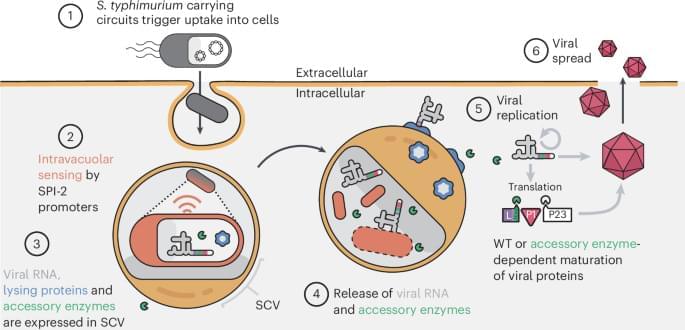
CAPPSID relies on an engineered S. typhimurium to act as a synthetic ‘capsid’ to transcribe and deliver viral RNA inside cancer cells, launching a virus that can directly lyse surrounding cells.

The US military is considering SpaceX’s Starship for rapid Earth-to-Earth transportation of cargo, leveraging its high-speed capabilities to revolutionize military logistics, humanitarian missions, and commercial shipping operations.
🚀 Q: How does Starship revolutionize military transport capabilities? A: Starship can carry 150 metric tons of cargo, including heavy artillery tanks and helicopters, with a payload capacity of 1M tall and 9m in diameter, enabling transport of large military equipment in a single trip.
🌍 Q: What advantage does Starship offer for global military operations? A: Starship’s orbital velocities make it 10 times faster than commercial aircraft, allowing transport of cargo and personnel globally in under an hour, significantly enhancing military response times and operational flexibility.

A Northwestern Medicine study has uncovered new insights that may aid in understanding and potentially treating one of the most common and aggressive forms of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, according to findings published in Science Advances.
The study described critical differences in B-cell receptor (BCR) types that may influence the progression and treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and other forms of B-cell leukemia and lymphomas, which affect more than 80,000 Americans each year.
“B-cells, which are responsible for producing antibodies, rely on BCRs for survival and growth. While most research has focused on the IgM variant of BCRs, this study sheds light on the lesser-understood IgG1 variant,” said Vipul Shukla, Ph.D., assistant professor of Cell and Developmental Biology, who was co-senior author of the study.

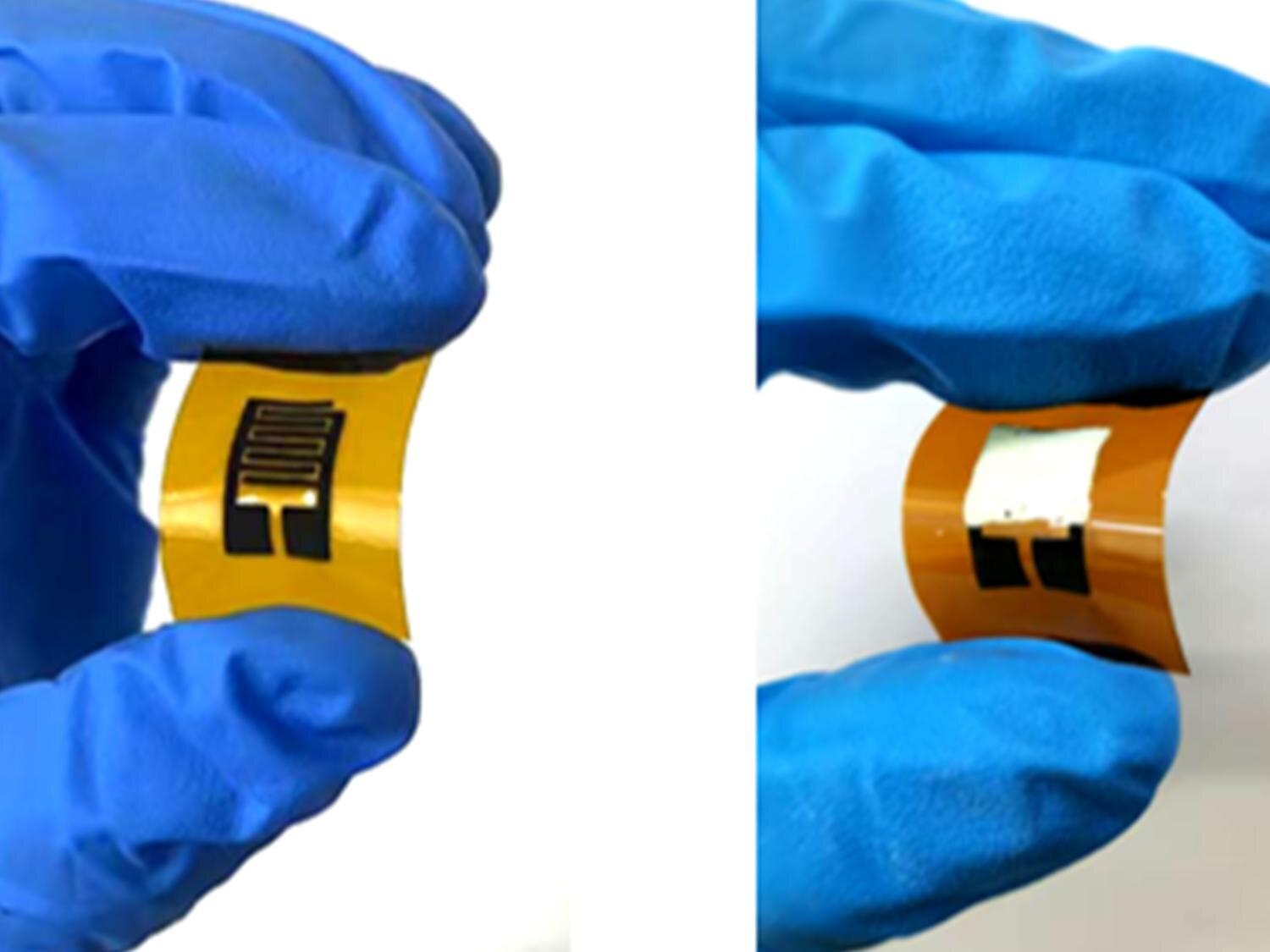
In the U.S., one in five of the 37 million adults who has diabetes doesn’t know it. Current methods of diagnosing diabetes and prediabetes usually require a visit to a doctor’s office or lab work, both of which can be expensive and time-consuming. Now, diagnosing diabetes and prediabetes may be as simple as breathing.
A research team led by Huanyu “Larry” Cheng, James L. Henderson, Jr. Memorial Associate Professor of Engineering Science and Mechanics at Penn State, has developed a sensor that can help diagnose diabetes and prediabetes on-site in a few minutes using just a breath sample. Their results are published in the Chemical Engineering Journal.
Previous diagnostic methods often used glucose found in blood or sweat, but this sensor detects acetone levels in the breath. While everyone’s breath contains acetone as a byproduct of burning fat, acetone levels above a threshold of about 1.8 parts per million indicate diabetes.

On Mars, the past is written in stone—but the present is written in sand. Last week, Perseverance explored inactive megaripples to learn more about the wind-driven processes that are reshaping the Martian landscape every day.
After wrapping up its investigation at the contact between clay and olivine-bearing rocks at Westport, Perseverance is journeying south once more. Previously, attempts were made to drive uphill to visit a new rock exposure called Midtoya. However, a combination of the steep slope and rubbly, rock-strewn soil made drive progress difficult, and after several attempts, the decision was made to return to smoother terrain., the effort wasn’t fruitless, as the rover was able to gather data on new spherule-rich rocks thought to have rolled downhill from Midtoya, including the witch hat or helmet-shaped rock “Horneflya,” which has attracted much online interest.
More recently, Perseverance explored a site called Kerrlaguna where the steep slopes give way to a field of megaripples: large windblown sand formations up to 1 meter (about 3 feet) tall. The science team chose to perform a mini-campaign to make a detailed study of these features. Why such interest? While often the rover’s attention is focused on studying processes in Mars’ distant past that are recorded in ancient rocks, we still have much to learn about the modern Martian environment.


The most common type of brain tumor in children, pilocytic astrocytoma (PA), accounts for about 15% of all pediatric brain tumors. Although this type of tumor is usually not life-threatening, the unchecked growth of tumor cells can disrupt normal brain development and function.
Current treatments focus mainly on removing the tumor cells, but recent studies have shown that non-cancerous cells, such as nerve cells, also play a role in brain tumor formation and growth, suggesting novel approaches to treating these cancers.
Scientists have long known that a nerve cell signaling chemical called glutamate can increase the growth of cancers throughout the body, but despite years of investigation, they haven’t figured out exactly how this happens, or how to stop it.