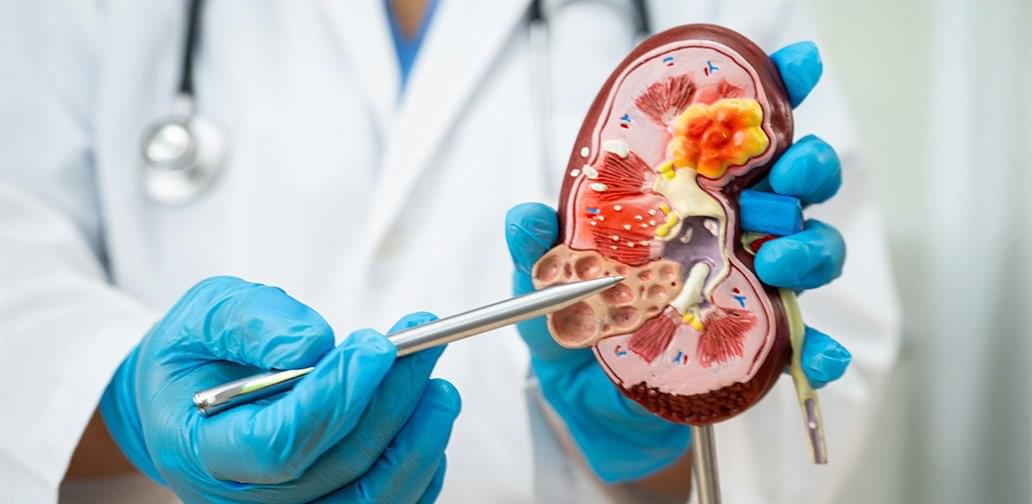
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a major health issue worldwide. Many patients end up requiring regular dialysis to avoid kidney failure and stay alive. Despite the severity of the condition, there are currently no drugs available that improve kidney function. A research group led by Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine’s Professor Takaaki Abe has found a remarkable solution to treat patients with CKD by co-opting a drug typically used for constipation. This is the first time that this drug (lubiprostone) was shown to prevent the decline of renal function in patients with CKD.
“We noticed that constipation is a symptom that often accompanies CKD, and decided to investigate this link further,” explains Abe. “Essentially, constipation disrupts the intestinal microbiota, which worsens kidney function. Working backwards, we hypothesized that we could improve kidney function by treating constipation.”
To address this issue, the group conducted a multicenter Phase II clinical trial (LUBI-CKD TRIAL) at nine Japanese medical institutions, enrolling 150 patients with moderate CKD. This study evaluated the effects of lubiprostone on kidney function. The results showed that, compared to the placebo group, the decline in kidney function (defined as the estimated glomerular filtration rate: eGFR) was suppressed in a dose-dependent manner in patients treated with 8 µg or 16 µg of lubiprostone.
A drug called lubiprostone — typically used for constipation — was remarkably shown to help patients with chronic kidney disease.