Terahertz radiation (THz), electromagnetic radiation with frequencies ranging between 0.1 and 10 THz, could be leveraged to develop various new technologies, including imaging and communication systems. So far, however, a lack of fast and sensitive detectors that can detect radiation across a wide range of frequencies has limited the development of these THz-sensing technologies.
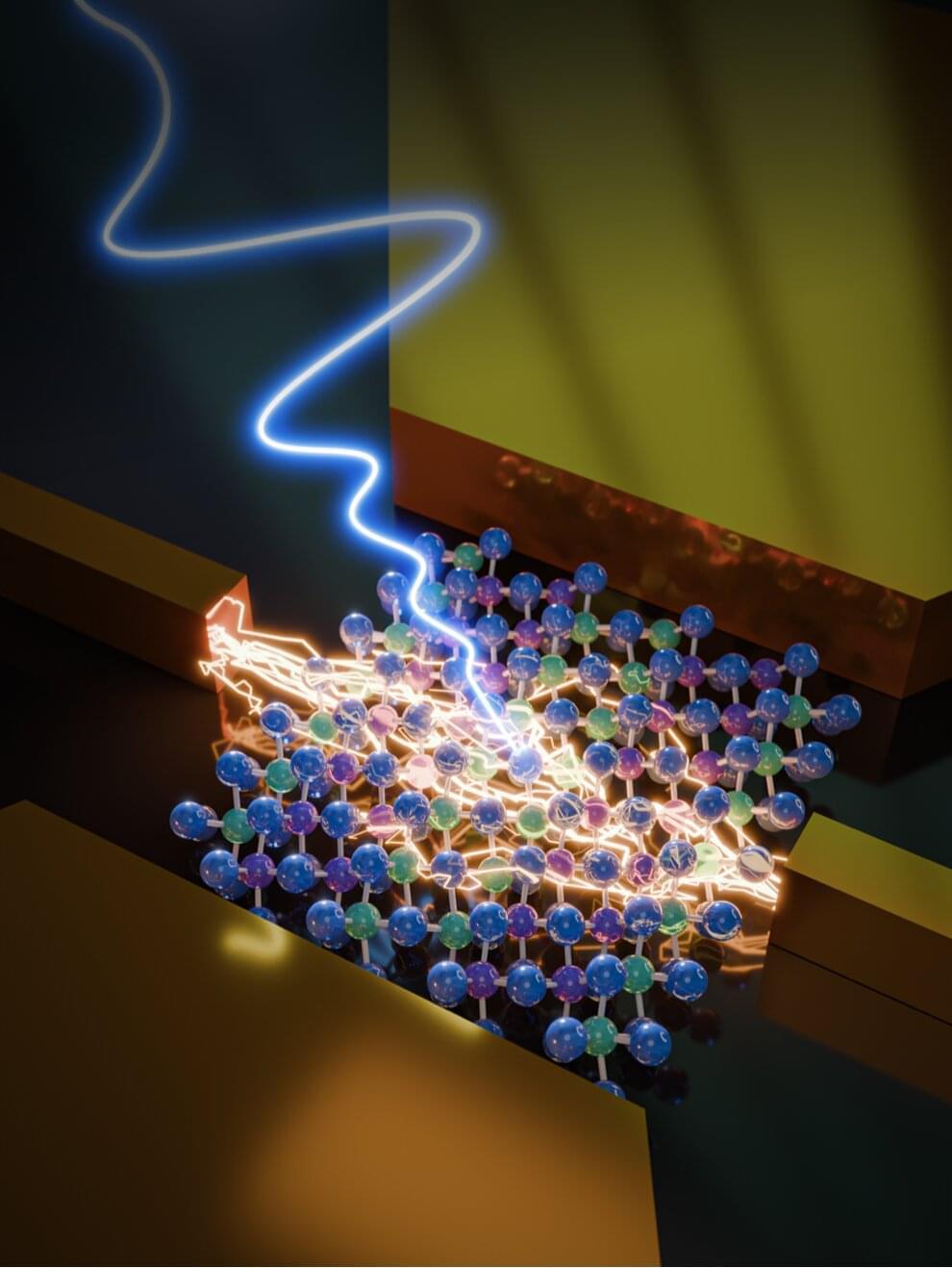
In a recent paper published in Nature Electronics, researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, the University of Tennessee and other institutes have introduced new photodetectors made of tantalum iridium telluride (TaIrTe₄), a 2D-correlated topological semimetal that exhibits advantageous properties. Most notably, this material exhibits a strong nonlinear Hall effect, a physical effect that entails a transverse voltage in the absence of an external magnetic field, which is nonlinearly proportional to an applied electric field or current.
“THz technology is critical in quantum information technology and biomedical sensing because its frequency resonates with low-energy collective excitations in quantum materials and molecular vibrations in biological matters,” Jun Xiao, senior author of the paper, told Phys.org.