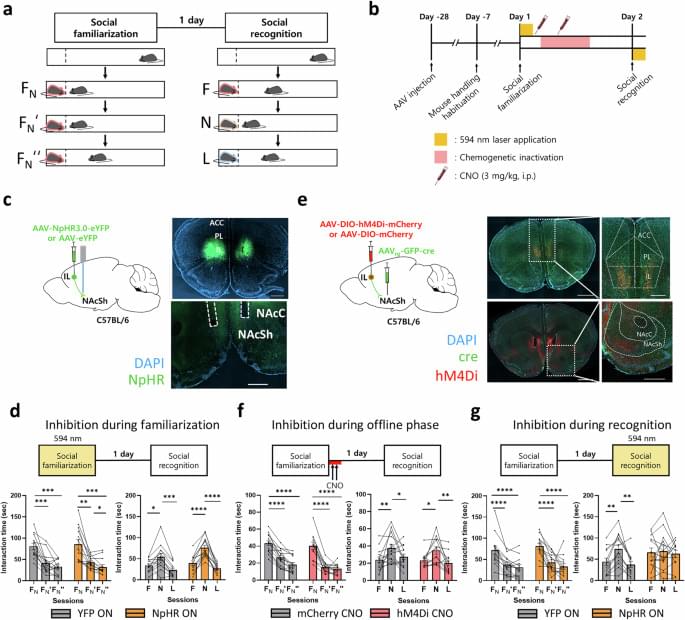
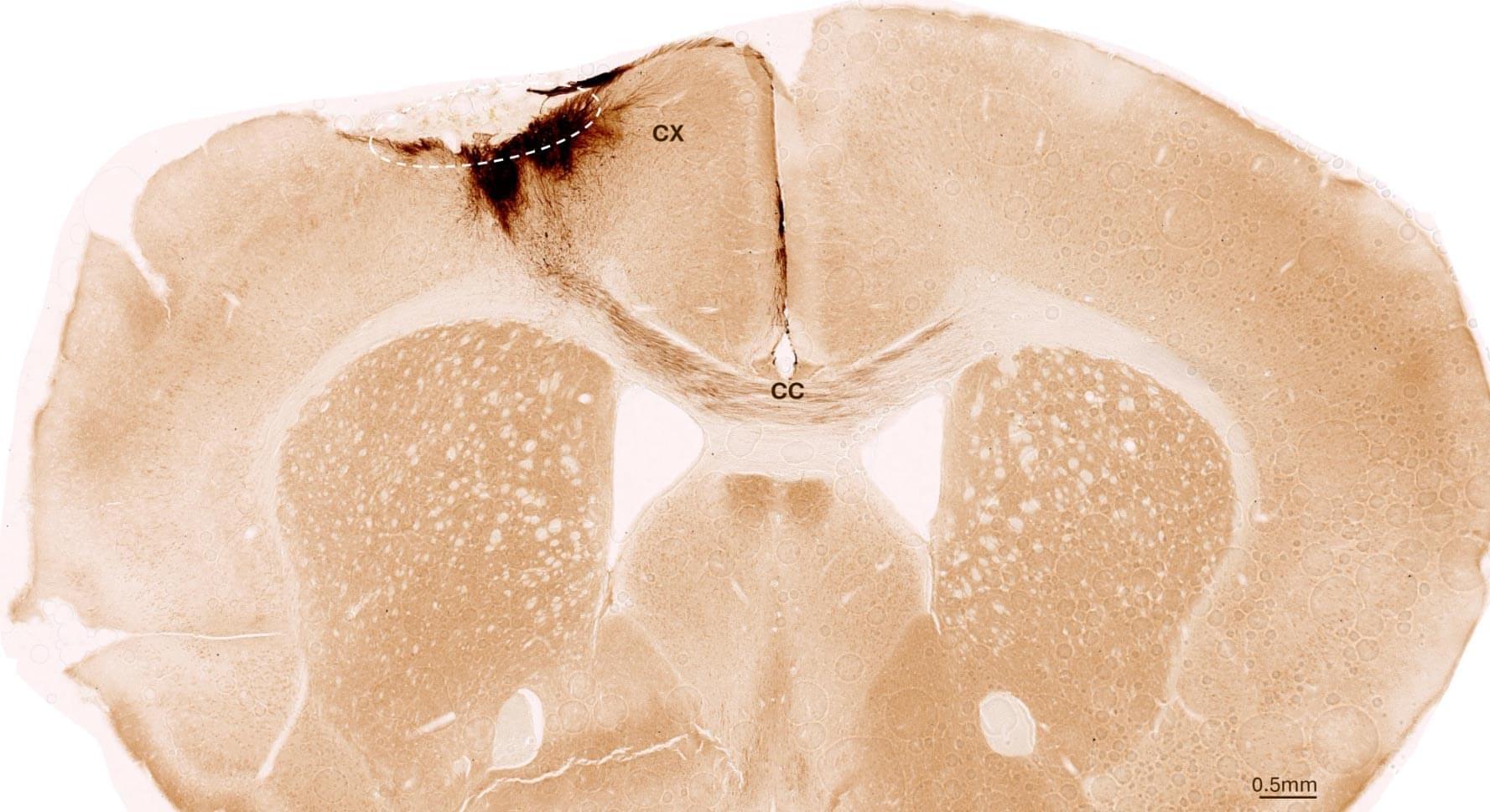
The neural basis of social familiarity remains unclear. This study finds hippocampal-cortical circuits that support generalized social memory, demonstrating where and how the brain stores information about familiar individuals.



Harvard Medical School, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Dell Medical School researchers report that rising rates of early-onset cancer in the United States may reflect more diagnoses rather than more disease.
Cancer awareness and prevention have intensified over many decades, removing potential environmental risk factors from daily life. Mortality of all cancers combined in adults under 50 has decreased by nearly half since the 1990s.
Still, public concern has climbed amidst rising diagnoses and high-profile early-onset cases. PubMed citations related to early-onset cancer more than tripled and screening ages have been shifted down to 45 for colorectal cancer and 40 for breast cancer. Uncertainty persists about whether the higher case counts signal greater cancer occurrence or more frequent detection.