Serving the chemical, life science, and laboratory worlds


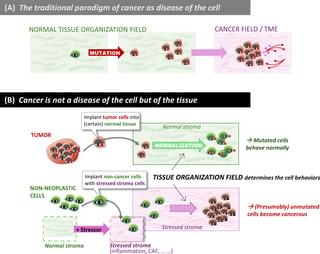
Genome sequencing of cancer and normal tissues, alongside single-cell transcriptomics, continues to produce findings that challenge the idea that cancer is a ‘genetic disease’, as posited by the somatic mutation theory (SMT). In this prevailing paradigm, tumorigenesis is caused by cancer-driving somatic mutations and clonal expansion. However, results from tumor sequencing, motivated by the genetic paradigm itself, create apparent ‘paradoxes’ that are not conducive to a pure SMT. But beyond genetic causation, the new results lend credence to old ideas from organismal biology. To resolve inconsistencies between the genetic paradigm of cancer and biological reality, we must complement deep sequencing with deep thinking: embrace formal theory and historicity of biological entities, and (re)consider non-genetic plasticity of cells and tissues. In this Essay, we discuss the concepts of cell state dynamics and tissue fields that emerge from the collective action of genes and of cells in their morphogenetic context, respectively, and how they help explain inconsistencies in the data in the context of SMT.
Citation: Huang S, Soto AM, Sonnenschein C (2025) The end of the genetic paradigm of cancer. PLoS Biol 23: e3003052. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.
Copyright: © 2025 Huang et al. This is an open access distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
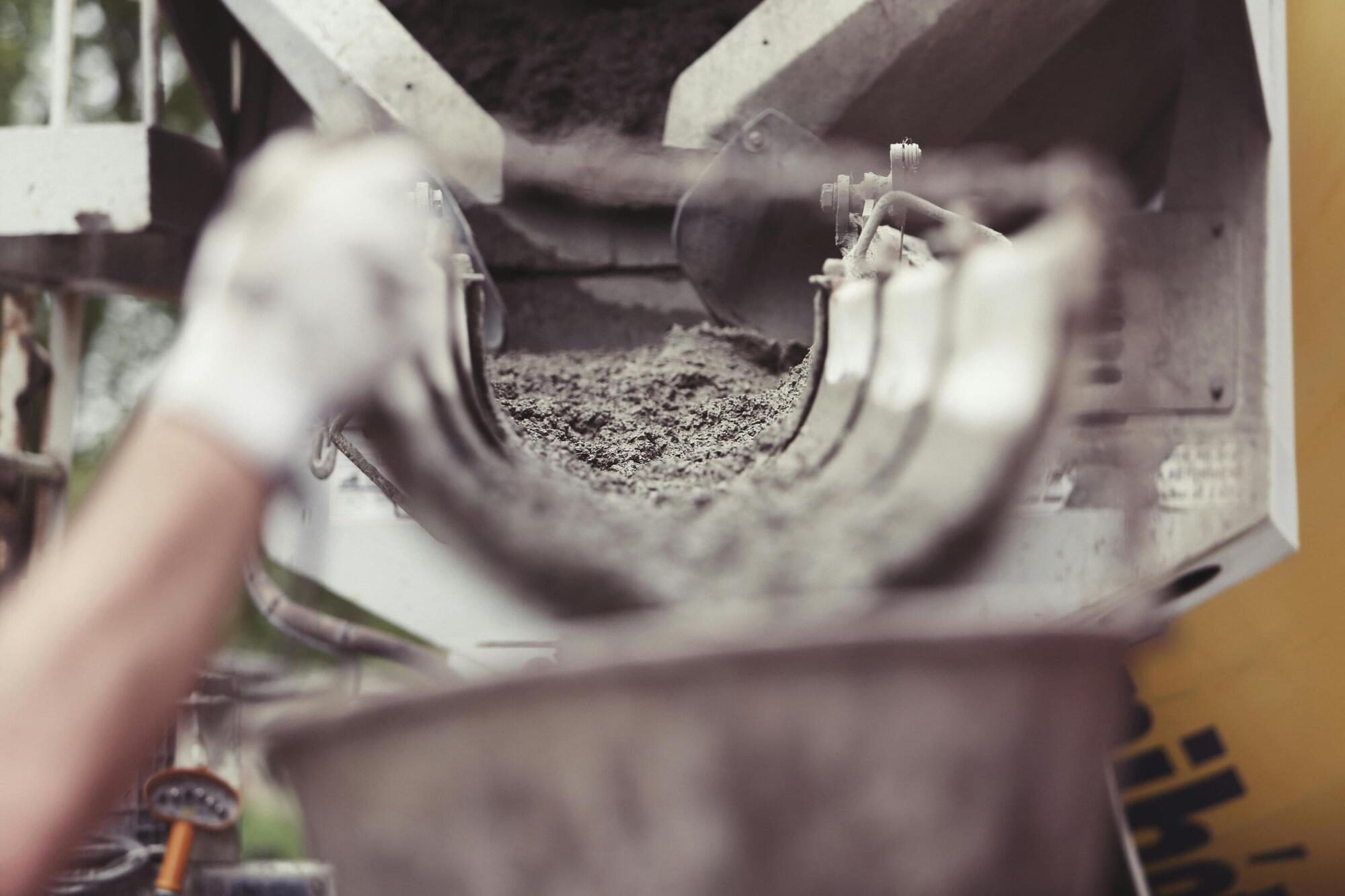

A new method inspired by coral reefs can capture carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and transform it into durable, fire-resistant building materials, offering a promising solution for carbon-negative construction.
