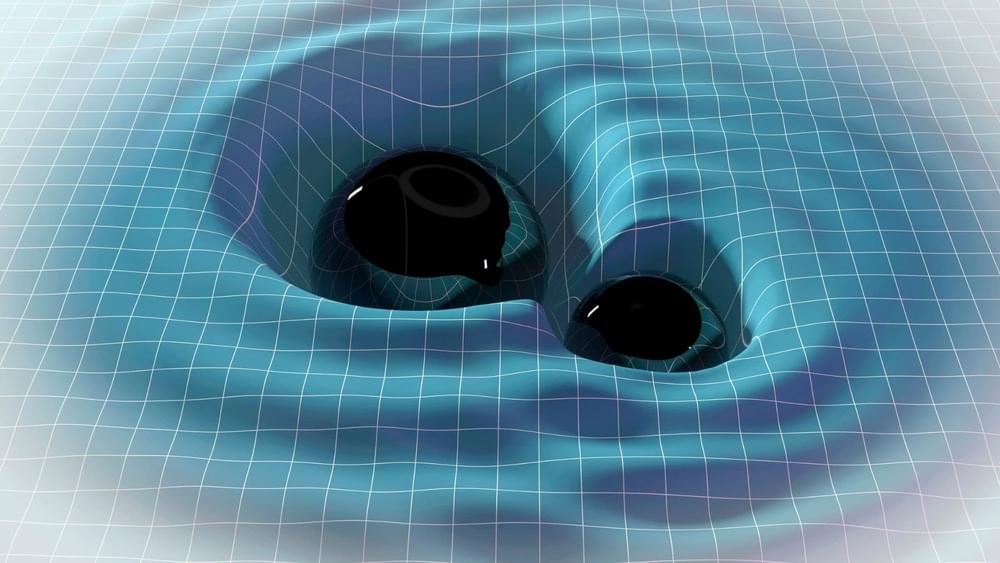
Explaining the hunt for continuous gravitational waves.
Lyons, B., Isaac, E., Choi, N.H. et al. The Simularium Viewer: an interactive online tool for sharing spatiotemporal biological models. Nat Methods (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-022-01442-1
View insights.
An April 8, 2024, solar eclipse will give tens of millions of skywatchers a chance to experience the celestial phenomenon – the last chance to do so from the U.S. until 2045, scientists say.
With two years to go, here’s what to know about the 2024 total solar eclipse.
The next total solar eclipse visible from the U.S. and North America will occur on April 8, 2024, beginning around 10 a.m. in Mexico and ending in the late afternoon over Maine and eastern Canada.
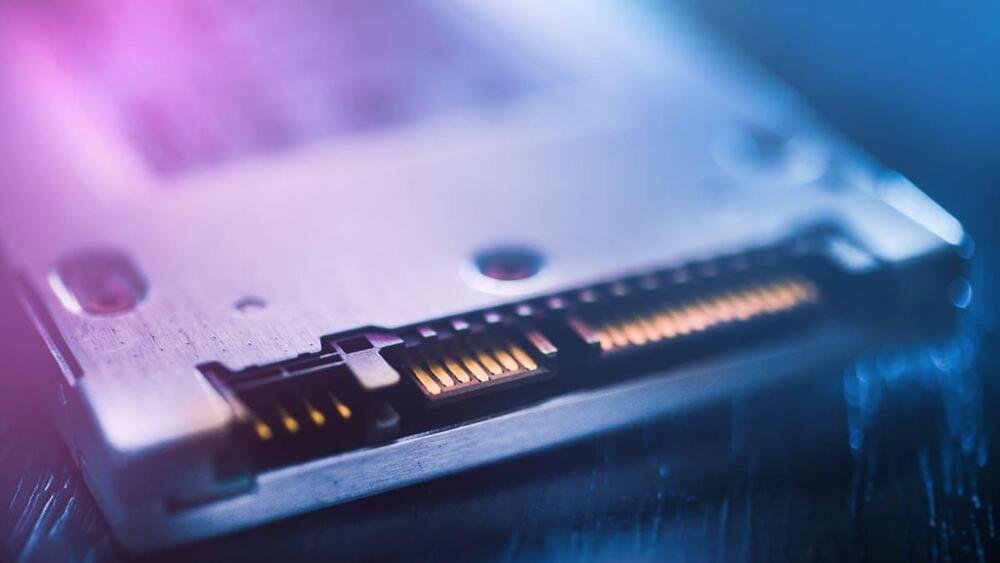
The CEO of the company behind the world’s biggest storage device spills the beans.
