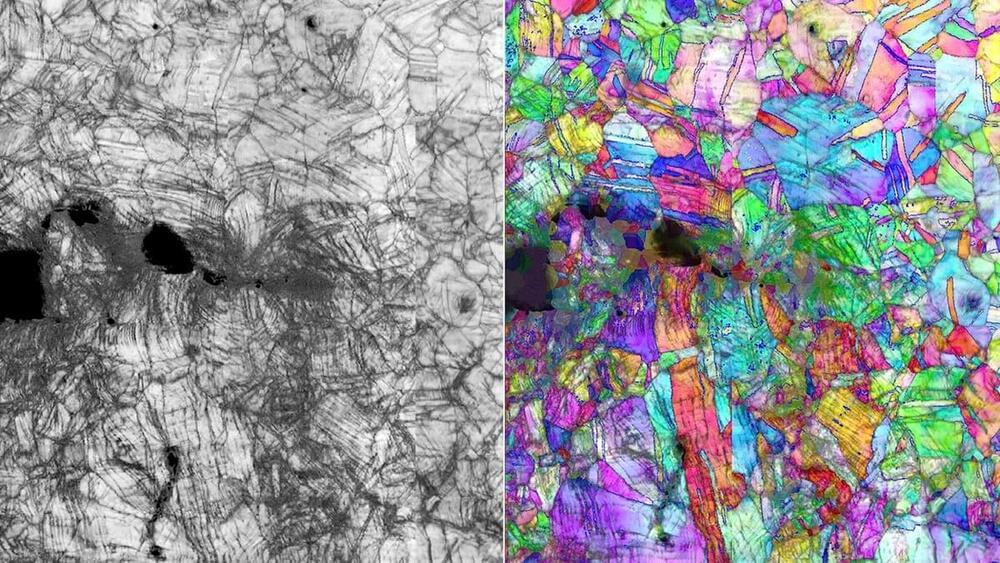
A simple alloy has claimed the crown for toughest material ever recorded. In a new study, a team led by researchers at Berkeley Lab ran the alloy through a series of tests and discovered not only its incredible toughness, but high strength and ductility that actually improve in colder temperatures, unlike most known materials.
The alloy in question contains chromium, cobalt and nickel (CrCoNi), and it belongs to a class of metals called high entropy alloys (HEAs). Most alloys are made up of one dominant element with smaller amounts of others added in, but HEAs contain equal amounts of each element. This can give them some impressive properties, such as high strength-to-weight ratios, an elastic modulus that rises with the temperature, or ultra strength and ductility.
In previous work, the researchers found that CrCoNi showed high strength and toughness at low temperatures of around −196 °C (−321 °F). For the new study, the team investigated how it would hold up at even colder temperatures of −253 °C (−424 °F), at which helium exists as a liquid. And sure enough, its toughness hit new heights in preventing cracks propagating.