Aug 13, 2024
Align or die: Revealing unknown mechanism essential for bacterial cell division
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in category: materials
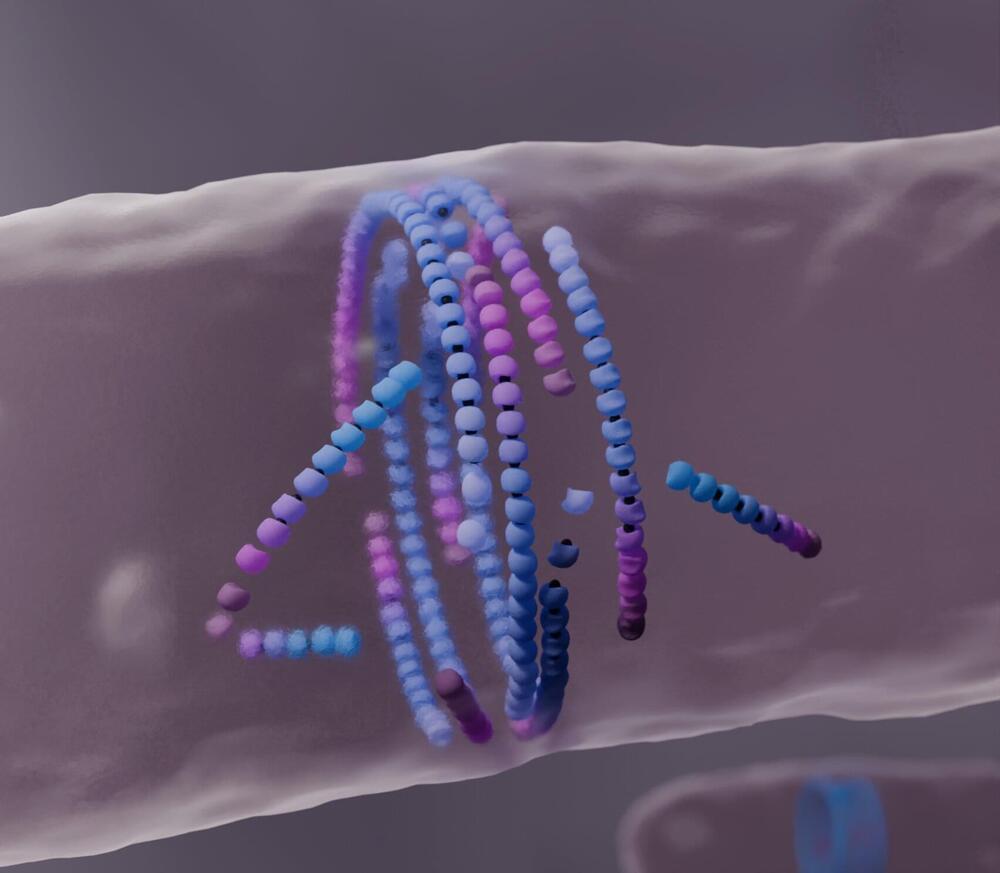
A previously unknown mechanism of active matter self-organization essential for bacterial cell division follows the motto “dying to align”: Misaligned filaments “die” spontaneously to form a ring structure at the center of the dividing cell. The study, led by the Šarić group at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA), was published in Nature Physics. The work could find applications in developing synthetic self-healing materials.