The best local & breaking news source in the US, featuring local weather, alerts, deals, events and more.



Scientists have been analyzing certain animals living within the CEZ for years, including bacteria, rodents, and even birds. One study back in 2016 found that Eastern tree frogs (Hyla orientalis), which are usually a green color, were more commonly black within the CEZ. The biologists theorize that the frogs experienced a beneficial mutation in melanin—pigments responsible for skin color—that helped dissipate and neutralize some of the surrounding radiation.
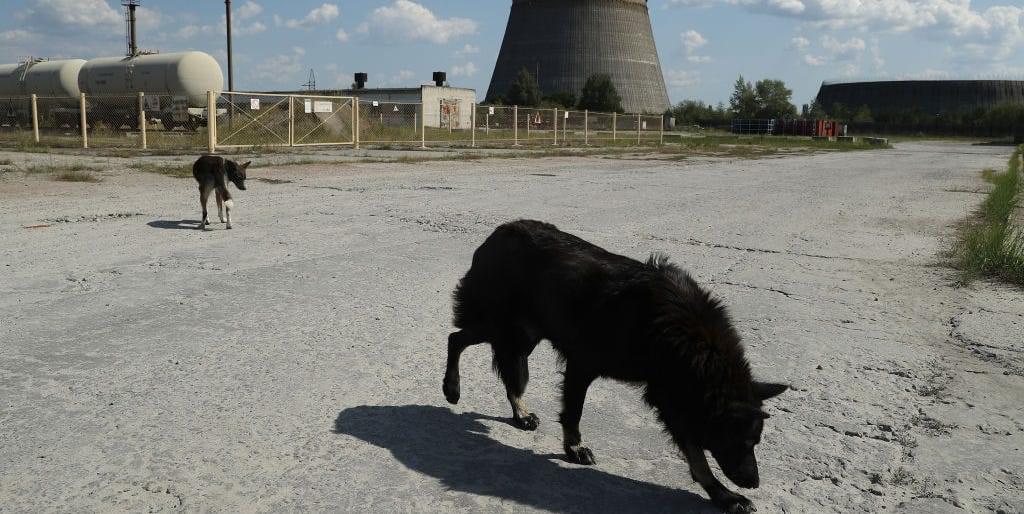
This made scientists ponder: could something similar be happening to Chernobyl’s wild dogs?
The study uncovered that the feral dogs living near the Chernobyl Power Plant showed distinct genetic differences from dogs living only some 10 miles away in nearby Chernobyl City. While this may seem to heavily imply that these dogs have undergone some type of rapid mutation or evolution due to radiation exposure, this study is only a first step in proving that hypothesis.

In a monumental breakthrough, scientists have measured the speed of quantum entanglement for the first time—an achievement that is set to radically transform the way we understand the quantum world. For years, quantum entanglement was thought to be an instantaneous process, but this new research, published in Physical Review Letters, has pushed the boundaries of our knowledge, providing new insights into the quantum realm and setting the stage for revolutionary advances in data security and computational technologies.
Physicists at the University of Oxford have set a new global benchmark for the accuracy of controlling a single quantum bit, achieving the lowest-ever error rate for a quantum logic operation—just 0.000015%, or one error in 6.7 million operations. This record-breaking result represents nearly an order of magnitude improvement over the previous benchmark, set by the same research group a decade ago.
To put the result in perspective: a person is more likely to be struck by lightning in a given year (1 in 1.2 million) than for one of Oxford’s quantum logic gates to make a mistake.
The findings, to be published in Physical Review Letters, are a major advance towards having robust and useful quantum computers.
One of the current hot research topics is the combination of two of the most recent technological breakthroughs: machine learning and quantum computing.
An experimental study shows that already small-scale quantum computers can boost the performance of machine learning algorithms.
This was demonstrated on a photonic quantum processor by an international team of researchers at the University of Vienna. The work, published in Nature Photonics, shows promising new applications for optical quantum computers.