A record-breaking 200TB solid state drive could be announced by Nimbus Data before the end of the year, the company has hinted.
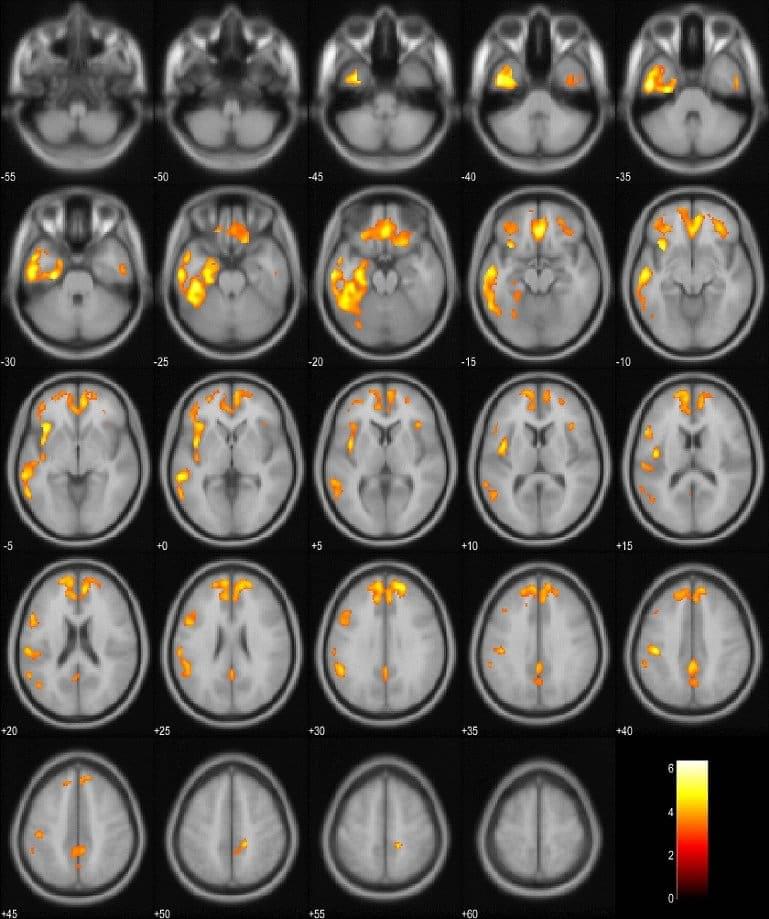
Patients who suffer from frontotemporal dementia with extrapyramidal symptoms have brainstem atrophy and reduced metabolic activity in specific brain regions compared to those with FTD without extrapyramidal symptoms.
Summary: Patients who suffer from frontotemporal dementia with extrapyramidal symptoms have brainstem atrophy and reduced metabolic activity in specific brain regions compared to those with FTD without extrapyramidal symptoms.
Source: University of Eastern Finland.
Frontotemporal dementia patients with extrapyramidal symptoms have brainstem atrophy and reduced metabolism in certain areas of the brain significantly more often than patients without extrapyramidal symptoms, a new study from the University of Eastern Finland shows. This observation can facilitate differential diagnostics in frontotemporal dementia.
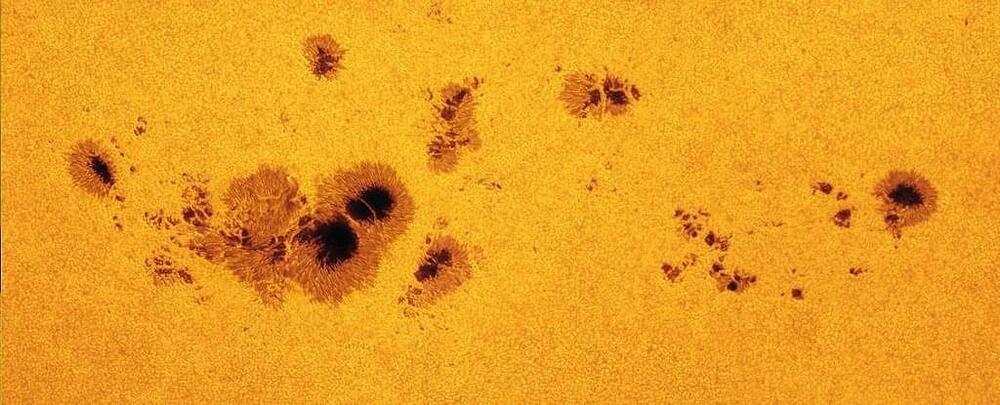
Weather predictions here on Earth are more accurate than they’ve ever been; trying to predict the behavior of our wild and wacky Sun is a little more tricky.
