They aren’t going backward — we’re just going forward. Our orbit to the Sun makes us closer to our large adult sons.
Though Boeing may redesign the capsule’s problematic valves before a crewed flight.
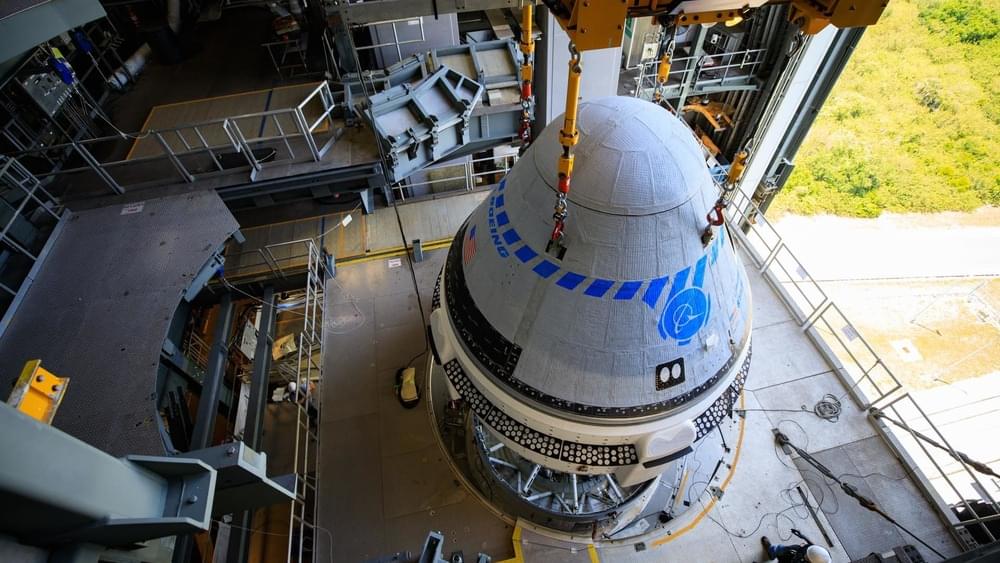
With Boeing’s next Starliner crew capsule launch attempt fast approaching, the company is considering redesigning the capsule’s propulsion valves, due to issues that have so far stopped the company from launching crewed flights to the ISS and competing with SpaceX, a report from *CNBC* reveals.
Boeing is developing the Starliner spacecraft thanks to a roughly $5 billion contract it was awarded under NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The next launch attempt, called OFT-2, is scheduled for next Thursday, May 19.
If the launch is successful, the uncrewed Starliner will then aim to dock with the International Space Station roughly a day later, on May 20.
Up until now, several issues have delayed the development and the first crewed flight of Starliner. In 2019, a software malfunction prevented the first orbital test flight from reaching the ISS after launching to orbit aboard an Atlas V N22; last August, a propulsion valve issue was noticed before the second launch attempt. 13 of the 24 oxidizer valves responsible for Starliner’s movement in orbit were damaged by corrosion caused by humidity at the launch site.
First, Boeing wants to do a little more testing\.
Alpha particles are also known as alpha radiation.
Alpha particles, also known as alpha radiation, are the star players in the game of alpha decay — here’s everything you need to know.
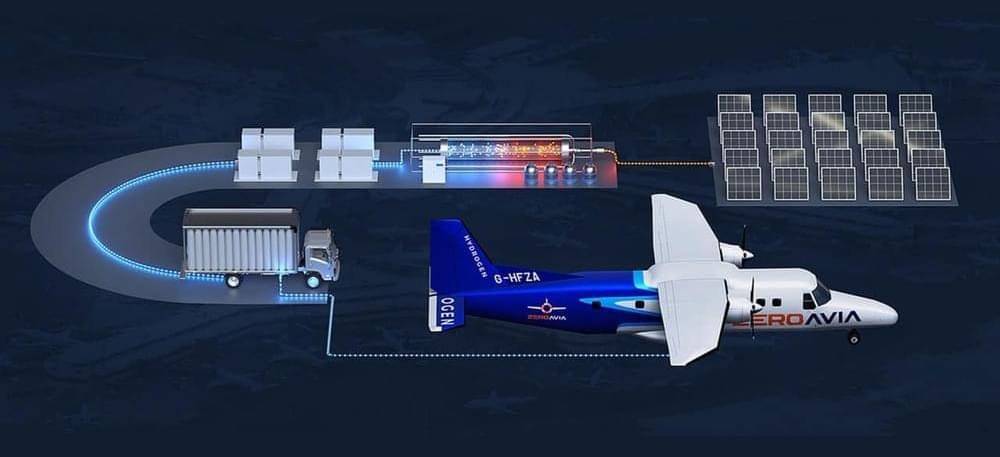
While many other companies in the industry are focusing on designing and developing hydrogen-fueled aircraft from scratch, ZeroAvia is gearing up to test its retrofitted Dornier 228 this summer.
The company has partnered with its strategic investor, Shell, to design and build two commercial-scale mobile hydrogen refuelers for use at ZeroAvia’s research and development site in Hollister, California. At ZeroAvia’s test facility in Hollister, Shell will also provide compressed, low-carbon hydrogen supply to the facility and other locations in the Western U.S.
This strategic collaboration will support the development of ZeroAvia’s flight testing program in the U.S. following the arrival of its second Dornier 228 at Hollister last month and will advance the company’s Hydrogen Airport Refueling Ecosystem (HARE) on a larger scale.
Learn More
Here at Lifespan.io, we publish fact-checked news and deep interviews with aging researchers to help people track the development of treatments targeting aging. These treatments aim at preventing and curing age-related diseases and may improve lives of thousands of people around the globe!
