Scientists have built a “microwave brain” chip that processes information at radar-like speeds while sipping power. It could revolutionize how AI and communication devices operate, from smartwatches to satellites.



Geophysicists have modeled how Earth’s magnetic field could form even when its core was fully liquid. By removing the effects of viscosity in their simulation, they revealed a self-sustaining dynamo that mirrors today’s mechanism. The results illuminate Earth’s early history, life’s origins, and the magnetism of other planets. Plus, it could help forecast future changes to our planet’s protective shield.
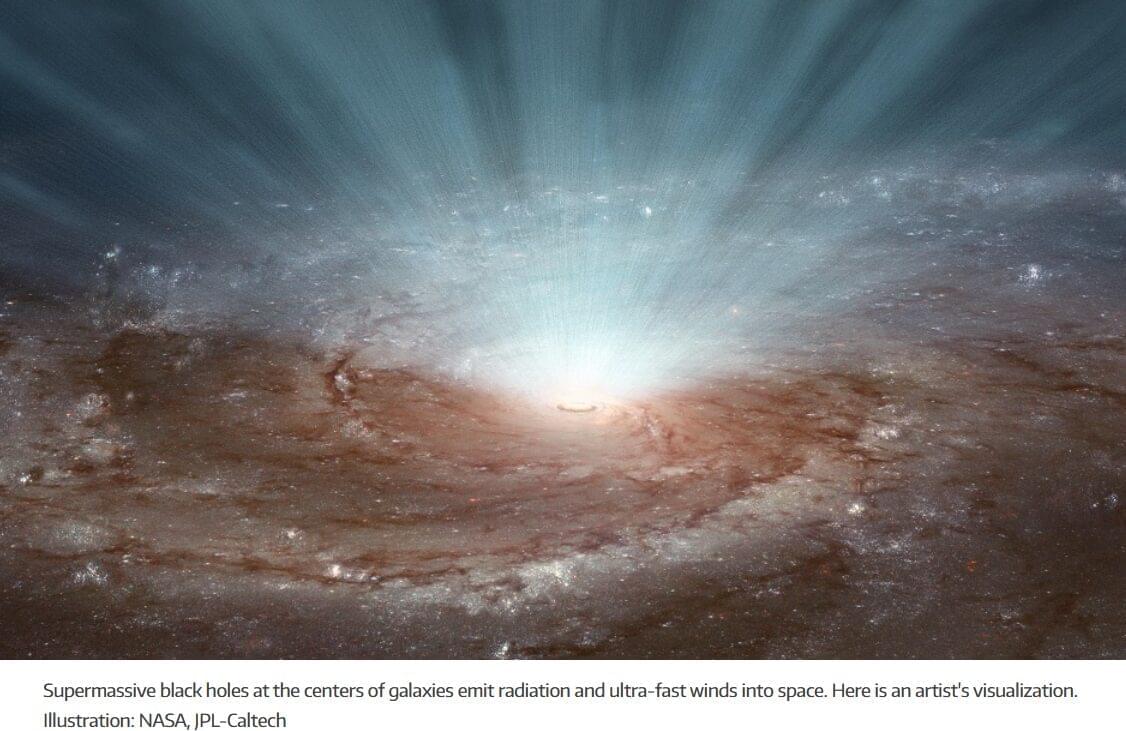



Could black holes help explain high-energy cosmic radiation?
Scientists may have finally uncovered the mystery behind ultra-high-energy cosmic rays — the most powerful particles known in the universe. A team from NTNU suggests that colossal winds from supermassive black holes could be accelerating these particles to unimaginable speeds. These winds, moving at half the speed of light, might not only shape entire galaxies but also fling atomic nuclei across the cosmos with incredible energy.
The universe is full of different types of radiation and particles that can be observed here on Earth. This includes photons across the entire range of the electromagnetic spectrum, from the lowest radio frequencies all the way to the highest-energy gamma rays. It also includes other particles such as neutrinos and cosmic rays, which race through the universe at close to the speed of light.
