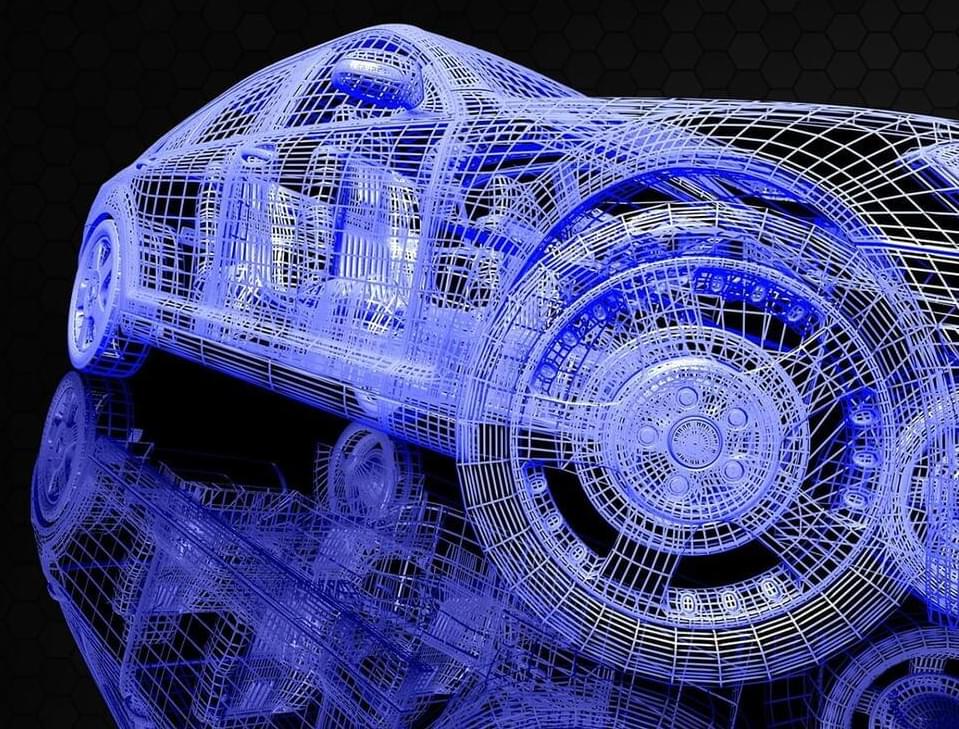
BMW’s adoption of Nvidia’s Omniverse helps the company overcome some of the most challenging barriers to expanding product lines.
Dr. Ben Goertzel with Philip K. Dick at the Web Summit in Lisbon 2019.
Ben showcases the use of OpenCog within the SingularityNET enviroment which is powering the AI of the Philip K. Dick Robot.
We apologise for the poor audio quality.
SingularityNET is a decentralized marketplace for artificial intelligence. We aim to create the world’s global brain with a full-stack AI solution powered by a decentralized protocol.
We gathered the leading minds in machine learning and blockchain to democratize access to AI technology. Now anyone can take advantage of a global network of AI algorithms, services, and agents.
Website: https://singularitynet.io.
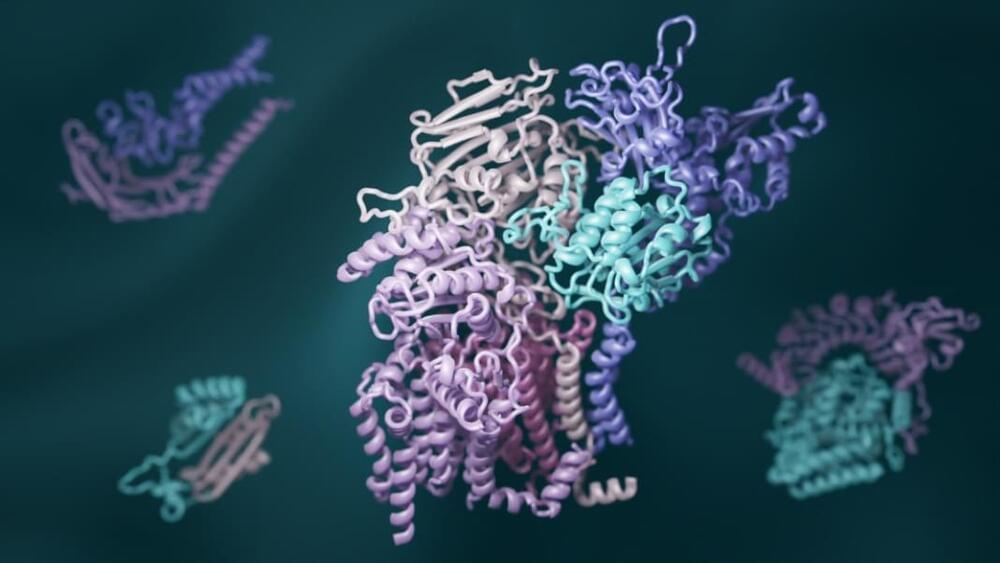
This month, the UW team upped their game.