The approach, developed by USC researchers and detailed in a study published in npj Advanced Manufacturing, draws inspiration from the ocean’s coral reefs’ natural ability to create robust structures by sequestering carbon dioxide. The resulting mineral-polymer composites demonstrate extraordinary mechanical strength, fracture toughness and fire-resistance capabilities.
“This is a pivotal step in the evolution of converting carbon dioxide,” said Qiming Wang, associate professor of civil and environmental engineering at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering. “Unlike traditional carbon capture technologies that focus on storing carbon dioxide or converting it into liquid substances, we found this new electrochemical manufacturing process converts the chemical compound into calcium carbonate minerals in 3D-printed polymer scaffolds.”
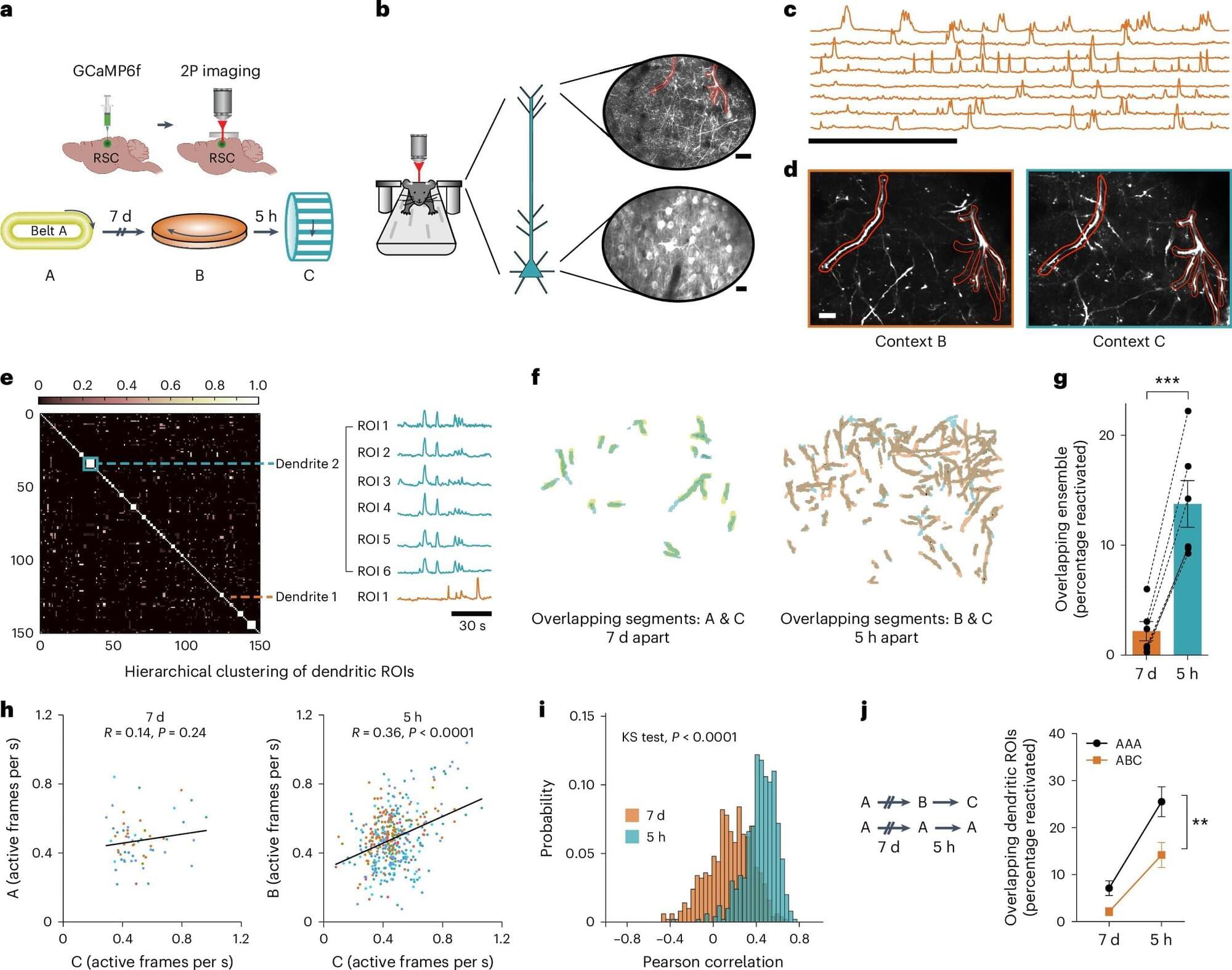
If you’ve ever noticed how memories from the same day seem connected while events from weeks apart feel separate, a new study reveals the reason: Our brains physically link memories that occur close in time not in the cell bodies of neurons, but rather in their spiny extensions called dendrites.
