Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
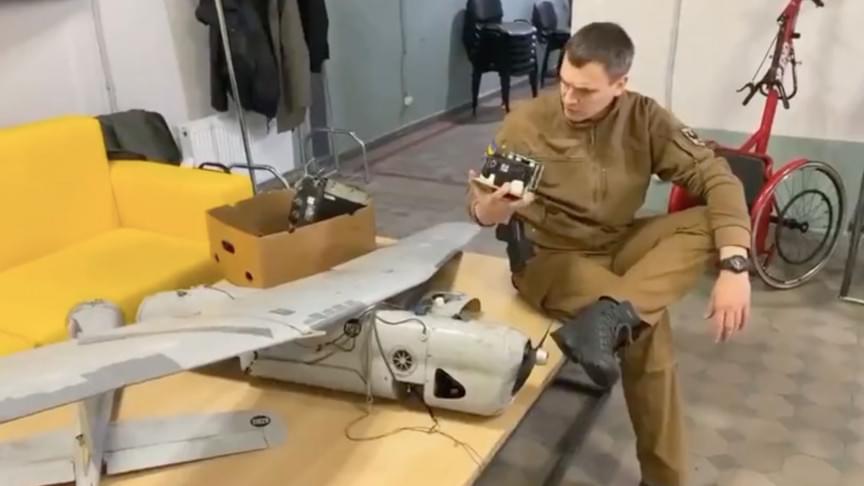




Video shows Ukrainian soldier allegedly taking apart a Russian drone and discovering its regular camera
With some parts held together by duct tape.
In the raging battle between Russia and Ukraine, Russia’s small drones have been reported to be taking a deadly toll on Ukrainian forces. A new video, however, is revealing that the highly efficient precision drones are not as advanced as one might expect.
Ukraine’s Defense Ministry shared a video on Sunday that shows a soldier allegedly dismantling a Russian military surveillance drone and pointing out several highly unsophisticated features. In fact, seeing what the whole drone consists of it seems like something a schoolchild could put together.
## A generic handheld Canon DSLR
The drone being taken apart is an Orlan-10 model that fell on Ukrainian soil. The first thing the soldier points out is that the drone’s camera is a simple generic handheld Canon DSLR, the kind you can find on any tourist’s camera. How can such a complex war tool have such a common feature?
Full Story:


Google Maps’ satellite images reveal the full scope of Russian military assets
The world seems to have taken notice of the level of details services like Google Maps offer on an everyday basis. A Twitter account supporting the Ukrainian forces recently shared some images of Russian military establishments that were in public view on Google Maps.
⚡️GOOGLE MAPS ВІДКРИВ ДОСТУП ДО ВІЙСЬКОВИХ ТА СТРАТЕГІЧНИХ ОБ’ЄКТІВ РОСІЇ. Тепер кожен може побачити різноманітні російські пускові установки, шахти міжконтинентальних балістичних ракет, командні пункти та секретні полігони з роздільною здатністю близько до 5 метра на піксель. pic.twitter.com/i75wR8Efwo — Armed Forces 🇺🇦 (@ArmedForcesUkr) April 18, 2022
As the caption reads, Google has opened access to Russian military and strategic facilities. The tweet was probably an attempt at virtue signaling that Google had taken a stance against Russian aggression. However, as a Google spokesperson told The Verge, the information was available in the public domain well before the Ukraine conflict.

7 Programming Languages to Use in Data Science
With the constant evolution of data science, you need to be skilled in cutting-edge technologies in the field. In this article, we will look at the top programming languages used in data science.
Data has become enormously valuable in the last decade.
Every big company out there has valuable data that, with the help of a good data scientist, can benefit the way they do their business. In other cases, pinpoint strategies that may not be working that well.