Tapping into both AlphaFold and RoseTTAFold, they tweaked the programs to predict which proteins are likely to tag-team and sketched up the resulting complexes into a 3D models.
Using AI, the team predicted hundreds of complexes—many of which are entirely new—that regulate DNA repair, govern the cell’s digestive system, and perform other critical biological functions. These under-the-hood insights could impact the next generation of DNA editors and spur new treatments for neurodegenerative disorders or anti-aging therapies.
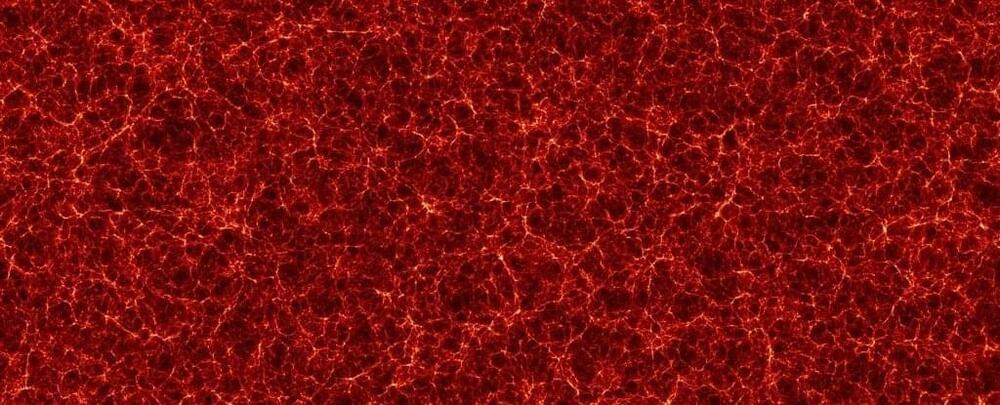
Today, the greatest mysteries facing astronomers and cosmologists are the roles gravitational attraction and cosmic expansion play in the evolution of the Universe.
To resolve these mysteries, astronomers and cosmologists are taking a two-pronged approach. These consist of directly observing the cosmos to observe these forces at work while attempting to find theoretical resolutions for observed behaviors – such as dark matter and dark energy.
In between these two approaches, scientists model cosmic evolution with computer simulations to see if observations align with theoretical predictions. The latest of which is AbacusSummit, a simulation suite created by the Flatiron Institute’s Center for Computational Astrophysics (CCA) and the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA).
*Food Out Of Thin Air. Just Might Work: Revolutionary protein production from renewable electricity and air.*
Solar Foods was chosen as one of the international winners of @NASA ‘s and @csa_asc ‘s @DeepSpaceFood Challenge Nov 15, 2021!
“I chose one whose cutting-edge technology can literally create food out of thin air,” said Martha Stewart, chef and judge. ## ## See also
**Three Minute Science Presentations that change the world. With examples of FAmeLab, ePatch, Solein ** https://youtu.be/6C8vECI77Oo.
