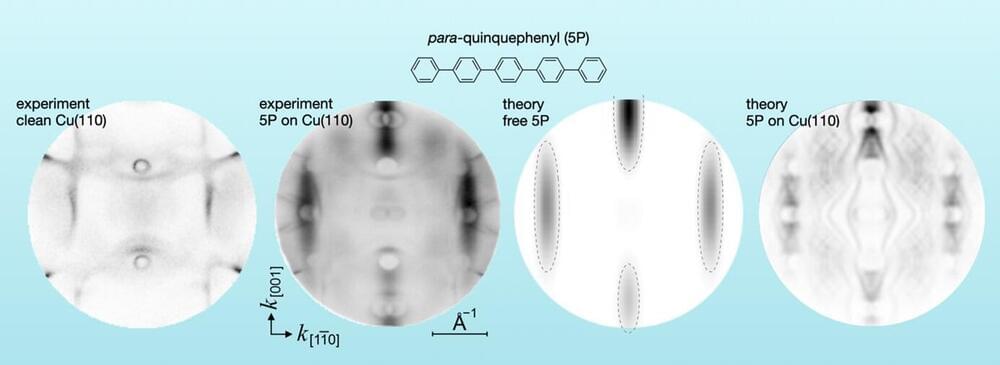
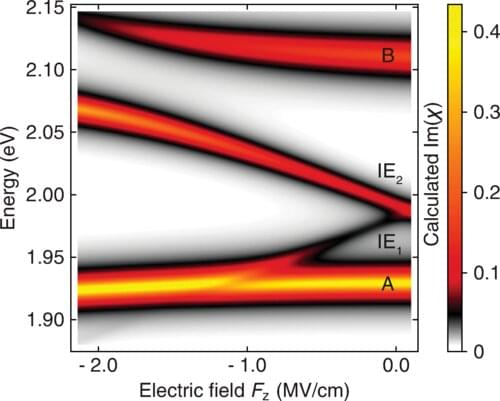
Title: Strong AI: Why we should be concerned about something nobody knows how to build.
Synopsis: At the moment, nobody fully knows how to create an intelligent system that rivals or exceed human capabilities (Strong AI). The impact and possible dangers of Strong AI appear to concern mostly those futurists that are not working in day-to-day AI research. This in turn gives rise to the idea that Strong AI is merely a myth, a sci fi trope and nothing that is ever going to be implemented. The current state of the art in AI is already sufficient to lead to irrevocable changes in labor markets, economy, warfare and governance. The need to deal with these near term changes does not absolve us from considering the implications of being no longer the most intelligent beings on this planet.
Despite the difficulties of developing Strong AI, there is no obvious reason why the principles embedded in biological brains should be outside of the range of what our engineering can achieve in the near future. While it is unlikely that current narrow AI systems will neatly scale towards general modeling and problem solving, many of the significant open questions in developing Strong AI appear to be known and solvable.
Talk held at ‘Artificial Intelligence / Human Possibilities’ event as adjunct to the AGI17 conference in Melbourne 2017.
Assessing emerging risks and opportunities in machine cognition.
With AI Experts Ben Goertzel, Marcus Hutter, Peter Cheeseman and Joscha Bach.
Event Focus:
Given significant developments in Artificial Intelligence, it’s worth asking: What aspects of ideal AI have not been achieved yet?
There is good reason for the growing media storm around AI — many experts agree on the big picture that with the development of Superintelligent AI (including Artificial General Intelligence) humanity will face great challenges (some polls suggest that AGI is not far). Though in order to best manage both the opportunities and risks we need to achieve a clearer picture — this requires sensitivity to ambiguity, precision of expression and attention to theoretical detail in understanding the implications of AI, communicating/discussing AI, and ultimately engineering beneficial AI.
Meetup details: https://www.meetup.com/Science-Technology-and-the-Future/events/242163071/