Webb’s Mid-Infrared Instrument reveals a network of scaffolding behind galaxy IC 5332’s iconic spiral structure.
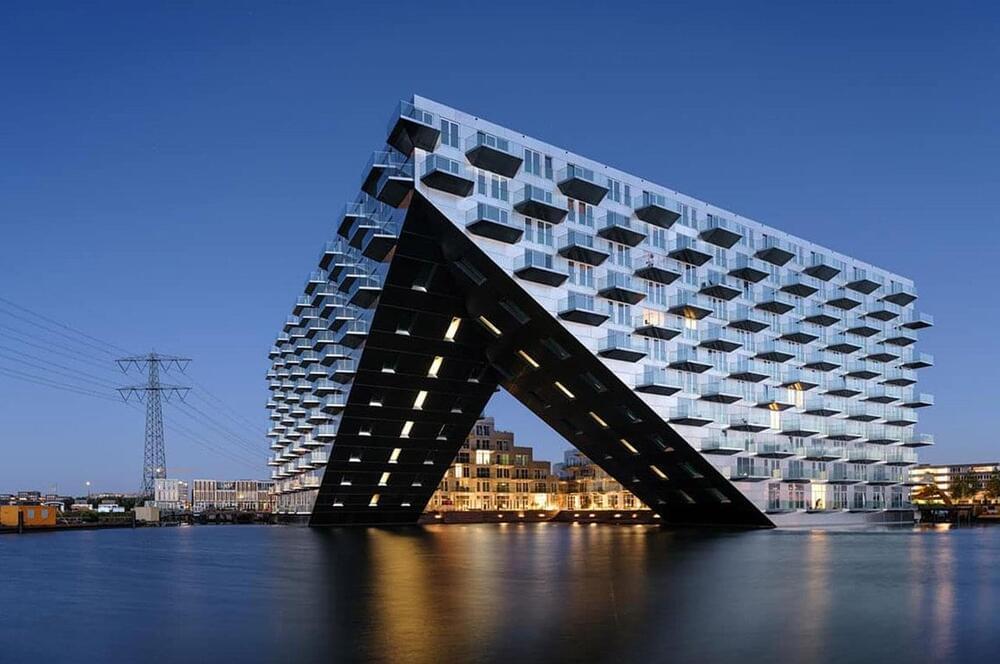





Bjarke Ingels Group and Barcode Architects collaborated to create ‘Sluishuis’ – an angular residential complex placed above the IJ Lake in Amsterdam. The structure’s sharp geometric ends meet in the air, water, and land, creating a mesmerizing structure that seems to be jutting into the sky while resembling the bow of a ship! It is constructed on an artificial island in the IJ Lake and forms a geometrically-intriguing gateway from the lake.
Designer: Bjarke Ingels Group x Barcode Architects.
A well-known game studio is allegedly using AI voices for a video game. A clarification includes a commitment to human creativity. It’s another footnote in the debate over the value of human labor that will become more common in the future.
It’s the very debate that has erupted so vehemently around AI-generated images in recent months. Are AI images art? If so, can they be equated with human art? Are they detrimental to art? Are they even plagiarism, because the AI examines human works during training – in the inspiration phase, so to speak – and then imitates them in trace elements?
Image generation machines like DALL-E 2, Stable Diffusion, and Midjourney alone raise myriad questions about the value and interplay of human and machine labor. These questions are likely to increase because generative AI will not stop at 2D images. Another area it is already tapping into is audio.

Scientists at the Krembil Brain Institute, part of the University Health Network, have proposed a new mechanistic model (AD2) for Alzheimer’s, looking at it not as a brain disease, but as a chronic autoimmune condition that attacks the brain.
This novel research is published today, in Alzheimer’s & Dementia.
“We don’t think of Alzheimer’s as fundamentally a disease of the brain. We think of it as a disease of the immune system within the brain,” says Dr. Donald Weaver, co-Director of the Krembil Brain Institute and author of the paper.


Methuselah Foundation recently announced a $1 million competition to.
encourage innovation that will enable medicine to move away from unreliable.
animal testing. The change is long overdue. In the U.S., all our food and.
drug research has been guided by the 1938 Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetics.
Act, which requires that every drug be tested on animals. While this was.
state-of-the-art scientific process 84 years ago, we can do much better today. The reason why is simple: Animal testing is unreliable, ineffective.
And costly.
Open source is fertile ground for transformative software, especially in cutting-edge domains like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. The open source ethos and collaboration tools make it easier for teams to share code and data and build on the success of others.
This article looks at 13 open source projects that are remaking the world of AI and machine learning. Some are elaborate software packages that support new algorithms. Others are more subtly transformative. All of them are worth a look.