**Zoomers of the Sunshine Coast ** Providing independent, moderated, timely, deep, gentle, clinical & community information regarding Covid19 and other topics. https://www.facebook.com/groups/1632045180447285
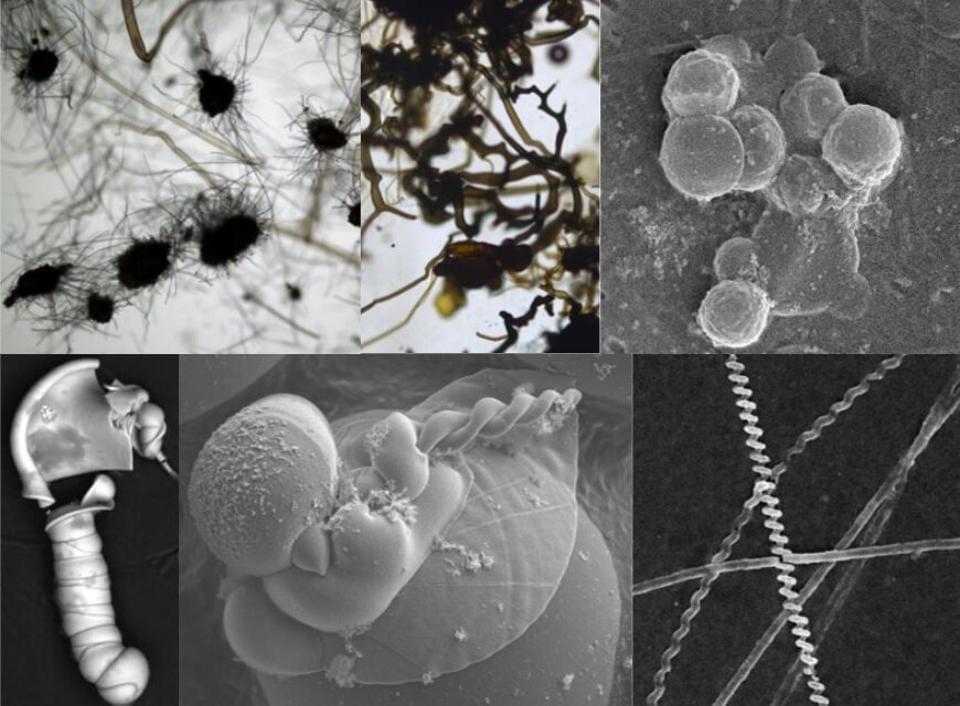
Geological evidence suggests that Mars was temporarily habitable three billion years ago when liquid water existed on the surface of the planet. Because life had little time to develop and flourish, possible microfossils found in the Martian rocks will likely resemble simple organisms. On Earth, life persisted for over three billion years in the form of single-celled bacteria and algae.
In a new open-access study published in the Journal of the Geological Society, the two authors, astrobiologists Sean McMahon and Julie Cosmidis from the Universities of Edinburgh and Oxford, note that the origins of any fossil-like specimens found on Mars are likely to be very ambiguous.
Rocks on Mars may contain numerous types of pseudofossils, structures formed by chemical processes or minerals resembling organic structures, that look similar to the kinds of fossils likely to be found if the planet ever supported life, a press release provided by University of Edinburgh explains.
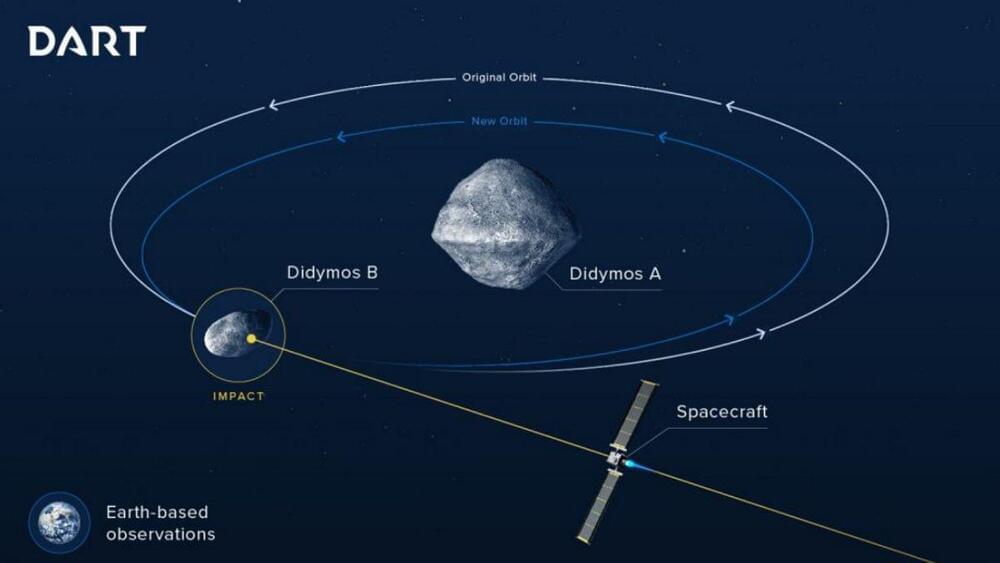
“We know of no asteroids that are coming in to hit the Earth,” Rivkin emphasizes. DART, he says, is part of a multi-pronged effort to examine the asteroid collision problem. “Asteroid impacts are really the only natural disaster that humanity can see coming years or decades in advance and do anything about.”
