SpaceX and NASA are gearing up towards the first crewed lunar landing since Apollo 17 in 1972.
NASA deputy associate administrator Mark Kirasich spoke highly of SpaceX’s progress on Starship in a subcommittee meeting of NASA’s Advisory Council on Monday, October 31, as per an Ars Technica report.
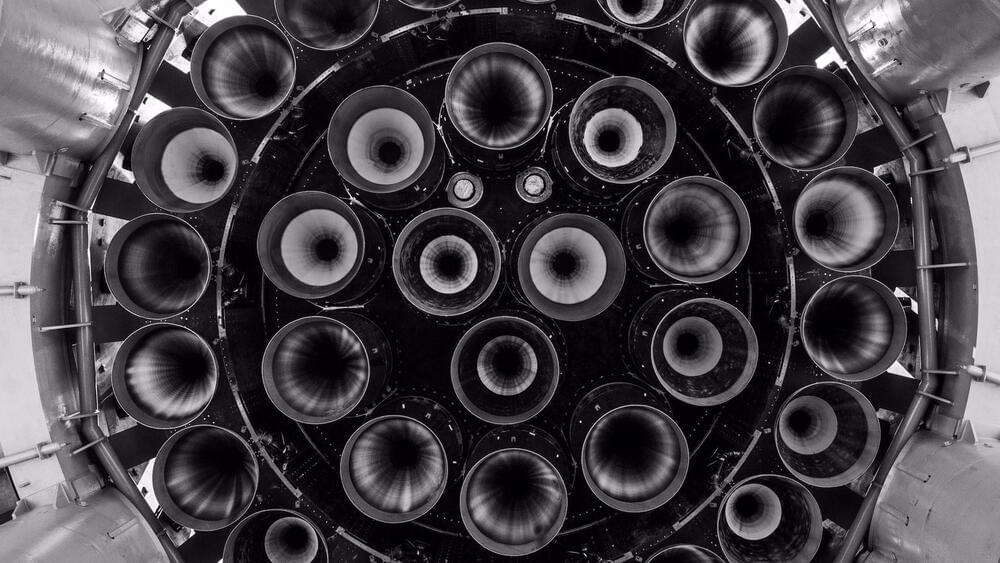
Now, Kirasich has provided an update on SpaceX’s fully reusable Starship launch system, stating that the private space firm is building one of its next-generation Raptor engines every day.
SpaceX / Twitter.
In 2021, NASA awarded SpaceX a $2.9 billion contract to build a modified version of Starship as a lunar lander for its upcoming Artemis III mission.