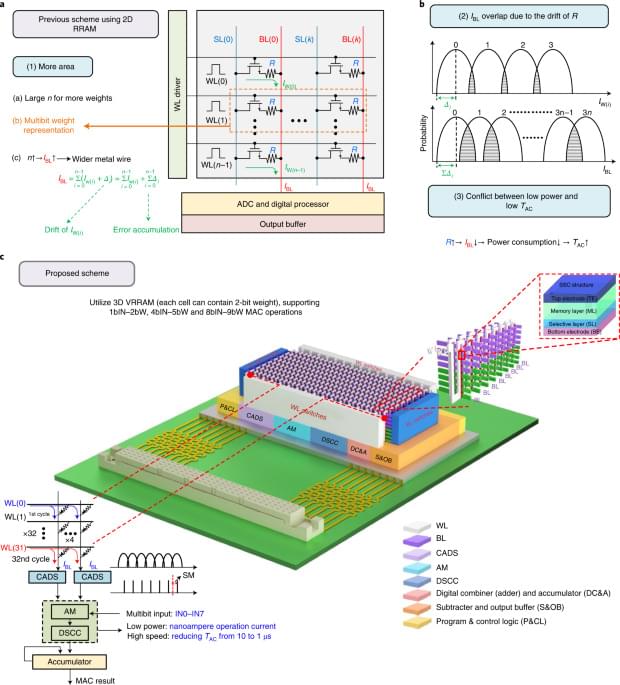
Three-dimensional computing-in-memory circuits based on vertical resistive random-access memory and complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor technologies can be used to create efficient hardware for artificial neural networks.

A team of researchers at Google’s Deep Mind London project, has taught animated players how to play a realistic version of soccer on a computer screen. In their paper published in the journal Science Robotics, the group describes teaching the animated players to play as solo players and also in teams.
For several years, robot engineers have been working diligently to create robots capable of playing soccer. Such work has resulted in competition between various groups to see who can devise the best robot players. And that has led to the creation of RoboCup, which has several leagues, both in the real world and simulated. In this new effort, the researchers applied a new degree of artificial intelligence programming and learning networks to teach simulated robots how to play soccer without ever giving them the rules.
The idea behind the new approach is to get simulated soccer players to learn to play the game the same way humans do—by watching how others do it. It also involved starting from pretty much ground zero. The simulated players first had to learn how to walk, then to run and kick a ball around. At each new level, the AI systems were shown video of real-world soccer players, which allowed them to learn not just the basics of soccer playing, but to mimic the way professional athletes move as they engage in high level sporting events.
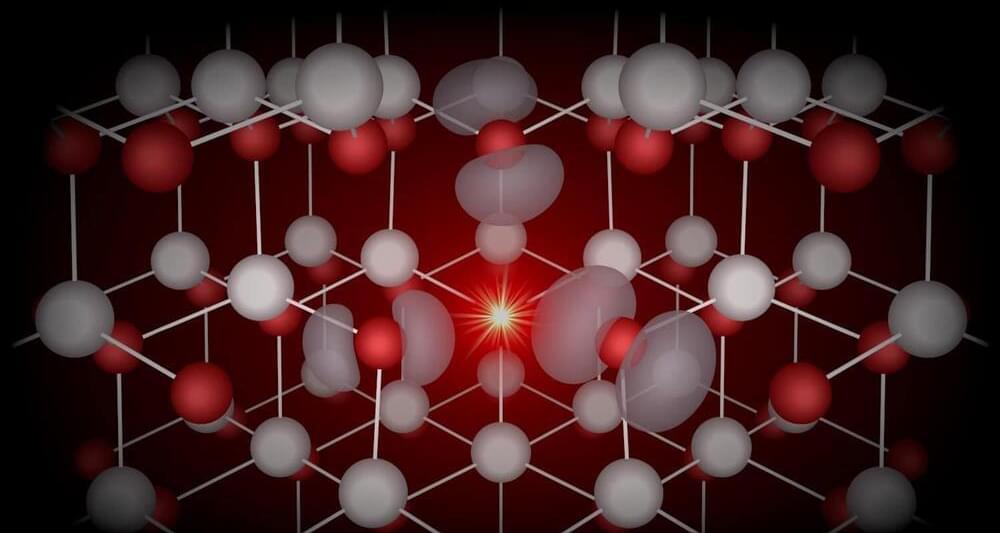
Researchers from North Carolina State University used computational analysis to predict how optical properties of semiconductor material zinc selenide (ZnSe) change when doped with halogen elements, and found the predictions were confirmed by experimental results. Their method could speed the process of identifying and creating materials useful in quantum applications.
Creating semiconductors with desirable properties means taking advantage of point defects—sites within a material where an atom may be missing, or where there are impurities. By manipulating these sites in the material, often by adding different elements (a process referred to as “doping”), designers can elicit different properties.
“Defects are unavoidable, even in ‘pure’ materials,” says Doug Irving, University Faculty Scholar and professor of materials science and engineering at NC State. “We want to interface with those spaces via doping to change certain properties of a material. But figuring out which elements to use in doping is time and labor intensive. If we could use a computer model to predict these outcomes it would allow material engineers to focus on elements with the best potential.”