NASA calls DART its “First Planetary Defense Test Mission.” Rivkin is the DART investigation team lead at Johns Hopkins University’s Applied Physics Laboratory, which is running the experiment for NASA.
Full Story:
Andy Rivkin remembers going to the arcade in the early 1980s to play the iconic video game “Asteroids.” Later this month, the team he leads is scheduled to launch a satellite aimed at an asteroid 7 million miles away to prove that Earthlings can save themselves from an asteroid impact by shooting first, Atari-style.
The launch window for NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) mission opens next week. DART is an experiment to see if by crashing a spacecraft directly into an asteroid, the asteroid can be nudged off its trajectory. If intercepted and struck far enough away, even a slight alteration in the path of an asteroid could cause it to miss Earth, avoiding a potentially catastrophic impact.
The year is almost at an end, and so it is once again time for the obligatory trends articles (Trends for 2022). We already know that AI is impacting every industry. In past articles I have covered “The tipping point”, the fact that AI is already immersed in our daily lives and with no end in sight. Here I outline seven areas where we can expect a greater involvement of AI in the lives of all of us, in 2022.
Data marketplaces.
AI thrives on data, and the rise and ubiquity of AI has placed a yet greater emphasis on the value of data as both a competitive advantage and a core asset to companies and countries alike. This in turn has risen to privacy laws and efforts to educate the public on how their data can be used. These efforts are geared towards giving individuals agency in exercising their data rights. The confluence of these factors is already leading to data marketplaces. Data marketplaces are online venues where individuals and corporations can buy and sell data. Data marketplaces have the potential to combine democratized access, privacy controls and monetization models to enable data owners to benefit from data use.
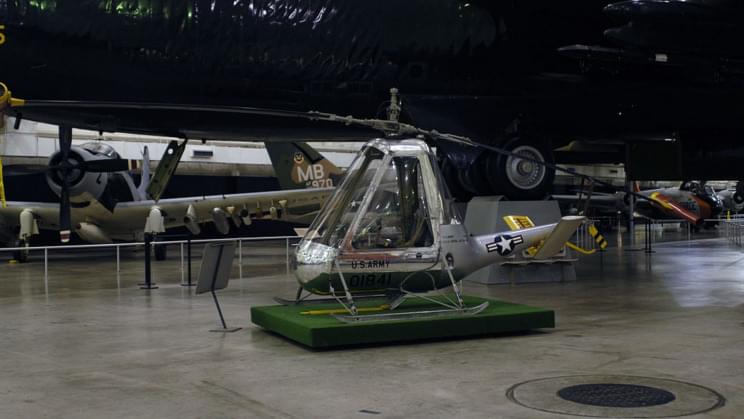
Five prototypes were tested before the project was shelved.
In what might seem counter-intuitive at first, the U.S. Army supported the development of a helicopter that had no engine. One can even visit the Army’s Aviation Museum at Fort Rucker in Alabama to catch a glimpse of this design by the American Helicopter Company that is fondly called Jet Jeep.
The Jet Jeep was thought of many decades ago as the solution for a light observation needed by the Army. The U.S. Army was looking for a flight-capable option for light surveillance and by that, it meant enough to carry one or two people at the most. This is quite like the problem jet pack makers are trying to solve these days. But this was way back in the 1950s and helicopters and aircraft were largely the way flying worked.
So, the U.S Air Force took upon this task and made a lighter version of the helicopter, XH-26, by skipping the bigger engine. Instead, it put two AJ7.5–1 pulse jets at the end of each of its rotors and was also successful in avoiding the transmission system, which reduced its weight further, the U.S. Army’s website said.
Full Story: