The whole person will be set on fire.
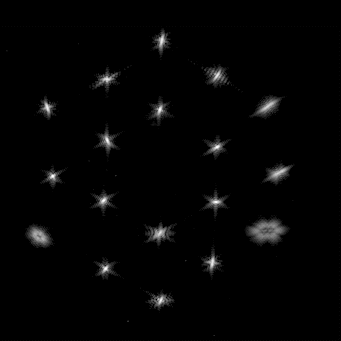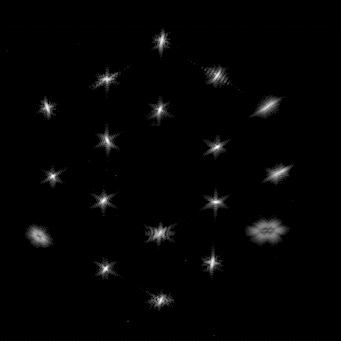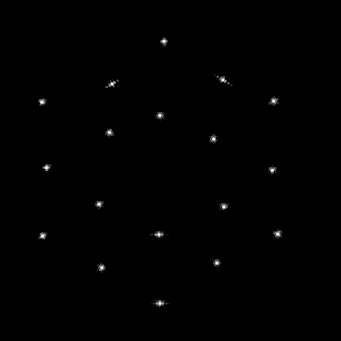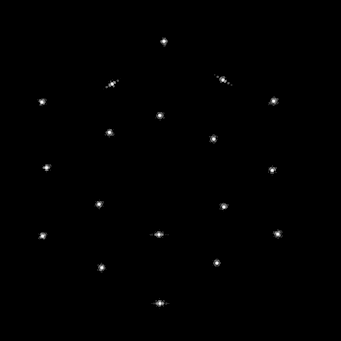
Stars are getting sharper in the James Webb Space Telescope’s field of view.
The team recently completed the third of seven planned steps to align the 18 hexagonal segments of Webb’s mirror, marking nearly the halfway point in a complex, weeks-long process.
While college tuition rises, businesses like Google are offering their own credentials — for a lot less. It might be the educational model we’ve needed for decades.
Ukraine supplies more than 90% of the US’s semiconductor-grade neon, a gas integral to the lasers used in the chip-making process,. Now what?
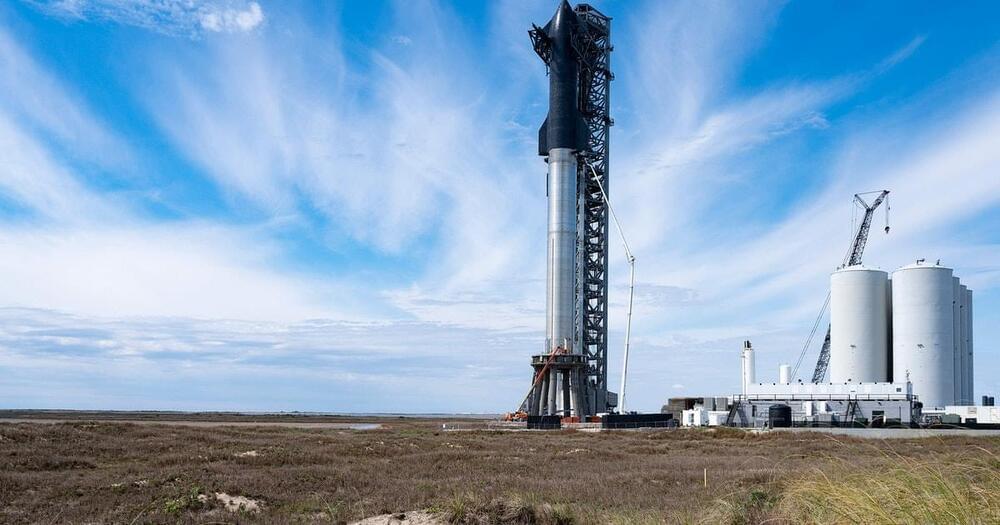
SpaceX prepares its first orbital Starship flight.
