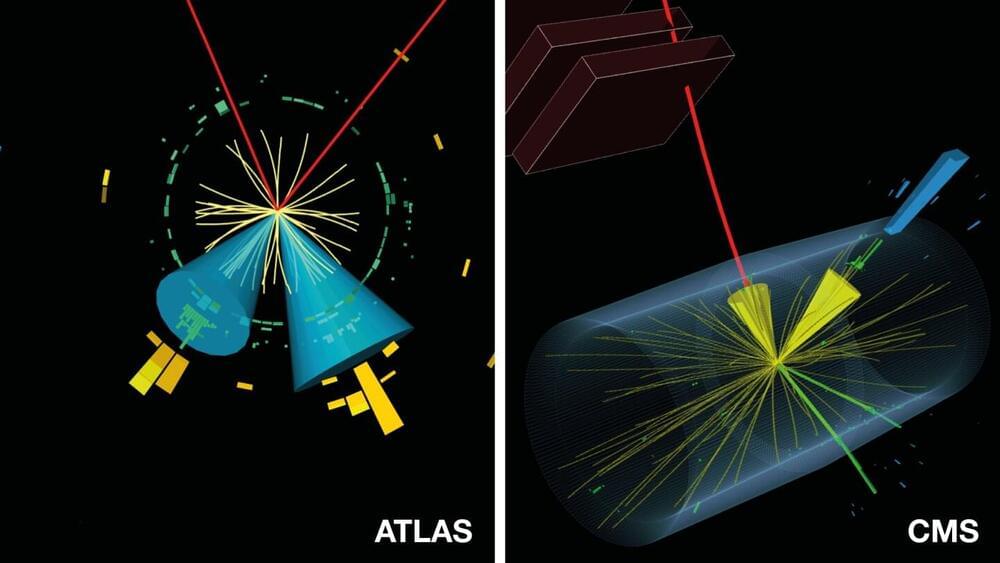
Since the discovery of the Higgs boson a decade ago, the ATLAS and CMS collaborations at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) have been hard at work trying to unlock the secrets of this special particle. In particular, the collaborations have been investigating in detail how the Higgs boson interacts with fundamental particles such as the particles that make up matter, quarks and leptons. In the Standard Model of particle physics, these matter particles fall into three “generations” of increasing mass, and the Higgs boson interacts with them with a strength that is proportional to their mass. Any deviation from this behavior would provide a clear indication of new phenomena.
ATLAS and CMS have previously observed the interactions of the Higgs boson with the heaviest quarks and leptons, of the third generation, which within the current measurement precision agree with the predictions from the Standard Model. And they have also obtained the first indications that the Higgs boson interacts with a muon, a lepton of the second generation. However, they have yet to observe it interacting with second-generation quarks. In two recent publications, ATLAS and CMS report analyses that place tight limits on the strength of the Higgs boson interaction with a charm quark, a second-generation quark.
ATLAS and CMS studied the Higgs boson interactions by looking at how the boson transforms, or “decays,” into lighter particles or how it is produced together with other particles. In their latest studies, using data from the second run of the LHC, the two teams searched for the decay of the Higgs boson into a charm quark and its antimatter counterpart, the charm antiquark.