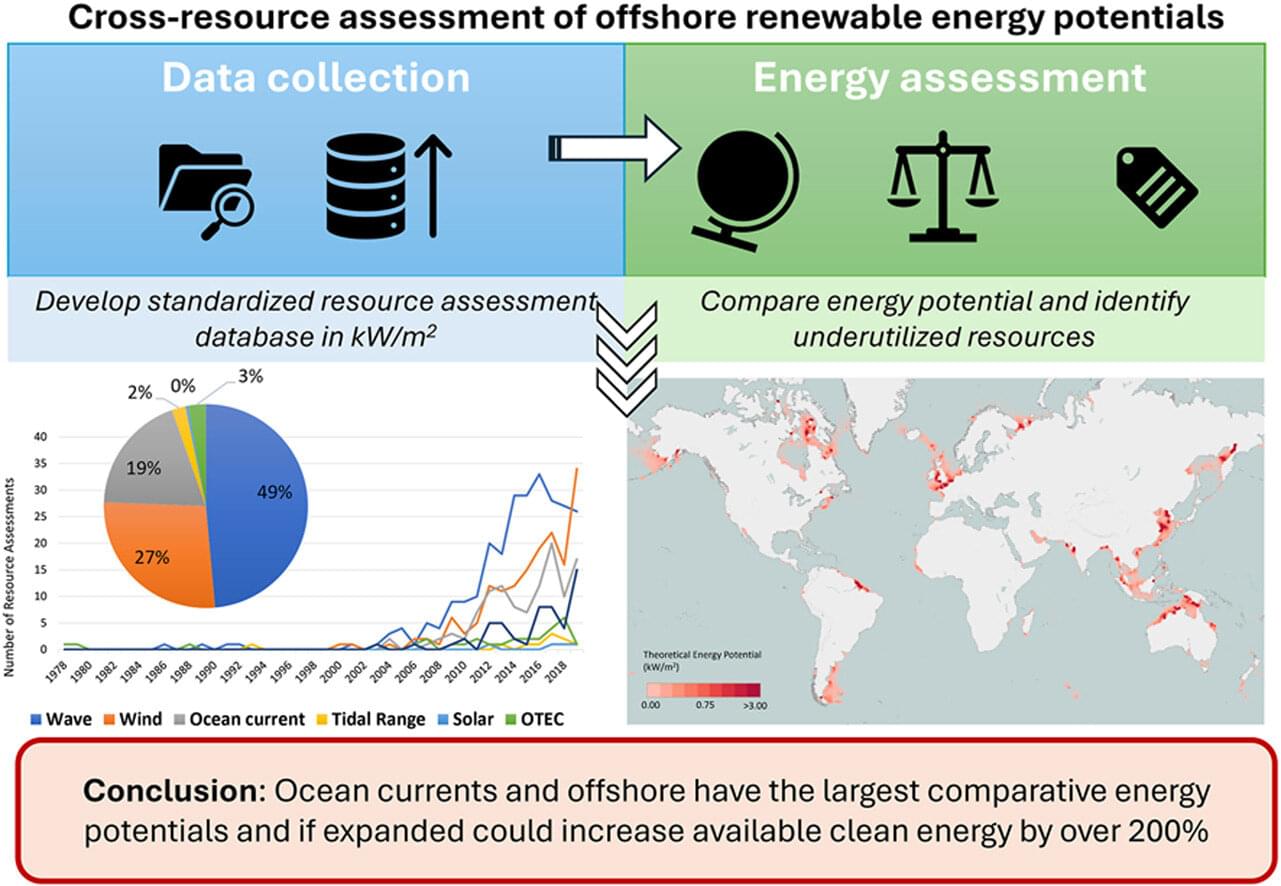
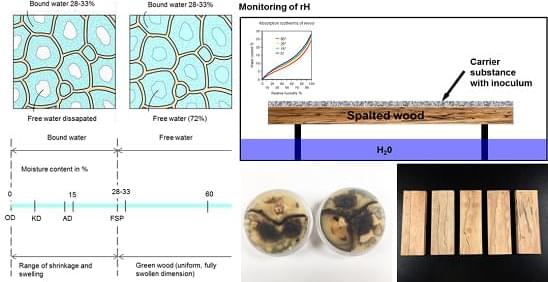
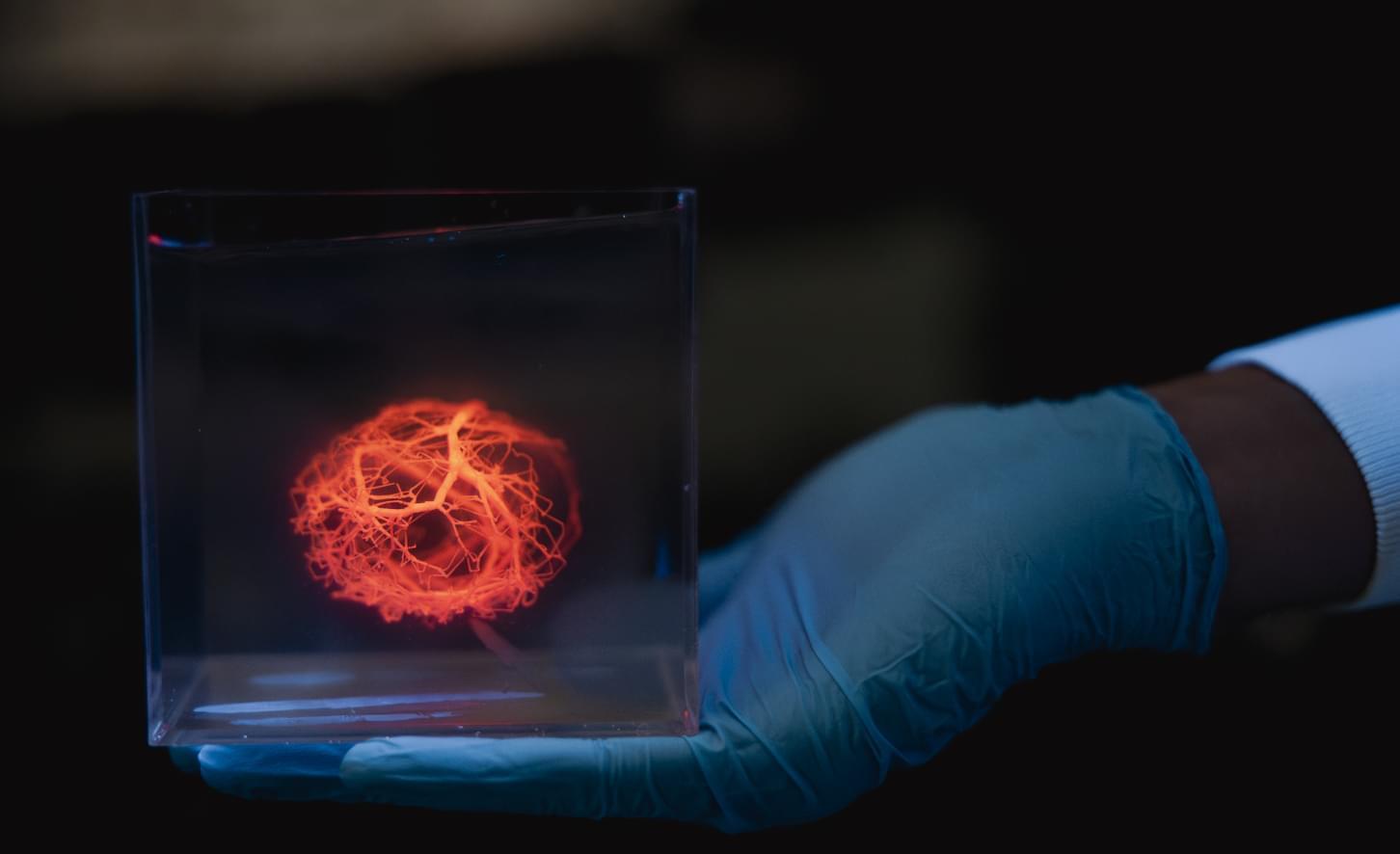
In the grand cosmology of Star Trek, the Prime Directive stands as both a legal doctrine and a quasi-religious tenet, the sacred cow of Federation ethics. It is the non-interference policy that governs Starfleet’s engagement with pre-warp civilizations, the bright line between enlightenment and colonial impulse. And yet, if one tilts their head and squints just a little, a glaring inconsistency emerges: UFOs. Our own real-world history teems with sightings, leaked military footage, close encounters of the caffeinated late-night internet variety — yet in the Star Trek universe, these are, at best, unacknowledged background noise. This omission, this gaping lacuna in Trek’s otherwise meticulous world-building, raises a disturbing implication: If the Prime Directive were real, then the galaxy is full of alien civilizations thumbing their ridged noses at it.
To be fair, Star Trek often operates under what scholars of narrative theory might call “selective realism.” It chooses which elements of contemporary history to incorporate and which to quietly ignore, much like the way a Klingon would selectively recount a battle story, omitting any unfortunate pratfalls. When the series does engage with Earth’s past, it prefers a grand mythos — World War III, the Eugenics Wars, Zephram Cochrane’s Phoenix breaking the warp barrier — rather than grappling with the more untidy fringes of historical record. And yet, our own era’s escalating catalog of unidentified aerial phenomena (UAPs, as the rebranding now insists) would seem to demand at least a passing acknowledgment. After all, a civilization governed by the Prime Directive would have had to enforce a strict policy of never being seen, yet our skies have been, apparently, a traffic jam of unidentified blips, metallic tic-tacs, and unexplained glowing orbs.
This contradiction has been largely unspoken in official Trek canon. The closest the franchise has come to addressing the issue is in Star Trek: First Contact (1996), where we see a Vulcan survey ship observing post-war Earth, waiting for Cochrane’s historic flight to justify first contact. But let’s consider the narrative implication here: If Vulcans were watching in 2063, were they also watching in 1963? If Cochrane’s flight was the green light for formal engagement, were the preceding decades a period of silent surveillance, with Romulan warbirds peeking through the ozone layer like celestial Peeping Toms?