Drone capture 360-degree video of SpaceX Starship.
SpaceX is currently developing its Starship rocket at the firm’s Starbase facility in Texas. The project could lead to a giant, fully-reusable rocket system.
Google, Apple and others were warned that they must comply with a new law, which would make them more vulnerable to the Kremlin’s censorship demands.
Vice Prime Minister Fedorov reached out to Elon Musk for Starlink internet service in a last-ditch effort to restore internet access. As Russian forces approach Kyiv, Ukraine has been suffering internet problems.
Mykhailo Fedorov, Ukraine’s Vice Prime Minister and Minister of Digital Transformation contacted SpaceX CEO Elon Musk about the company’s Starlink satellite broadband service.
“While you are attempting to conquer Mars, Russia is attempting to invade Ukraine!” Fedorov said on Twitter. Russian missiles hit Ukrainian civilians as your rockets successfully land in orbit! We request that you send Starlink stations to Ukraine and direct all rational Russians to take a position.”
At the Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, SpaceX launched its second shipment of internet-bearing satellites on Friday. The satellites will deliver internet access to users all across the world.
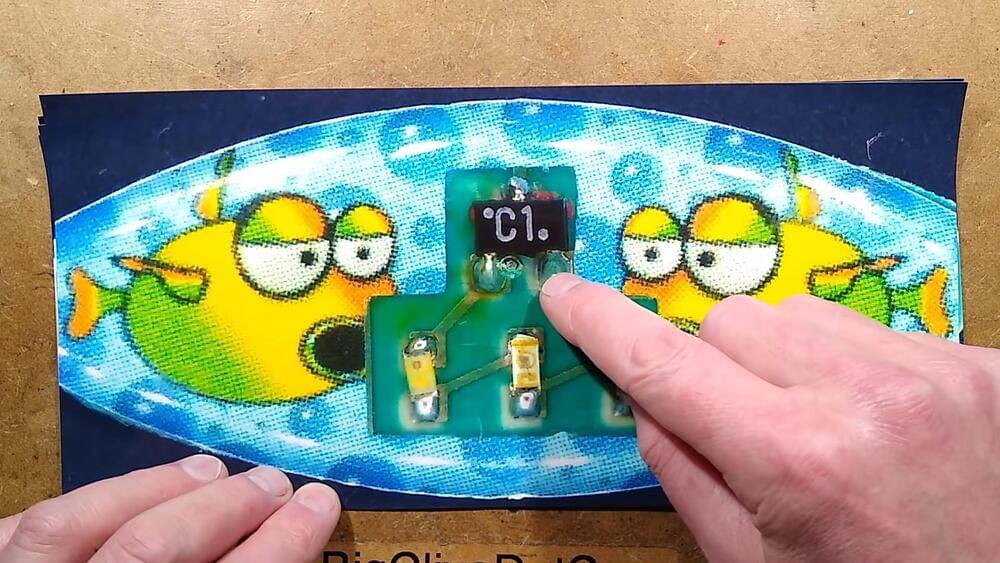
The late 90s and early 2000s were a breakout time for mobile phones, with cheap GSM handsets ushering in the era in which pretty much everybody had a phone. Back then, a popular way to customize one’s phone was to install a sticker that would flash when the phone rang. These required no batteries or any other connection to the phone, and [Big Clive] has dived in to explain how they worked.
It’s an old-fashioned teardown that requires a bit of cutting to get inside the sticker itself. A typical example had three LEDs in series for a total voltage drop of around 7V, hooked up to two diodes and a PCB trace antenna. A later evolution used raw unpackaged components bonded to the PCB. Future versions went down to a single diode, using the LEDs to serve as the second. The basic theory was that the PCB traces would pick up RF transmitted by the phone when a call was coming in, lighting the LEDs.
In the 2G era, the freuqencies used were on the order of 300 MHz to 1.9GHz. A combination of the change in frequencies used by modern phone technology and the lower transmit powers used by handsets means that the stickers don’t work properly with modern phones according to [Big Clive].