In today’s digital age, computational tasks have become increasingly complex. This, in turn, has led to an exponential growth in the power consumed by digital computers. Thus, it is necessary to develop hardware resources that can perform large-scale computing in a fast and energy-efficient way.
In this regard, optical computers, which use light instead of electricity to perform computations, are promising. They can potentially provide lower latency and reduced power consumption, benefiting from the parallelism that optical systems have. As a result, researchers have explored various optical computing designs.
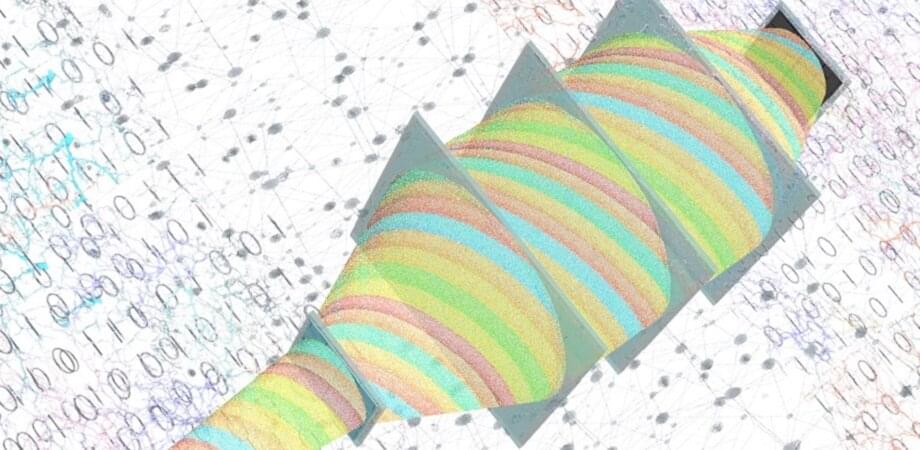
For instance, a diffractive optical network is designed through the combination of optics and deep learning to optically perform complex computational tasks such as image classification and reconstruction. It comprises a stack of structured diffractive layers, each having thousands of diffractive features/neurons. These passive layers are used to control light-matter interactions to modulate the input light and produce the desired output. Researchers train the diffractive network by optimizing the profile of these layers using deep learning tools. After the fabrication of the resulting design, this framework acts as a standalone optical processing module that only requires an input illumination source to be powered.