By Subscription? – In California, You Can and it’s a Tesla Model 3 EV.
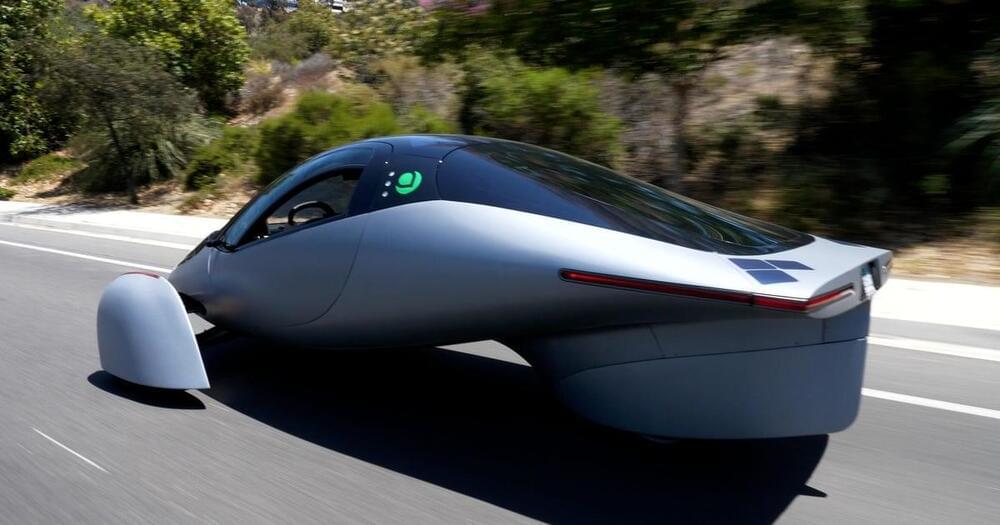
A Santa Monica, California-based company can put you into a Tesla Model 3 using its cellphone app which is now available for both Android and iPhones. The company offering the Car-as-a-service (CaaS) model is Autonomy. Although currently available only in California, the future plans include rolling it out to other U.S. states.
Until the outset of the global pandemic, owning a car was on a dramatic decline. Ride-sharing was exploding, and because cars were becoming pricier, young people entering the workforce were less inclined to join their parents’ generation of car owners.
Isolation and lockdowns temporarily took drivers off the road, as did sticker shock. The latter has been particularly true for electric vehicles (EV) which without government rebates and incentives can cost tens of thousands of dollars more than cars running on gasoline and diesel.