When California announces anything to do with automobiles we tend to sit up and take notice.
New policy along with the federal Inflation Reduction Act should accelerate the production and adoption of EVs in the U.S. and elsewhere.

NASA is about to perform the first-ever launch of its next-generation rocket and spacecraft in a highly anticipated lunar mission, and you can watch the entire event online.
The Artemis I mission, which is scheduled to launch from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, August 29, will usher in a new era of space exploration as NASA eyes lengthy crewed stays on the moon and the first astronaut voyage to Mars.
Monday’s launch involves the 98-meter-tall Space Launch System (SLS), the most powerful rocket NASA has ever built, and the Orion spacecraft, the space agency’s next-generation crew capsule.
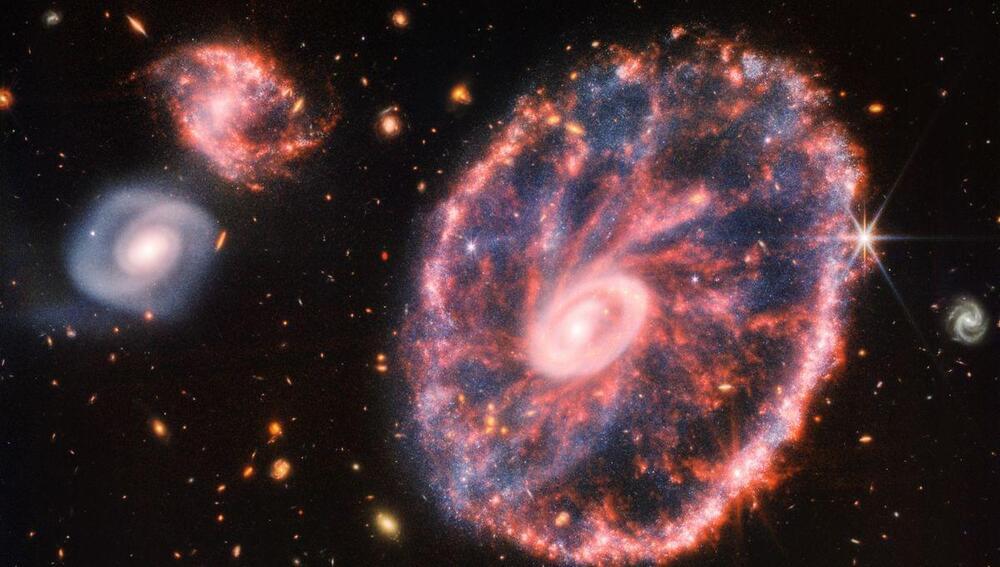

The stunning observation of the Cartwheel galaxy by JWST has revealed the exceptional ability that the latest space observatory has. The birthplace of new stars, the hot gas, and the activity of the supermassive black hole are all shining in this incredible photograph. But there’s more. Now you can sit back, relax, and fly towards that galaxy like a starship captain thanks to a video reconstruction that takes you from here to there.
It is located 500 million light-years away and you’ll start by passing a lot of nearby stars and the odd galaxy until the cartwheel galaxy and some near and far galaxies come into view and get closer and closer. The released image itself was incredible but seeing in the video how a little speck of darkness becomes a galaxy 145,000 light-years across is absolutely mind-blowing.
The Cartwheel is a galaxy merger. It underwent a bullseye-style collision with a smaller companion within the last one billion years, causing the spiral arms that would be expected for such a galaxy to disappear into two expanding circles. And the “spokes” are the galaxy slowly trying to reform its normal spiral shape. This is a process that will last for millions of years so we can continue to enjoy the incredible object for a long time yet.
SUSTech.
Researchers succeeded in a 3D printing strategy to construct flexible and stretchable light-emitting devices that can be integrated with soft robots.

