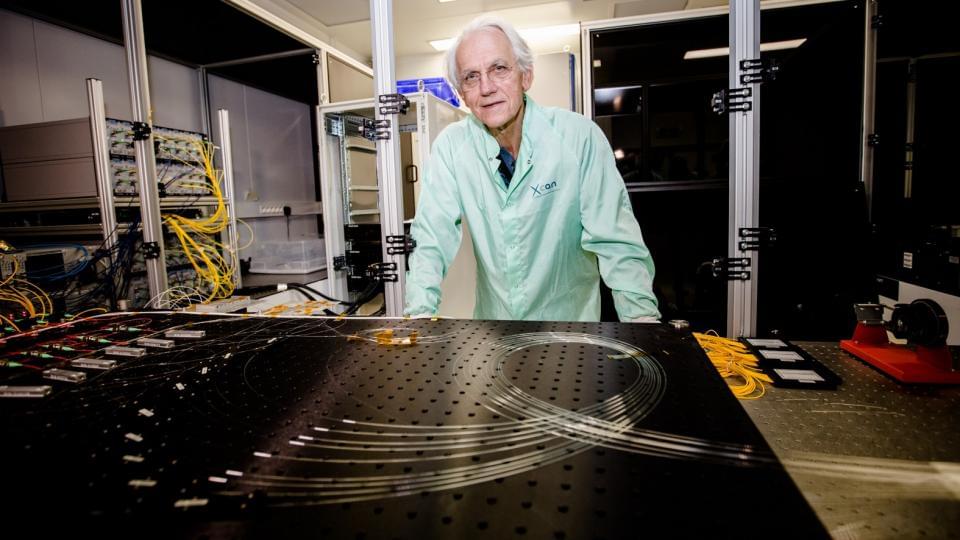
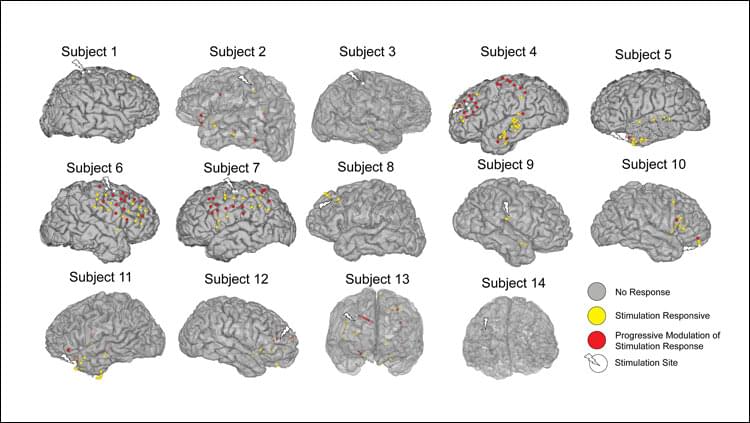
Nobel Prize in physics in 2018 and professor emeritus at the École polytechnique, Gérard Mourou is a scientist that nothing can stop. After revolutionizing ophthalmic surgery with the invention of a new laser technique, the physicist launched a challenging scientific project, which only a researchers of this fame could imagine: the transmutation of radioactive waste by high-power laser. Andra met him to find out more.
It is on the plateau of Saclay, south of Paris, that we meet Gérard Mourou. Here at École Polytechnique, the Nobel Prize in Physics has been working in his laboratory for many years. His enthusiasm remains intact when it comes to addressing the issue of lasers. His research on the subject represents the project of a lifetime. “For a long time, the power of lasers was limited, due to the risk of destroying them. Alongside Donna Strickland, with whom I share the Nobel Prize, we invented the technique of CPA (Chirped Pulse Amplification): the laser emits an ultrashort pulse that we will stretch a colossal factor before amplifying it. Thanks to the CPA one can produce considerable power, to the order of the petawatt (10e15W), without destroying the laser. This represents the equivalent of a hundred times the world electricity grid, ” explains Gérard Mourou.
For the physicist, this new invention opens perspectives in several areas, starting with ophthalmic surgery. An application that came to light as a result of an unlikely combination of circumstances: One of my students was aligning the laser for an experiment when it got the pulse in the eye. We went to the hospital where an intern found that the damage to the retina was absolutely perfect. This laser was the cleanest knife possible…