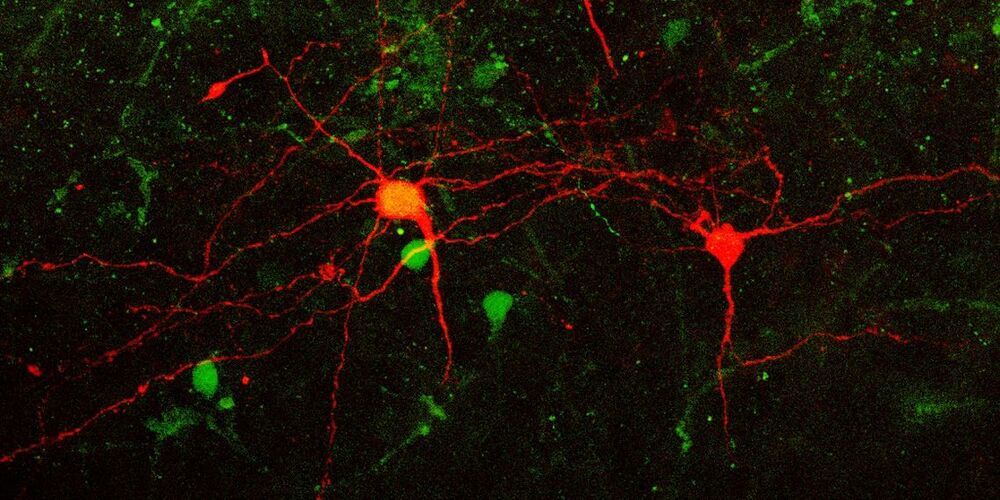
Scientists in Denmark believe the psychedelic substance psilocybin might produce rapid and lasting antidepressant effects in part because it enhances neuroplasticity in the brain. Their new research, published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, has found evidence that psilocybin increases the number of neuronal connections in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus of pig brains.
Psilocybin — the active component in so-called “magic” mushrooms — has been shown to have profound and long-lasting effects on personality and mood. But the mechanisms behind these effects remain unclear. Researchers at Copenhagen University were interested in whether changes in neuroplasticity in brain regions associated with emotional processing could help explain psilocybin’s antidepressant effects.
“Both post-mortem human brain and in vivo studies in depressed individuals have shown a loss of synapses through the down-regulation of synaptic proteins and genes,” the authors of the study wrote. “Hence, upregulation of presynaptic proteins and an increase in synaptic density may be associated with the potential antidepressive effects of psychedelics.”