President Biden praised Ford and General Motors for investing billions of dollars into building electric vehicles – but didn’t mention Tesla.
Quanta Magazine.
In The Structure of Scientific Revolutions, the philosopher of science Thomas Kuhn observed that scientists spend long periods taking small steps. They pose and solve puzzles while collectively interpreting all data within a fixed worldview or theoretical framework, which Kuhn called a paradigm. Sooner or later, though, facts crop up that clash with the reigning paradigm. Crisis ensues. The scientists wring their hands, reexamine their assumptions and eventually make a revolutionary shift to a new paradigm, a radically different and truer understanding of nature. Then incremental progress resumes.
For several years, the particle physicists who study nature’s fundamental building blocks have been in a textbook Kuhnian crisis.
The crisis became undeniable in 2016, when, despite a major upgrade, the Large Hadron Collider in Geneva still hadn’t conjured up any of the new elementary particles that theorists had been expecting for decades. The swarm of additional particles would have solved a major puzzle about an already known one, the famed Higgs boson. The hierarchy problem, as the puzzle is called, asks why the Higgs boson is so lightweight — a hundred million billion times less massive than the highest energy scales that exist in nature. The Higgs mass seems unnaturally dialed down relative to these higher energies, as if huge numbers in the underlying equation that determines its value all miraculously cancel out.
Sanctions mean joint Russian-European ExoMars mission is likely to be postponed for a third time.
A new, third, data wiper malware — dubbed “IsaacWiper” — is now targeting Ukrainian governmental systems.
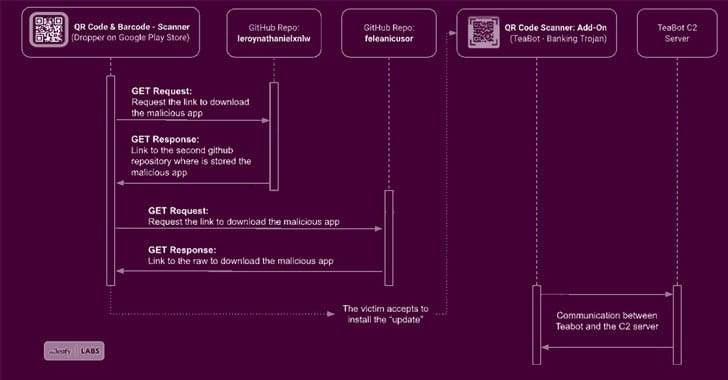
Teabot android banking malware spreads again through google play store apps.
An Android banking trojan designed to steal credentials and SMS messages has been observed once again sneaking past Google Play Store protections to target users of more than 400 banking and financial apps, including those from Russia, China, and the U.S.
As many as five security vulnerabilities have been disclosed in the PJSIP open-source multimedia communication library that could be abused by an attacker to trigger arbitrary code execution and denial-of-service (DoS) in applications that use the protocol stack.