Case in point: according to official predictions, the current cycle of solar activity should be mild. But the gap between the prediction and what’s actually happening is pretty significant – and it’s getting wider. Sunspot counts, used as a measure for solar activity, are way higher than the predicted values calculated by the NOAA, NASA, and the International Space Environmental Service.
In fact, sunspot counts have been consistently higher than predicted levels since September 2020. This could mean that, in contrast to predictions, the Sun is in the swing of an unusually strong activity cycle.
A team of scientists has discovered how working memory is “formatted”—a finding that enhances our understanding of how visual memories are stored.
“For decades researchers have wondered about the nature of the neural representations that support our working memory,” explains Clayton Curtis, professor of psychology and neural science at New York University and the senior author of the paper, which appears in the journal Neuron. “In this study, we used both experimental and analytical techniques to reveal the format of working memory representations in the brain.”
The ability to store information for brief periods of time, or “working memory,” is a building block for most of our higher cognitive processes, and its dysfunction is at the heart of a variety of psychiatric and neurologic symptoms, including schizophrenia.
Chemical engineers and materials scientists are continuously looking for the following groundbreaking material, chemical, or medication. The emergence of machine-learning technologies has accelerated the discovery process, which may typically take years. Ideally, the objective is to train a machine-learning model on a few known chemical samples and then let it build as many manufacturable molecules of the same class with predictable physical attributes as feasible. You can develop new molecules with ideal characteristics if you have all of these components and the know-how to synthesize them.
However, current approaches need large datasets for training models. Many class-specific chemical databases only contain a few example compounds, restricting their capacity to generalize and construct biological molecules that might be generated in the real world.
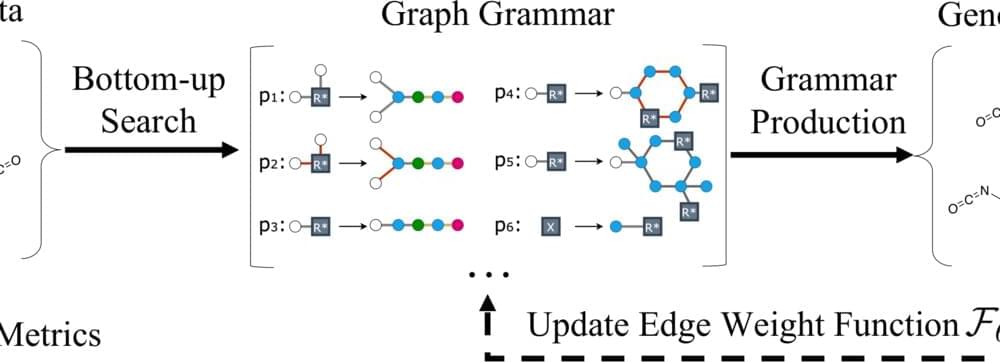
This issue was addressed by a team of researchers from MIT and IBM by employing a generative graph model to create new synthesizable compounds within the same training data’s chemical class. The research was presented in a research paper. They model the production of atoms and chemical bonds as a graph and create a graph grammar — a linguistic analog of systems and structures for word ordering — that provides a set of rules for constructing compounds like monomers and polymers.
Not a solution, but a positive and interesting step. 2 mins.
Researchers have rejuvenated a 53-year-old woman’s skin cells so they are the equivalent of a 23-year-old’s.
Scientists in Cambridge believe that they can do the same thing with other tissues in the body which could lead to treatments for age-related diseases such as diabetes, heart disease and neurological disorders.
The technology is built on the techniques used to create Dolly the cloned sheep more than 25 years ago.
Please subscribe HERE http://bit.ly/1rbfUog.