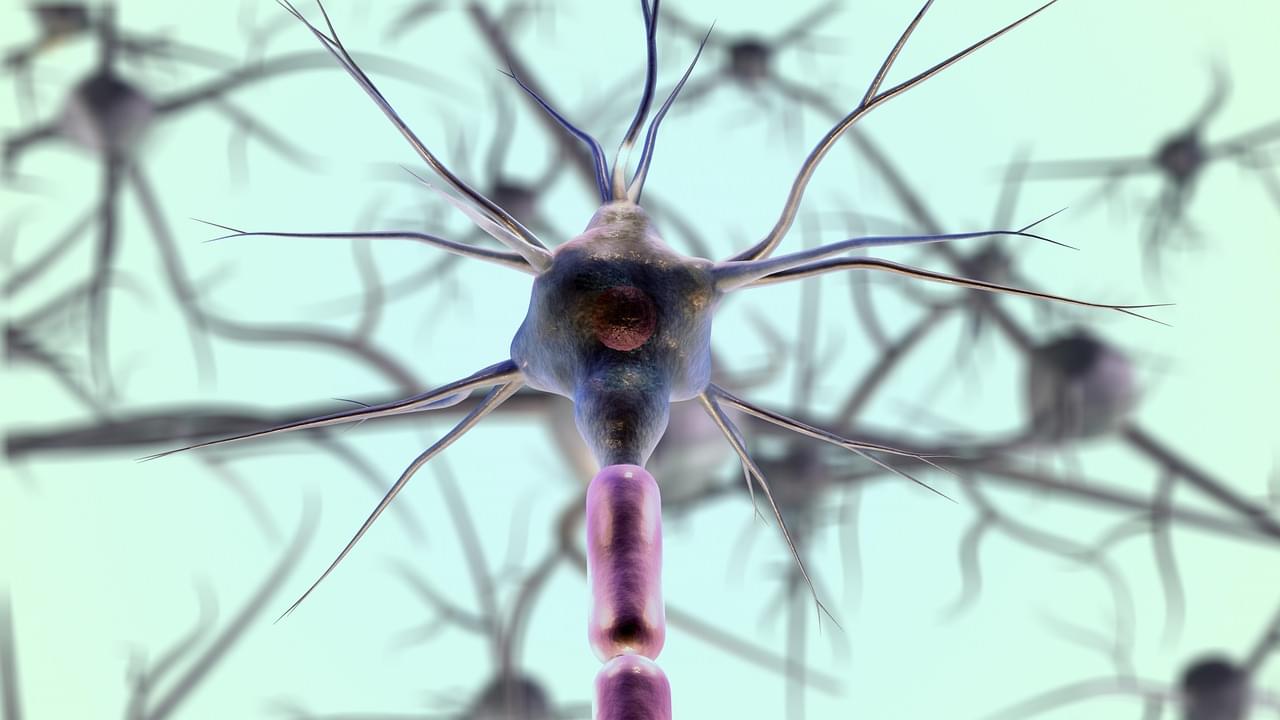
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, is a neurodegenerative disease that affects the neurons in the brain and spinal cord. In the United States alone there are fewer than 20,000 cases a year. However, the disease is fatal with a 5-year survival rate of 10–20% after diagnosis. This progressive disorder impedes voluntary muscle movement and can dramatically impact an individual’s quality of life. Symptoms of ALS include gradual muscle weakness and fatigue which spreads throughout the body. Difficulty moving and slurred speech is accompanied by muscle spasms, cramps, and twitching. Diagnosis is based on an exam led by a healthcare physician who also considers medical history and analyzes neuroimaging. Unfortunately, there are no blood tests to detect ALS. Additionally, the exact cause of ALS is unknown. However, many physicians and scientists believe that it is a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Currently, there is no cure for ALS and medication works to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatments include medication that slows disease progression, physical and speech therapy, and devices that help make movement and breathing easier (including wheelchairs and ventilators). It is unknown how this disease progresses and scientists are working to develop optimal therapies for patients.
A recent article in Nature, by Dr. Alessandro Sette and others, revealed that ALS is an autoimmune disorder. This discovery is extremely novel and progresses the field of ALS, especially since very little was known before. Sette is a Professor in the Centers for Autoimmunity and Inflammation, and Cancer Immunotherapy, and is Co-Director of the Center for Vaccine Innovation at La Jolla Institute for Immunology. Sette’s work focuses on understanding the immune system and measuring its activity in various diseases. More specifically, he focuses on cellular biomarkers that elicit robust immune reactions.
Quantum mechanics describes the weird behavior of microscopic particles. Using quantum systems to perform computation promises to allow researchers to solve problems in areas from chemistry to cryptography that have so many possible solutions that they are beyond the capabilities of even the most powerful nonquantum computers possible.
Quantum computing depends on researchers developing practical quantum technologies. Superconducting electrical circuits are a promising technology, but not so long ago it was unclear whether they even showed quantum behavior. The 2025 Nobel Prize in physics was awarded to three scientists for their work demonstrating that quantum effects persist even in large electrical circuits, which has enabled the development of practical quantum technologies.
I’m a physicist who studies superconducting circuits for quantum computing and other uses. The work in my field stems from the groundbreaking research the Nobel laureates conducted.