The trial was only on 8 people, but it appears to have worked well across the board.
Published in GeroScience, a groundbreaking study from the renowned Conboy lab has confirmed that plasma dilution leads to systemic rejuvenation against multiple proteomic aspects of aging in human beings.
This paper takes the view that much of aging is driven by systemic molecular excess. Signaling molecules, antibodies, and toxins, which gradually accumulate out of control, cause cells to exhibit the gene expression that characterizes older cells.
While the bloodstreams of old and young mice have been joined in previous experiments with substantial effects [1], this heterochronic parabiosis approach is neither feasible nor necessary for human beings. Instead, this paper focuses on therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE), a procedure that simply replaces blood plasma with saline solution and albumin. This procedure has already been used to dilute pathogenic, toxic compounds [2], the systemic problems associated with autoimmune and neurological disorders, including Alzheimer’s [3], and even the lingering aftereffects of viral infection [4].
The aircraft is one of Northrop Grumman’s best models.
The Northrop Grumman E-2 Hawkeye is an American all-weather, carrier-capable tactical airborne early warning aircraft. Its latest and most advanced version is the E-2D Advanced Hawkeye.
which features the AN/APY-9 radar (capable of detecting fighter-sized stealth aircraft), radio suite, mission computer, integrated satellite communications, flight management system, improved T56-A-427A engines, a glass cockpit and aerial refueling.
The E-2D Advanced Hawkeye provides warfighters with the necessary situational awareness to compress the time between initial awareness and active engagement.
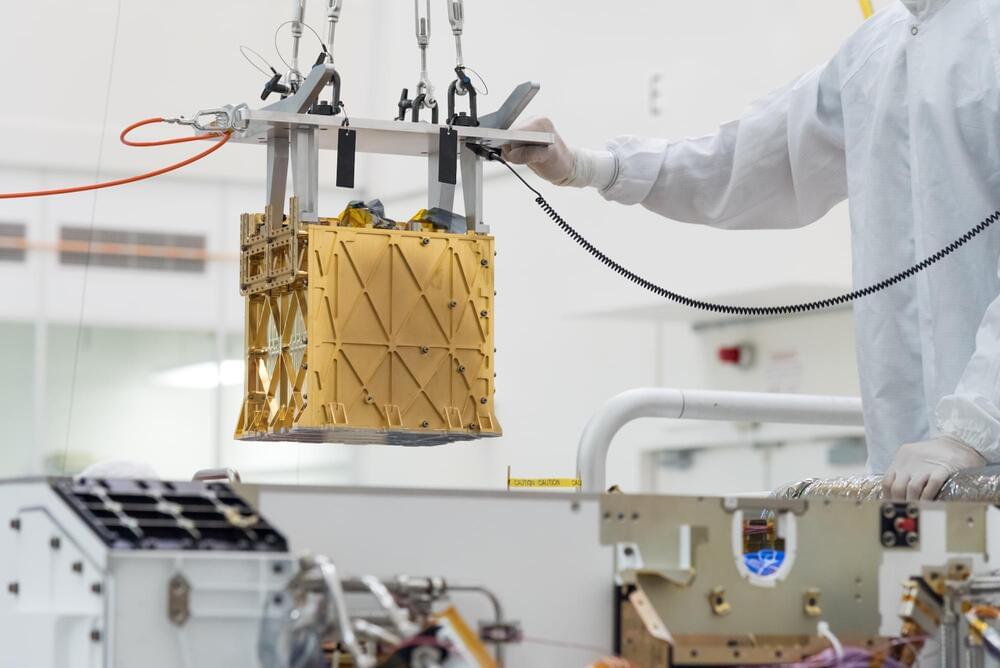

“It’s historic,” says MIT scientists.
In a significant breakthrough, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s (MIT) lunchbox-sized machine has been producing oxygen from the Red Planet’s atmosphere for more than a year, giving hope of life on Mars one day.
Since April 2021, the MIT-led Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment (MOXIE) successfully made oxygen from the Red Planet’s carbon-dioxide-rich atmosphere, according to a press release published by the institute on Wednesday.
“It’s historic,” said MOXIE’s deputy principal investigator Jeffrey Hoffman, a professor of the practice in MIT’s Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics.
MIT’s MOXIE experiment has now produced oxygen on Mars. It is the first demonstration of in-situ resource utilization on the Red Planet, and a key step in the goal of sending humans on a Martian mission.

To smash atoms with unimaginable power.
Cern’s Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is back online after a three-year technical shutdown period. The expert scientists at the famous research facility ran the powerful accelerator at the end of April, and Run 3 physics started in early July. The entire process ran at the highest energy level ever achieved in an accelerator.
The LHC experiments are expected to collect so much data on nature at its smallest levels that it is measured in petabytes.
(LHC) is the world’s largest and most powerful particle accelerator. It consists of a 27-kilometre ring of superconducting magnets with a number of accelerating structures to boost the energy of the particles along the way.

The contract will run through 2030 and makes SpaceX over $4.9 billion in total.
You haven’t seen the tail end of SpaceX launches to the International Space Station (ISS) quite yet. NASA awarded the Elon Musk-founded company a $1.4 billion contract to send five more astronaut missions to the ISS, per NASA’s press release.
The contract, part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Transportation Capability (CCtCap), runs through 2030 and brings the total value of the signed agreement with SpaceX to over $4.9 billion.
NASA has awarded five additional missions to Space Exploration Technologies Corporation (SpaceX) of Hawthorne, California, for crew transportation services to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Transportation Capability (CCtCap) contract.