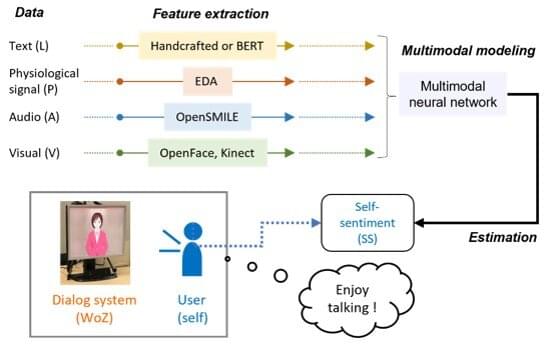
Speech and language recognition technology is a rapidly developing field, which has led to the emergence of novel speech dialog systems, such as Amazon Alexa and Siri. A significant milestone in the development of dialog artificial intelligence (AI) systems is the addition of emotional intelligence. A system able to recognize the emotional states of the user, in addition to understanding language, would generate a more empathetic response, leading to a more immersive experience for the user.
“Multimodal sentiment analysis” is a group of methods that constitute the gold standard for an AI dialog system with sentiment detection. These methods can automatically analyze a person’s psychological state from their speech, voice color, facial expression, and posture and are crucial for human-centered AI systems. The technique could potentially realize an emotionally intelligent AI with beyond-human capabilities, which understands the user’s sentiment and generates a response accordingly.
However, current emotion estimation methods focus only on observable information and do not account for the information contained in unobservable signals, such as physiological signals. Such signals are a potential gold mine of emotions that could improve the sentiment estimation performance tremendously.