Researchers discovered these large, lethargic creatures only need to eat a few ounces of fish per day to survive.



We should assume that animals can have feelings too. From an ethical point of view this should inform our dealings with animals, researchers from Leiden University and Utrecht University argue in an opinion article that was published in the scientific journal Affective Science on Thursday 10 March.
Some of the leading behavioral scientists in the world have hypothesized that many animal species can have emotions. But whether animals also have feelings is the subject of much debate, and some behavioral scientists believe they do not. This is incorrect, say cognitive psychologist Mariska Kret (Leiden University) and behavioral biologists Jorg Massen (Utrecht University) and Frans de Waal (Emory University and endowed professor in Utrecht). Based on observations, there is a good chance that animals can also have feelings; it is just very difficult to investigate this.

Summary: Mindful meditation may help people cope when faced with action crises, researchers say.
Source: Leibniz Institute for Psychology.
Faced by one too many obstacles on the way to achieving their personal goals—whether an important, valuable or fun one—people may experience an action crisis where they start questioning their pursuit and even feel like giving up.
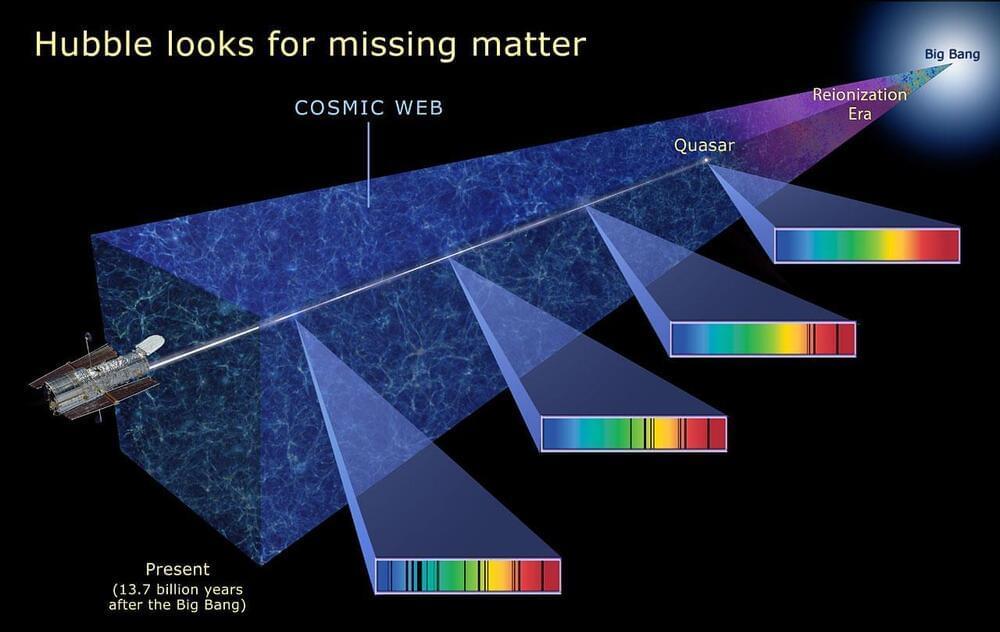
The problem is that transitions from one s-orbital to another are forbidden, quantum mechanically. There’s no way to emit one photon from an s-orbital and have your electron wind up in a lower energy s-orbital, so the transition we talked about earlier, where you emit a Lyman-series photon, can only occur from the 2 p state to the 1s state.
But there is a special, rare process that can occur: a two-photon transition from the 2s state (or the 3s, or 4s, or even the 3 d orbital) down to the ground (1s) state. It occurs only about 0.000001% as frequently as the Lyman-series transitions, but each occurrence nets us one new neutral hydrogen atom. This quantum mechanical quirk is the primary method of creating neutral hydrogen atoms in the Universe.
If it weren’t for this rare transition, from higher energy spherical orbitals to lower energy spherical orbitals, our Universe would look incredibly different in detail. We would have different numbers and magnitudes of acoustic peaks in the cosmic microwave background, and hence a different set of seed fluctuations for our Universe to build its large-scale structure out of. The ionization history of our Universe would be different; it would take longer for the first stars to form; and the light from the leftover glow of the Big Bang would only take us back to 790,000 years after the Big Bang, rather than the 380,000 years we get today.
Janice Chen, Ph.D., one of Olympic gold medalist Nathan Chen’s siblings, is on a mission to build a $100 billion biotech company.
In 2018, she co-founded Mammoth Biosciences with Trevor Martin, Lucas Harrington and Jennifer Doudna 0, who won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry two years later for her pioneering work in CRISPR gene editing. Doudna also served as Chen’s mentor while she pursued her doctorate degree in molecular and cell biology at the University of California at Berkeley.
Mammoth is built on Chen’s work as a graduate student researcher in Doudna’s lab. Since the dawn of COVID-19 in 2020, the startup has seen accelerated growth as it snagged $100 million in multiple contracts and government grants.