This discovery stems from studies in mice, in which researchers observed memory formation using advanced imaging techniques, including miniature microscopes that captured single-cell resolution in live animals.
The study shows that memories are stored in dendritic compartments: When one memory forms, the affected dendrites are primed to capture new information arriving within the next few hours, linking memories formed close in time.
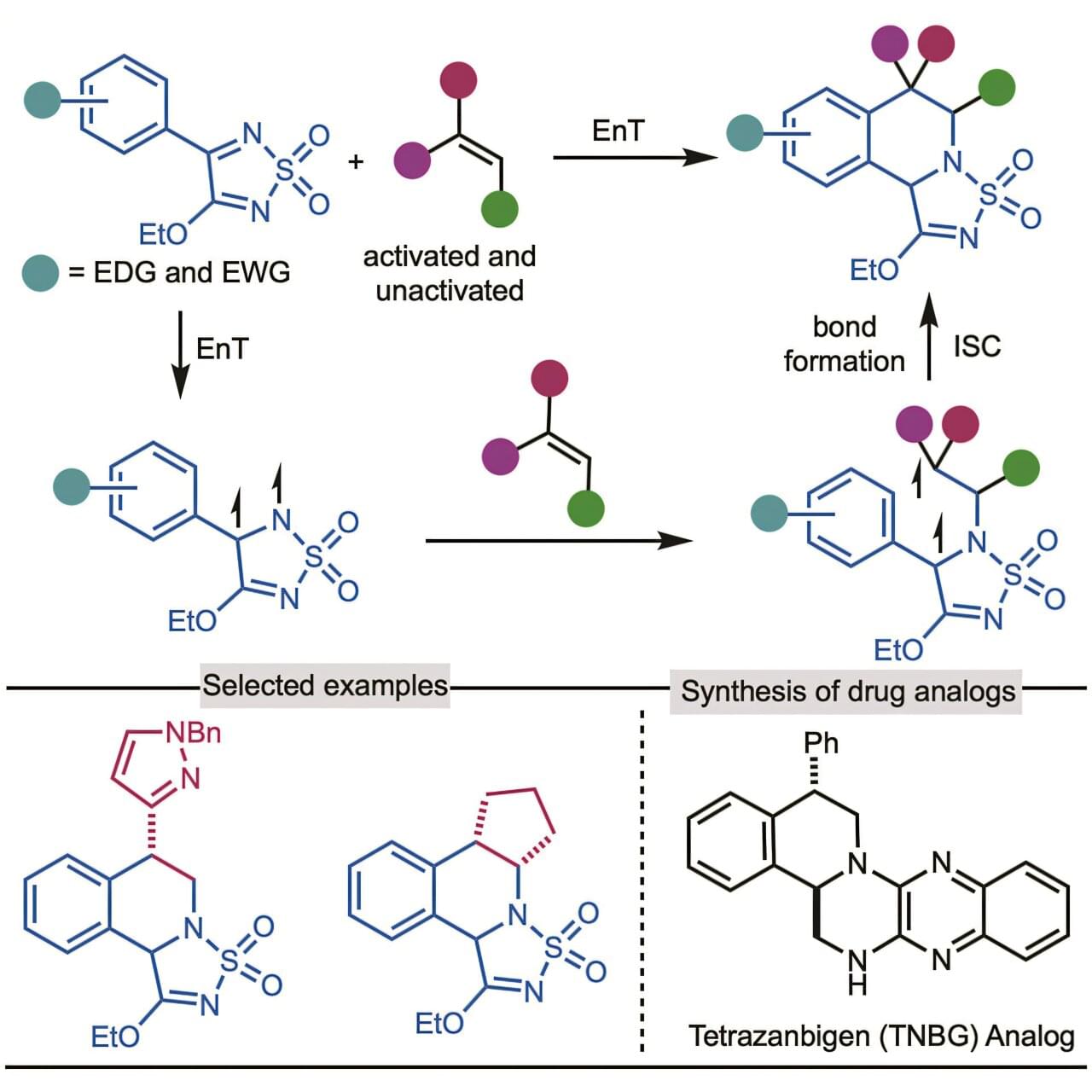
Researchers at Indiana University and Wuhan University in China have unveiled a groundbreaking chemical process that could streamline the development of pharmaceutical compounds, chemical building blocks that influence how drugs interact with the body. Their study, published in Chem, describes a novel light-driven reaction that efficiently produces tetrahydroisoquinolines, a group of chemicals that play a crucial role in medicinal chemistry.