It’s official: Apple has just sent out invites for its next hardware event. As expected, the company will share what it’s been working on for the past year on September 7th, with a live broadcast from Apple Park starting at 1PM ET. The invite features the words “Far out.” Make of that what you will.
The company is widely expected to announce four new iPhone models at the event. Leading up to today’s announcement, most reports have suggested the 2022 iPhone lineup will consist of a 6.1-inch iPhone 14, a 6.7-inch iPhone 14 Max, a 6.1-inch iPhone 14 Pro and a 6.7-inch iPhone 14 Pro Max. Apple reportedly won’t offer a new “mini” model this year due to lackluster sales of the iPhone 12 mini and iPhone 13 mini.
Enhancements on the standard iPhone 14 models reportedly include the addition of more RAM, longer-lasting batteries and a better selfie camera with autofocus. Meanwhile, the Pro models are expected to feature a new design that trades away Apple’s signature display notch for a Samsung-style hole-punch front camera cutout. Additionally, the Pro variants will reportedly feature a new 48-megapixel main camera and thinner display bezels. They’re also expected to be the only models to ship with Apple’s next-generation A16 chip.
SURPRISE BECAUSE SCIENCE CHANNEL! Subscribe now and click the shiny notifications bell so you don’t miss out on all things science and pop culture.
http://bit.ly/BecSciSub.
Subscribe for more Because Science: http://nerdi.st/subscribe.
Watch the last episode: http://nerdi.st/1KBPBhK
With the release of Nerdist Presents: The Hive, we have to wonder are there any NON-evil Hive minds in real life?? Kyle explores real life collective intelligence on this week’s Because Science!
More science: https://nerdist.com/topic/science-tech/
Watch more Because Science: http://nerdi.st/BecSci.
Follow Kyle Hill: https://twitter.com/Sci_Phile.
Follow Us: https://twitter.com/NerdistDotCom.
Because Science every Thursday.
Artist: Andrew Bowser.
TABLE OF CONTENTS —————
0:00–15:11 : Introduction.
15:11–36:12 CHAPTER 1: POSTHUMANISM
a. Neurotechnology b. Neurophilosophy c. Teilhard de Chardin and the Noosphere.
TWITTER https://twitter.com/Transhumanian.
PATREON https://www.patreon.com/transhumania.
BITCOIN 14ZMLNppEdZCN4bu8FB1BwDaxbWteQKs8i.
BITCOIN CASH 1LhXJjN4FrfJh8LywR3dLG2uGXSaZjey9f.
ETHEREUM 0x1f89b261562C8D4C14aA01590EB42b2378572164
LITECOIN LdB94n8sTUXBto5ZKt82YhEsEmxomFGz3j.
CHAINLINK 0xDF560E12fF416eC2D4BAECC66E323C56af2f6666.
POSTHUMAN TECHNOLOGY
36:12–54:39 CHAPTER 2 : TELEPATHY/ MIND-READING
a. MRI
b. fMRI
c. EEG
d. Cognitive Liberty e. Dream-recording, Dream-economies f. Social Credit Systems g. Libertism VS Determinism.
1:02:07–1:25:48 : CHAPTER 3 : MEMORY/ MIND-AUGMENTING
a. Memory Erasure and Neuroplasticity b. Longterm Potentiation (LTP/LTD)
c. Propanolol d. Optogenetics e. Neuromodulation f. Memory-hacking g. Postmodern Dystopias h. Total Recall, the Matrix, and Eternal Sunshine of the Spotless Mind i. Custom reality and identity.
1:25:48–1:45:14 CHAPTER 4 : BCI/ MIND-UPGRADING
Start listening with a 30-day Audible trial and your first audiobook plus two Audible Originals are free. Visit.
http://www.audible.com/isaac or text “isaac” to 500–500.
Cloning people is a staple of science fiction, and now something science can do, but what are the future social and legal consequences of cloning, and can we learn to make fully grown clones or even duplicate our memories?
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Support us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/IsaacArthur.
SFIA Merchandise available: https://www.signil.com/sfia/
Social Media:
Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/1583992725237264/
Reddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/IsaacArthur/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Isaac_A_Arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: https://discord.gg/53GAShE
Listen or Download the audio of this episode from Soundcloud: Episode’s Audio-only version: https://soundcloud.com/isaac-arthur-148927746/cloning-duplication.
Episode’s Narration-only version: https://soundcloud.com/isaac-arthur-148927746/cloning-duplication-narration-only.
Credits: me, myself, and I: cloning & duplication.
Written by:
All around smart guy Dr Goerge Church talking about genetic engineering technologies.
George Church, Ph.D. is a professor of genetics at Harvard Medical School and of health sciences and technology at both Harvard and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Dr. Church played an instrumental role in the Human Genome Project and is widely recognized as one of the premier scientists in the fields of gene editing technology and synthetic biology.
EPISODE LINKS:
Show notes and transcript: https://www.foundmyfitness.com/episodes/george-church.
Dr. George Church on Twitter: https://twitter.com/geochurch.
Dr. George Church on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/george.church.
Church lab: https://arep.med.harvard.edu/
Regenesis Book: https://www.amazon.com/Regenesis-Synthetic-Biology-Reinvent-…atfound-20
PODCAST INFO:
Email: https://www.foundmyfitness.com/newsletter.
Apple Podcasts: https://podcasts.apple.com/us/podcast/foundmyfitness/id818198322
Spotify: https://open.spotify.com/show/5QjpaU0o1Q2MkVZwwG3y7d.
RSS: https://podcast.foundmyfitness.com/rss.xml.
CHAPTERS: