Europol’s Operation SIMCARTEL dismantled a SIM farm used for 49M fake accounts and €5M in fraud.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.


Unified Equation: A Berry-Curvature Theory of Quantum Gravity, Entanglement, and Mass Emergence
Many Thanks to Sabine Hossenfelder for giving me puzzles.
What if everything — gravity, light, particles, and even the flow of time — came from a single equation? In Chavis Srichan’s Unified Theory, the universe isn’t built from matter, but from the curvature of entanglement — the twists and turns of quantum information itself. Space, energy, and even consciousness are simply different ways this curvature vibrates.
The One Equation.
At the smallest scale, every motion and interaction follows one rule:
[D_μ, D_ν]Ψ = (i/ħ) [(8πG/c⁴)⟨T_μν(Ψ)⟩ − Λ_q g_μν + λ ∇_μ∇_ν S]Ψ
It means that the “shape” of space itself bends in response to energy and information — and that same bending is quantum mechanics, gravity, and thermodynamics combined.
Mass: When Curvature Loops Back.


Netherlands tightens export restrictions on microchip machines, mainly targeting ASML
The Dutch government is tightening its export restrictions on microchip-making machines, specifically deep ultraviolet (DUV) lithographic machines. A licensing requirement will apply to the export of older types of DUV machinery beginning on Saturday, a decision which primarily impacts Dutch business ASML. Foreign Trade Minister Reinett Klever cited national security concerns when announcing the measure on Friday.
According to ASML, the licensing requirement update is a technical change that mainly means that the company will apply for export licenses from the government of the Netherlands, not the United States, for two older types of DUV immersion lithography systems (1970i and 1980i). The Dutch government already implemented a licensing requirement for the newer generations of DUV machines (2000i and later) in September last year.
DUV lithography machines are the second-most advanced microchip-making machines, after extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography machines. Dutch company ASML is the world’s only manufacturer of EUV lithography machines and is also a global leader in the production, refurbishment, and repair of DUV lithography machines. DUV machines can still be used to make highly sophisticated microchips, and some of China’s leading tech companies, like Huawei, are actively pushing the limits of the older technology.


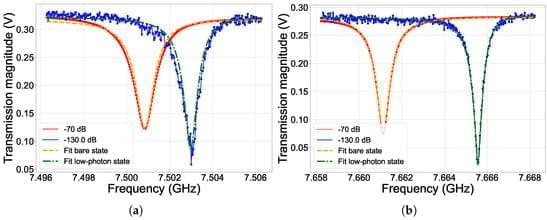
Investigating the Individual Performances of Coupled Superconducting Transmon Qubits
The strong requirement for high-performing quantum computing led to intensive research on novel quantum platforms in the last decades. The circuital nature of Josephson-based quantum superconducting systems powerfully supports massive circuital freedom, which allowed for the implementation of a wide range of qubit designs, and an easy interface with the quantum processing unit. However, this unavoidably introduces a coupling with the environment, and thus to extra decoherence sources. Moreover, at the time of writing, control and readout protocols mainly use analogue microwave electronics, which limit the otherwise reasonable scalability in superconducting quantum circuits.

AI model could boost robot intelligence via object recognition
Stanford researchers have developed an innovative computer vision model that recognizes the real-world functions of objects, potentially allowing autonomous robots to select and use tools more effectively.
In the field of AI known as computer vision, researchers have successfully trained models that can identify objects in two-dimensional images. It is a skill critical to a future of robots able to navigate the world autonomously. But object recognition is only a first step. AI also must understand the function of the parts of an object—to know a spout from a handle, or the blade of a bread knife from that of a butter knife.
Computer vision experts call such utility overlaps “functional correspondence.” It is one of the most difficult challenges in computer vision. But now, in a paper that will be presented at the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV 2025), Stanford scholars will debut a new AI model that can not only recognize various parts of an object and discern their real-world purposes but also map those at pixel-by-pixel granularity between objects.