Tetrahydroisoquinolines serve as the foundation for treatments targeting Parkinson’s disease, cancer, and cardiovascular disorders. These compounds are commonly found in medications such as painkillers and drugs for high blood pressure, as well as in natural sources like certain plants and marine organisms.
Traditionally, chemists have relied on well-established but limiting methods to synthesize these molecules. The new research, co-authored by Kevin Brown, the James F. Jackson Professor of Chemistry in the College of Arts and Sciences at Indiana University Bloomington, and Professors Xiaotian Qi, Wang Wang, and Bodi Zhao of Wuhan University, presents a fundamentally different approach.

From laundry detergent to dishwasher tablets, cleaning products are an indispensable part of life. Yet the chemicals that make these products so effective can be difficult to break down or could even trigger ecosystem-altering algal blooms. Now, researchers reporting in ACS’ Langmuir have addressed those challenges with an environmentally compatible detergent made of tiny wood fibers and corn protein that removes stains on clothes and dishes just as well as commercial products.
Increased public concern about household products’ impact on the environment has spurred interest in replacing traditional cleaners containing ingredients such as alkylphenol polyethoxylates and phosphates with natural alternatives. Efforts to date have produced mixed results because these cleaners are difficult to make and hard to rinse off, resulting in high manufacturing and retail costs, as well as potential damage to surfaces and fabrics. Therefore, there is a desire for low-cost, easily produced, effective alternatives that are gentle on the environment and the items they are designed to clean. To address this need, Pengtao Liu and colleagues developed an eco-friendly detergent from ingredients found in abundant renewable sources.
The researchers combined cellulose nanofibers from wood with zein protein from corn to create an emulsion. Cellulose can attract and repel water, so it is effective at forming such emulsions and attracting different types of stains. The zein protein, on the other hand, helps stabilize the emulsion and trap oils. Liu and colleagues then tested the cleaning capacity of the cellulose/zein detergent on cotton fabrics and dishes stained with ink, chili oil and tomato paste. They compared the performance of their new detergent to laundry powder and commercial dish soap solutions with deionized water.

Y Combinator CEO Garry Tan told CNBC that this group is growing significantly faster than past cohorts and with actual revenue. The winter 2025 batch of YC companies in aggregate grew 10% per week, he said.
“It’s not just the number one or two companies — the whole batch is growing 10% week on week,” said Tan, who is also a Y Combinator alum. “That’s never happened before in early-stage venture.”
That growth spurt is thanks to leaps in artificial intelligence, Tan said.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho’s research team has recently been highlighted for their work on developing an original technology for cancer reversal treatment that does not kill cancer cells but only changes their characteristics to reverse them to a state similar to normal cells. This time, they have succeeded in revealing for the first time that a molecular switch that can induce cancer reversal at the moment when normal cells change into cancer cells is hidden in the genetic network.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th of February that Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho’s research team of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has succeeded in developing a fundamental technology to capture the critical transition phenomenon at the moment when normal cells change into cancer cells and analyze it to discover a molecular switch that can revert cancer cells back into normal cells.
A critical transition is a phenomenon in which a sudden change in state occurs at a specific point in time, like water changing into steam at 100℃. This critical transition phenomenon also occurs in the process in which normal cells change into cancer cells at a specific point in time due to the accumulation of genetic and epigenetic changes.