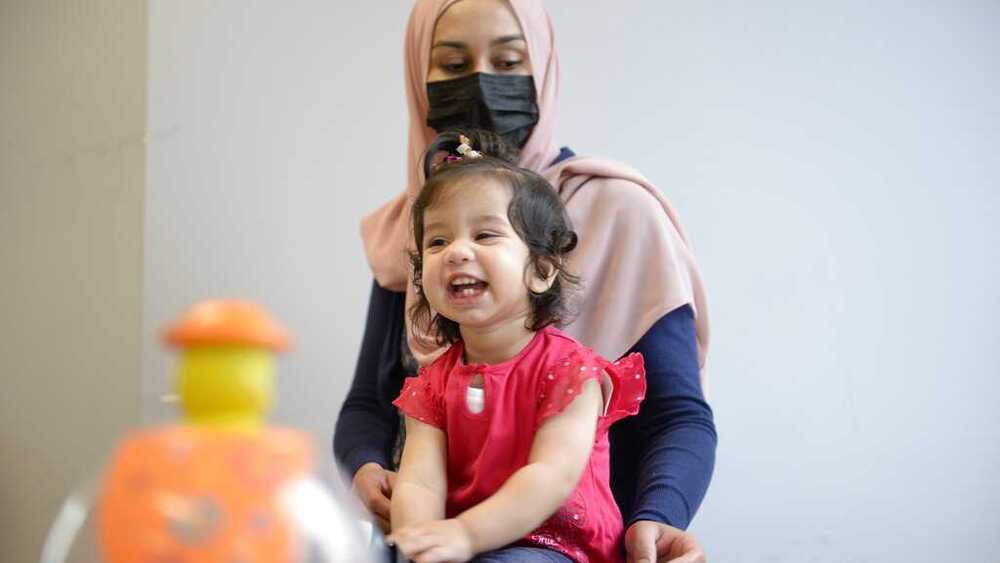


A toddler is thriving after doctors in the U.S. and Canada used a novel technique to treat her before she was born for a rare genetic disease that caused the deaths of two of her sisters.
Ayla Bashir, a 16-month-old from Ottawa, Ontario, is the first child treated as a fetus for Pompe disease, an inherited and often fatal disorder in which the body fails to make some or all of a crucial protein.

Arthur C. Clarke, science fiction author and futurist, crossed paths with the scientists of the Bell System on numerous occasions. In 1945, he concurrently, but independently, conceived of the first concept for a communications satellite at the same time as Bell Labs scientist, John Robinson Pierce too, was a science fiction writer. To avoid any conflict with his day job at Bell Labs, Pierce published his stories under the pseudonym J.J. Coupling.
In the early 1960s, Clarke visited Pierce at Bell Labs. During his visit, Clarke saw and heard the voice synthesis experiments going on at the labs by John L. Kelly and Max Mathews, including Mathews’ computer vocal version of “Bicycle Built for Two”. Clarke later incorporated this singing computer into the climactic scene in the screenplay for the movie 2001: A Space Odyssey, where the computer HAL9000 sings the same song. According to Bob Lucky, another Bell Labs scientist, on the same visit, Clarke also saw an early Picturephone, and incorporated that into 2001 as well.
In 1976, AT&T and MIT held a conference on futurism and technology, attended by scientists, theorists, academics and futurists. This interview with Clarke during this conference is remarkably prescient—especially about the evolution of communications systems for the next 30+ years.
The interview was conducted for an episode of a Bell System newsmagazine, but this is the raw interview footage.
Footage courtesy of AT&T archives and history center, warren, NJ.
Ukraine’s president says he wants to start raising funds to buy “a whole fleet of sea drones.” Kyiv used sea drones to attack the Russian Black Sea fleet in the end of October, and according to the Ukrainian military, they hit three Russian warships.
Meanwhile, for weeks now the Russian military has been flying explosive-laden “Iranian drones” into critical Ukrainian infrastructure facilities and residential areas. Although British intelligence says most of the drones are now intercepted by air defenses, a third still reach their targets. Ukraine’s prime minister, Denys Shmyhal, has said the Russians use “20 to 30 Iranian ‘kamikaze’ drones’” every day.
Subscribe: https://www.youtube.com/user/deutschewelleenglish?sub_confirmation=1
For more news go to: http://www.dw.com/en/
Follow DW on social media:
►Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/deutschewellenews/
►Twitter: https://twitter.com/dwnews.
►Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/dwnews.
►Twitch: https://www.twitch.tv/dwnews_hangout.
Für Videos in deutscher Sprache besuchen Sie: https://www.youtube.com/dwdeutsch.
#Ukraine #Russia #Drones
