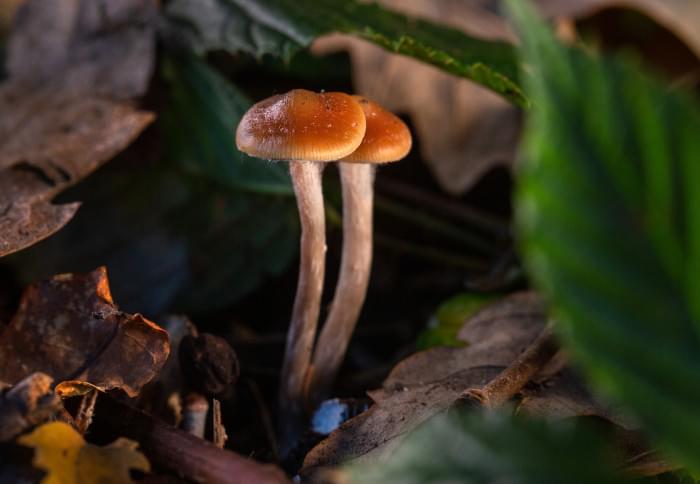
The new results, taken from two combined studies, reveal that people who responded to psilocybin-assisted therapy showed increased brain connectivity not just during their treatment, but up to three weeks afterwards. This “opening up” effect was associated with self-reported improvements in their depression.
Psilocybin, the psychedelic compound found in magic mushrooms, helps to “open up” depressed people’s brains, even weeks after use, a study has found.
These are the findings of a new analysis of brain scans from close to 60 people receiving treatment for depression, led by Imperial College London’s Centre for Psychedelic Research. The team behind the study believes it may have untangled how psilocybin exerts its therapeutic effects on the brain.
Psilocybin is one of a number of psychedelics being explored as a potential therapy for psychiatric disorders. Several studies have trialled a synthesised form of the drug to treat patients with depression and anxiety, with promising results.