Everyone deserves to know about the emerging opportunities in the field of healthy life extension research. Knowledge is empowering. In our articles and popular science videos, we discuss the progress, pros, cons, and social implications of innovative medicine for controlling aging, and the steps that are needed to accelerate its clinical implementation.
How your giving made a difference in 6 years
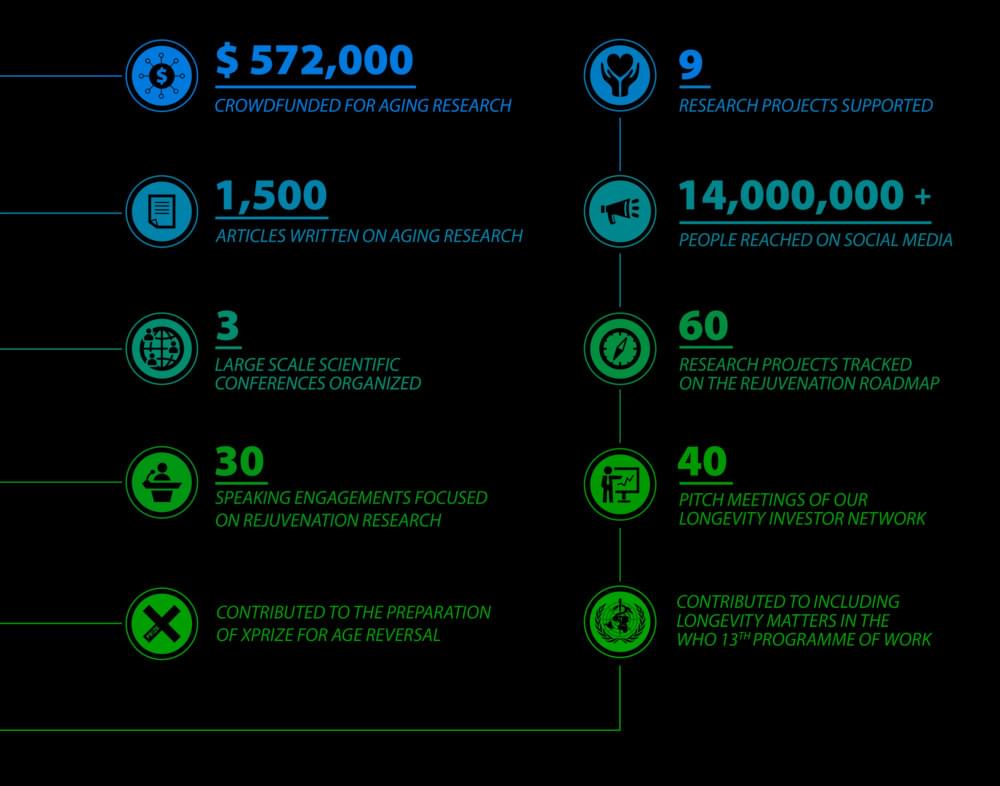
Research on aging and life extension can allow people to be healthier for longer, and with your help, we can reach out to more people! Please consider supporting our work with a monthly donation!
Microsoft announces new security category to combat rising cybercrime and a shortage of cybersecurity professionals.
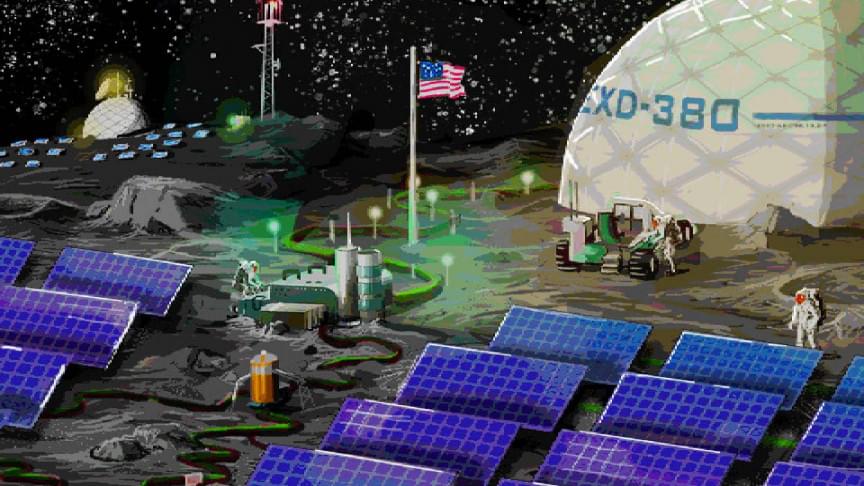
Called the Artemis lunar base, it will include a habitation unit (for up to four astronauts) and separate mining and fuel processing facilities. These facilities would be built far away from the base camp and would serve to produce rocket fuel, water, oxygen, and other materials needed for extended exploration of the lunar surface while decreasing supply needs from Earth.
Get more updates on this story and more with The Blueprint, our daily newsletter: Sign up here for free.
There will also be an electrical grid for the two units which will be connected during emergencies for resiliency and robustness. Sandia’s researchers note that the electrical system controller for the habitation unit will be very similar to the International Space Station (ISS)’s direct current electrical system with some notable differences.
NVIDIA has published the source code of its Linux kernel modules for the R515 driver, allowing developers to provide greater integration, stability, and security for Linux distributions.
The source code has been published to NVIDIA’s GitHub repository under a dual licensing model that combines the GPL and MIT licenses, making the modules legally re-distributable.
The products supported by these drivers include all models built on the Turing and Ampere architecture, released after 2018, including the GeForce 30 and GeForce 20 series, the GTX 1,650 and 1,660, and data center-grade A series, Tesla, and Quadro RTX.