As part of a $1 billion initiative, Google has hired researchers at Sydney’s biggest unis to find applications for the quantum computer it’s building in the US.


Why we need AI to compete against each other. Does a Great Filter Stop all Alien Civilizations at some point? Are we Doomed if We Find Life in Our Solar System?
David Brin is a scientist, speaker, technical consultant and world-known author. His novels have been New York Times Bestsellers, winning multiple Hugo, Nebula and other awards.
A 1998 movie, directed by Kevin Costner, was loosely based on his book The Postman.
His Ph.D in Physics from UCSD — followed a masters in optics and an undergraduate degree in astrophysics from Caltech. He was a postdoctoral fellow at the California Space Institute and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
Brin serves on advisory committees dealing with subjects as diverse as national defense and homeland security, astronomy and space exploration, SETI and nanotechnology, future/prediction and philanthropy. He has served since 2010 on the council of external advisers for NASA’s Innovative and Advanced Concepts group (NIAC), which supports the most inventive and potentially ground-breaking new endeavors.
https://www.davidbrin.com/books.html.
https://twitter.com/DavidBrin.
https://www.newsweek.com/soon-humanity-wont-alone-universe-opinion-1717446
Youtube Membership: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCz3qvETKooktNgCvvheuQDw/join.
Podcast: https://anchor.fm/john-michael-godier/subscribe.
Apple: https://apple.co/3CS7rjT
More JMG
https://www.youtube.com/c/JohnMichaelGodier.
Want to support the channel?
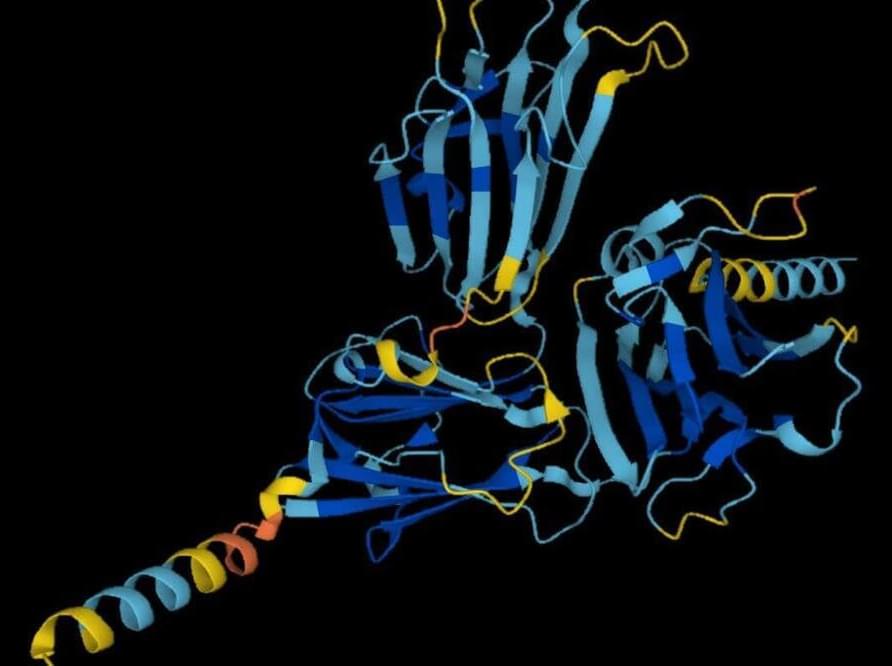
DeepMind has predicted the structure of almost every protein so far catalogued by science, cracking one of the grand challenges of biology in just 18 months thanks to an artificial intelligence called AlphaFold. Researchers say that the work has already led to advances in combating malaria, antibiotic resistance and plastic waste, and could speed up the discovery of new drugs.
Determining the crumpled shapes of proteins based on their sequences of constituent amino acids has been a persistent problem for decades in biology. Some of these amino acids are attracted to others, some are repelled by water, and the chains form intricate shapes that are hard to accurately determine.
Thinking long-term to save the world Martin Rees at New Scientist Live this October.
Use code HISTORY16 for up to 16 FREE MEALS + 3 Surprise Gifts across 7 HelloFresh boxes plus free shipping at https://bit.ly/3Rkknac!
If you like this video, check out writer Geraint Lewis´ excellent book, co-written with Chris Ferrie:
Where Did the Universe Come From? And Other Cosmic Questions: Our Universe, from the Quantum to the Cosmos.
AND check out his Youtube channel:
https://www.youtube.com/c/AlasLewisAndBarnes.
Incredible thumbnail art by Ettore Mazza, the GOAT: https://www.instagram.com/ettore.mazza/?hl=en.
Art created by soso112429, and Joe from History Dose: www.youtube.com/historydose.
Quantum mechanic discoveries are some of the most groundbreaking discoveries that scientists can make as they allow us to get a better understand of the space and matter around us. From multiple dimensions to quantum superposition, there are many things that are difficult for scientists and physicists to explain. Hopefully we can clear up some of the confusion!
Thanks for watching Matter!
🔔 Hit the bell next to Subscribe so you never miss a video!
❤️ Like, Comment and Subscribe if you are new to the channel!
Topics Discussed/Related:
- Amazing Discoveries.
- Quantum Tunneling.
- Quantum Entanglement.
- Quantum Computing
It was once thought that gravity and quantum mechanics were inconsistent with one another. Instead, we are discovering that they are so closely connected that one can almost say they are the same thing. Professor Susskind will explain how this view came into being over the last two decades, and illustrate how a number of gravitational phenomena have their roots in the ordinary principles of quantum mechanics.
Leonard Susskind is an American physicist, who is a professor of theoretical physics at Stanford University, and founding director of the Stanford Institute for Theoretical Physics. His research interests include string theory, quantum field theory, quantum statistical mechanics, and quantum cosmology.
The Brain Computer Interface industry is progressing quickly and it’s not just Neuralink. Synchron…
The Brain Computer Interface industry is progressing quickly and it’s not just Neuralink. Synchron has been approved for human trials by the FDA and Neuralink might not be far behind.
Last video: The Real Reason SpaceX Developed The Raptor Engine!
► Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/theteslaspace.
► Subscribe to The Tesla Space newsletter: https://www.theteslaspace.com.


A new AI program observed physical phenomena and uncovered relevant variables—a necessary precursor to any physics theory.