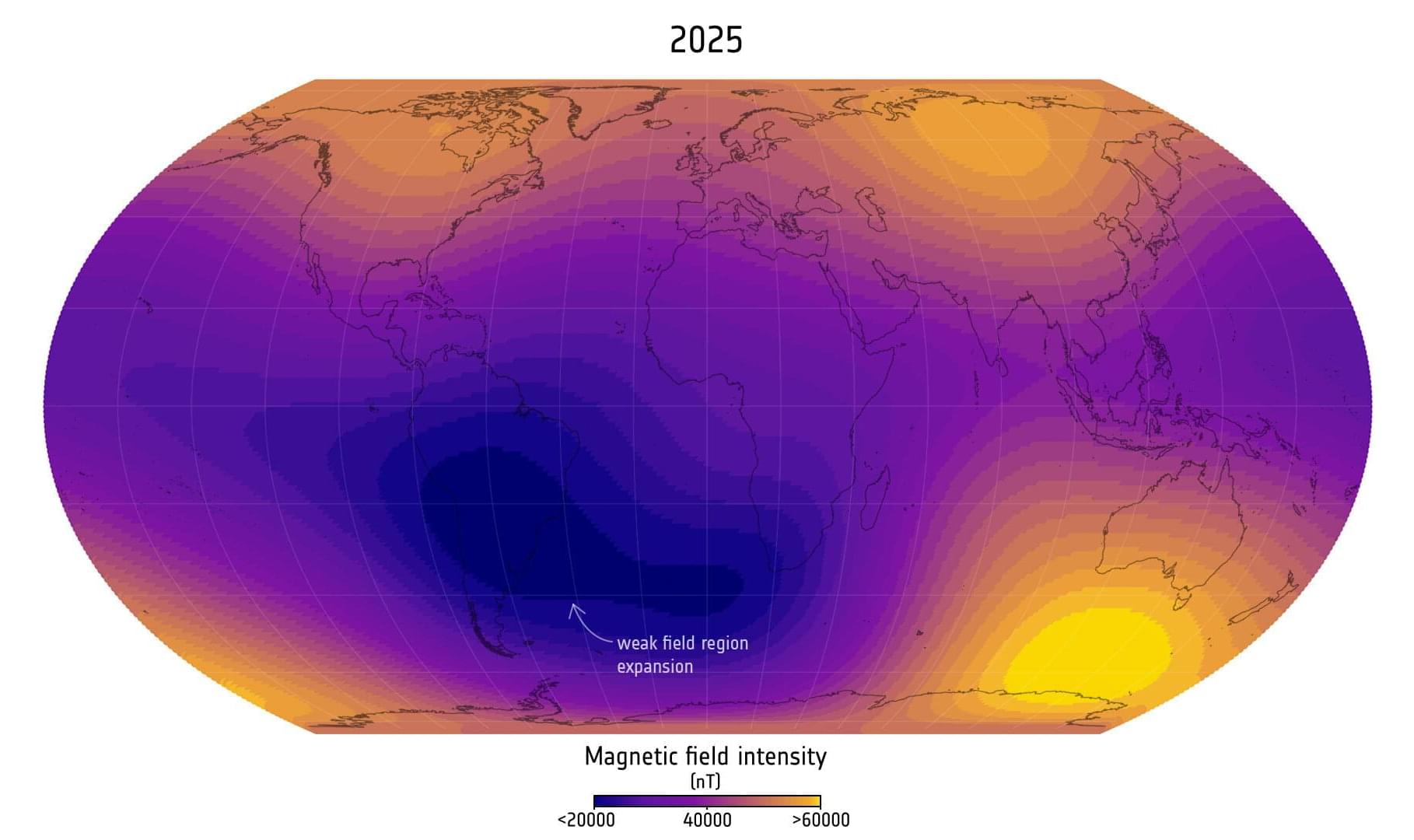
Using 11 years of magnetic field measurements from the European Space Agency’s Swarm satellite constellation, scientists have discovered that the weak region in Earth’s magnetic field over the South Atlantic—known as the South Atlantic Anomaly—has expanded by an area nearly half the size of continental Europe since 2014.
Earth’s magnetic field is vital to life on our planet. It is a complex and dynamic force that protects us from cosmic radiation and charged particles from the sun.
It is largely generated by a global ocean of molten, swirling liquid iron that makes up the outer core around 3,000 km beneath our feet. Acting like a spinning conductor in a bicycle dynamo, it creates electrical currents, which in turn, generate our continuously changing electromagnetic field —but in reality the processes that generate the field are far more complex.