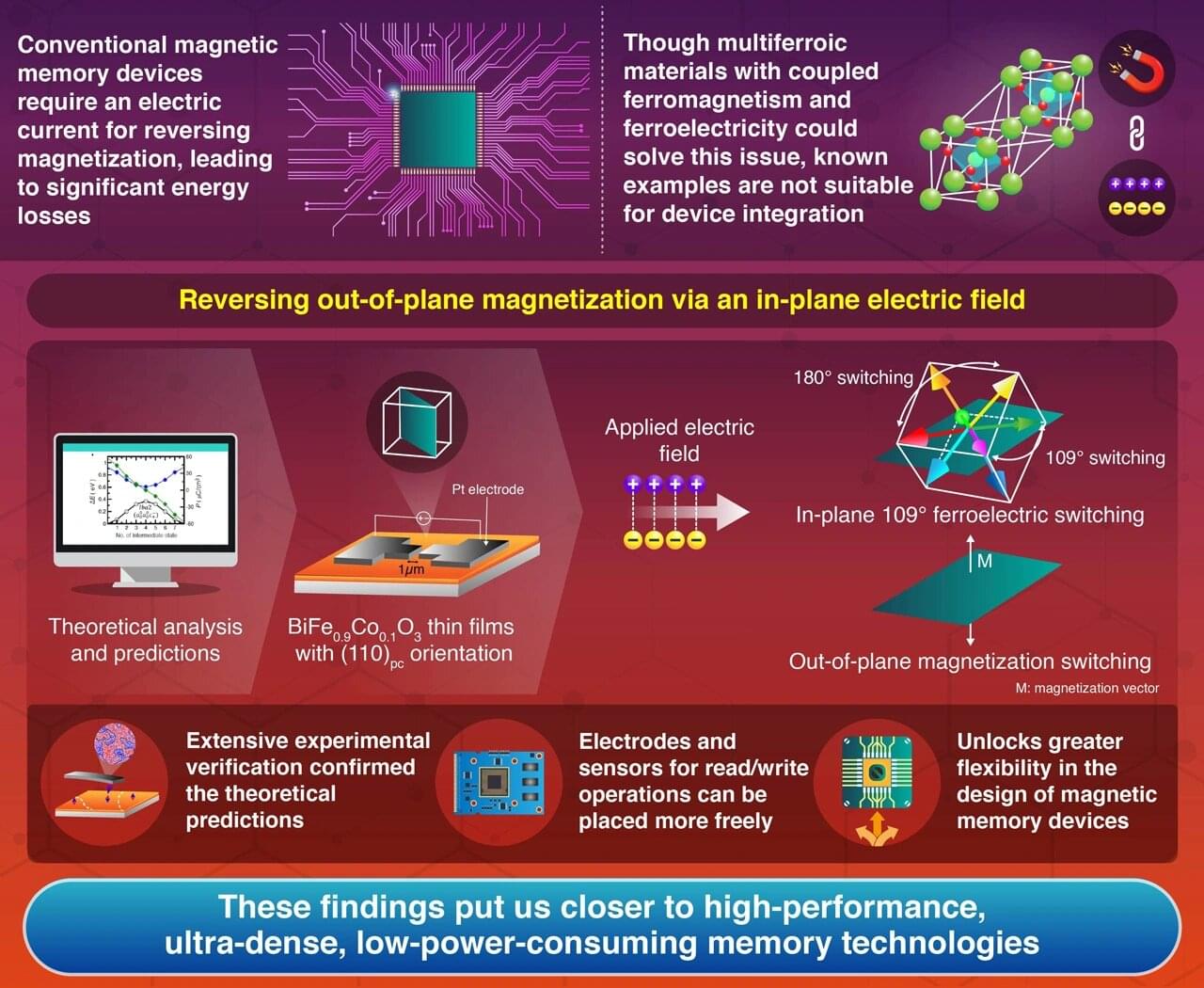
As the digital world demands greater data storage and faster access times, magnetic memory technologies have emerged as a promising frontier. However, conventional magnetic memory devices have an inherent limitation: they use electric currents to generate the magnetic fields necessary to reverse their stored magnetization, leading to energy losses in the form of heat.
This inefficiency has pushed researchers to explore approaches that could further reduce power consumption in magnetic memories while maintaining or even enhancing their performance.
Multiferroic materials, which exhibit both ferroelectric and ferromagnetic properties, have long been considered potential game changers for next-generation memory devices.