Let’s look at some of the best emerging technologies!
Sources & Credits:
7. Atomic 3D Printer.
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCtXHu_nugZF3uxgJJjZfcoA
(Snapmaker)
https://www.ge.com/additive/ebm (Electron Beam Melting)
6. Biohybrid Robot.
https://www.popsci.com/soft-robotic-stingray/
(Xenobots)
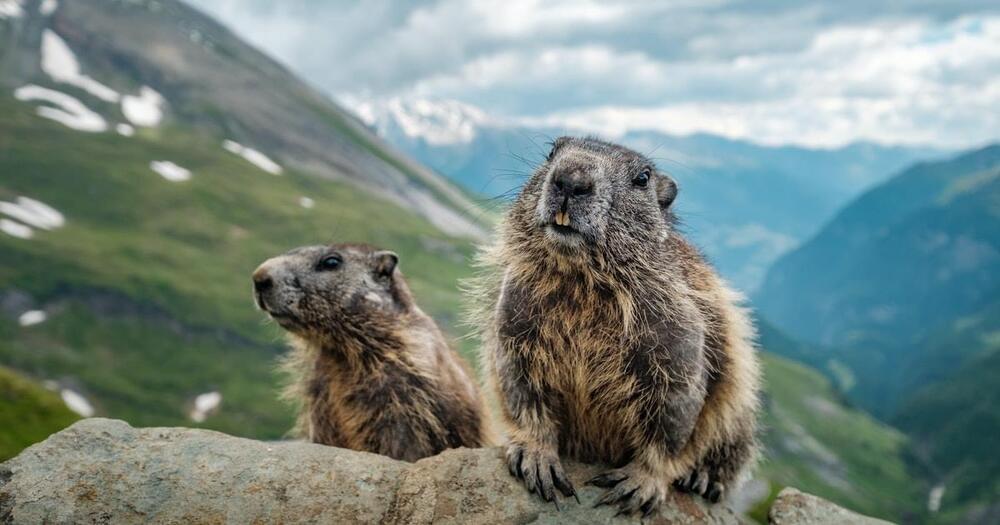

This disparity gets at the difference between one’s chronological age — how old they are in years — and their biological age, which is how their body has aged naturally and in response to its environment. The two can diverge in ways that are either blessings or curses. Hence why those who grow up under extreme stress or in polluted environments may look much older than they actually are.
And yellow-bellied marmots can tell us something about these two ages.
Yellow-bellied marmots (Marmota flaviventer) are no burrow-dwelling meteorologists like the groundhog. They may sound craven, but these quirky critters, also known as whistle pigs, make for fascinating subjects: the cat-sized rodents have a longer lifespan than expected for a mammal of their size. On average, marmots live 15 years.
Researchers have discovered a wholly-in tact Roman vessel that sank around the fourth century AD off the coast of Mallorca in Spain.
