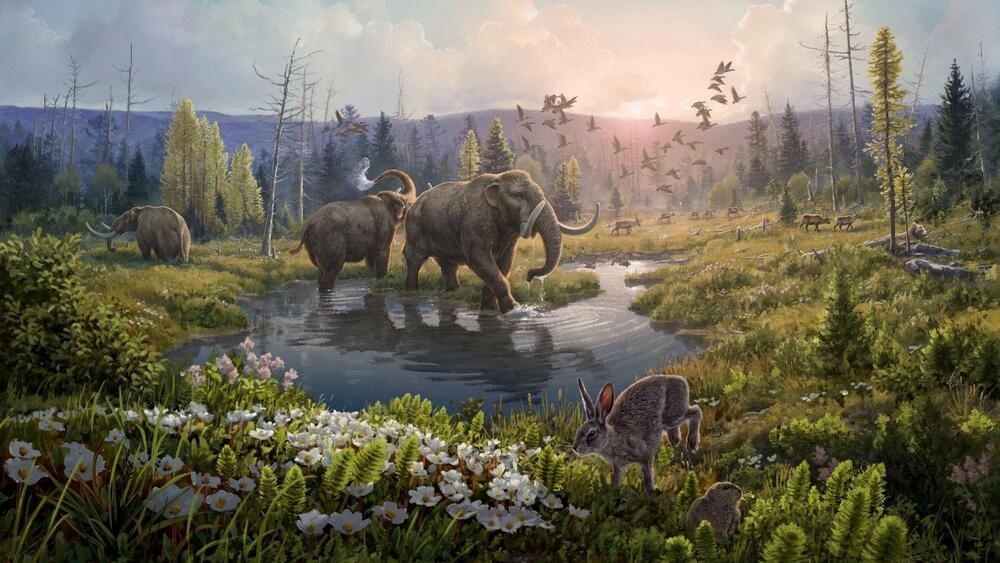
Fragments of the DNA were found in an Ice Age sediment in Northern Greenland.
The discovery of two-million-year-old DNA has changed all the history that has been recorded so far. It revealed that we should go back one million years to understand Earth’s environment.
The results of the 41 usable samples were found hidden in clay and quartz.
Beth Zaikenjpg.
Led by St. John College and the University of Cambridge, the microscopic fragments of environmental DNA were found in Ice Age sediment in the northern part of Greenland. By using the latest technology in its field, the study found that the fragments are one million older than a Siberian mammoth bone, which was thought to be the Earth’s oldest.