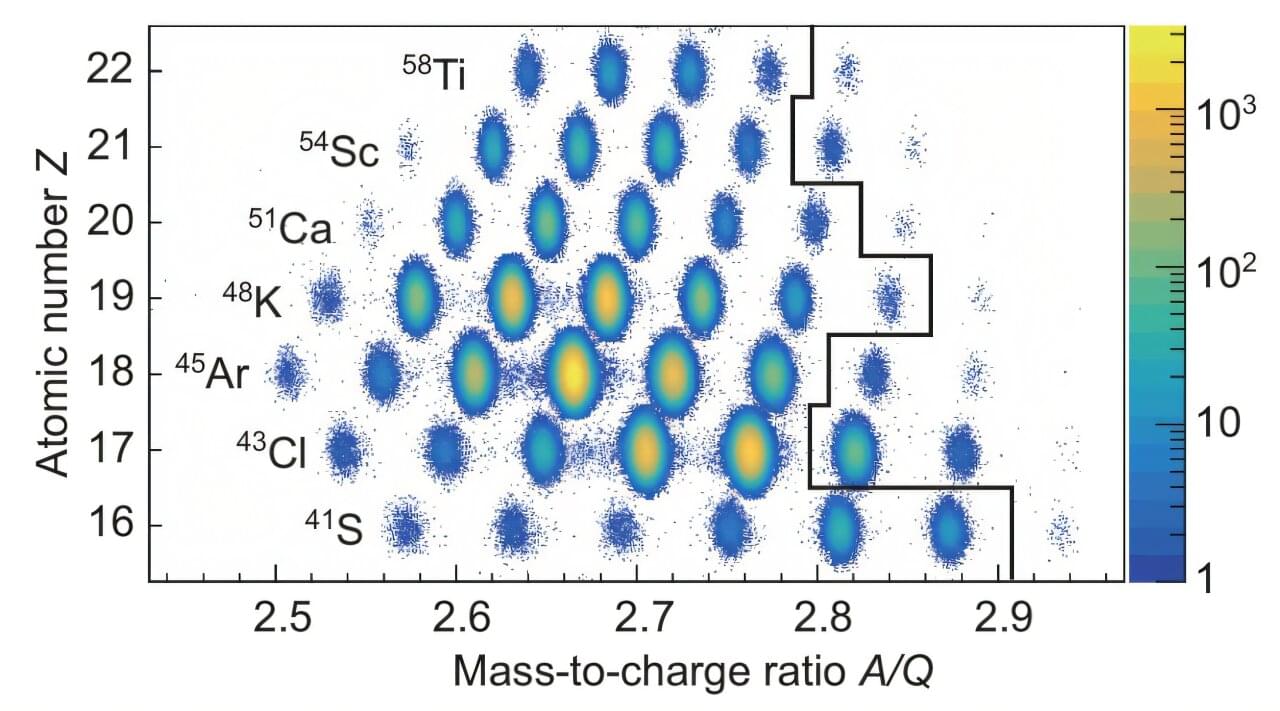
An international team of researchers has systematically measured the β-decay half-lives of 40 nuclei near calcium-54, providing key experimental data for understanding the structure of extremely neutron-rich nuclei.
The study, published in Physical Review Letters, was led by researchers from the Institute of Modern Physics (IMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with institutions including RIKEN in Japan and Peking University.
Atomic nuclei exhibit exceptional stability when the proton (Z) or neutron (N) number reaches certain “magic numbers,” such as 2, 8, 20, 28, 50, 82, or 126. The shell model successfully explained these magic numbers by introducing spin-orbit coupling, a contribution for which M. Mayer and J. Jensen were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1963.