Researchers led by Aurore Perrault at Concordia University, Canada and Valeria Kebets at McGill University, Canada, have used a complex data-driven analysis to uncover relationships among multiple aspects of sleep and individual variation in health, cognition, and lifestyle.
Published in PLOS Biology, the study reveals five sleep –biopsychosocial profiles and their associated patterns of functional connectivity among brain regions.
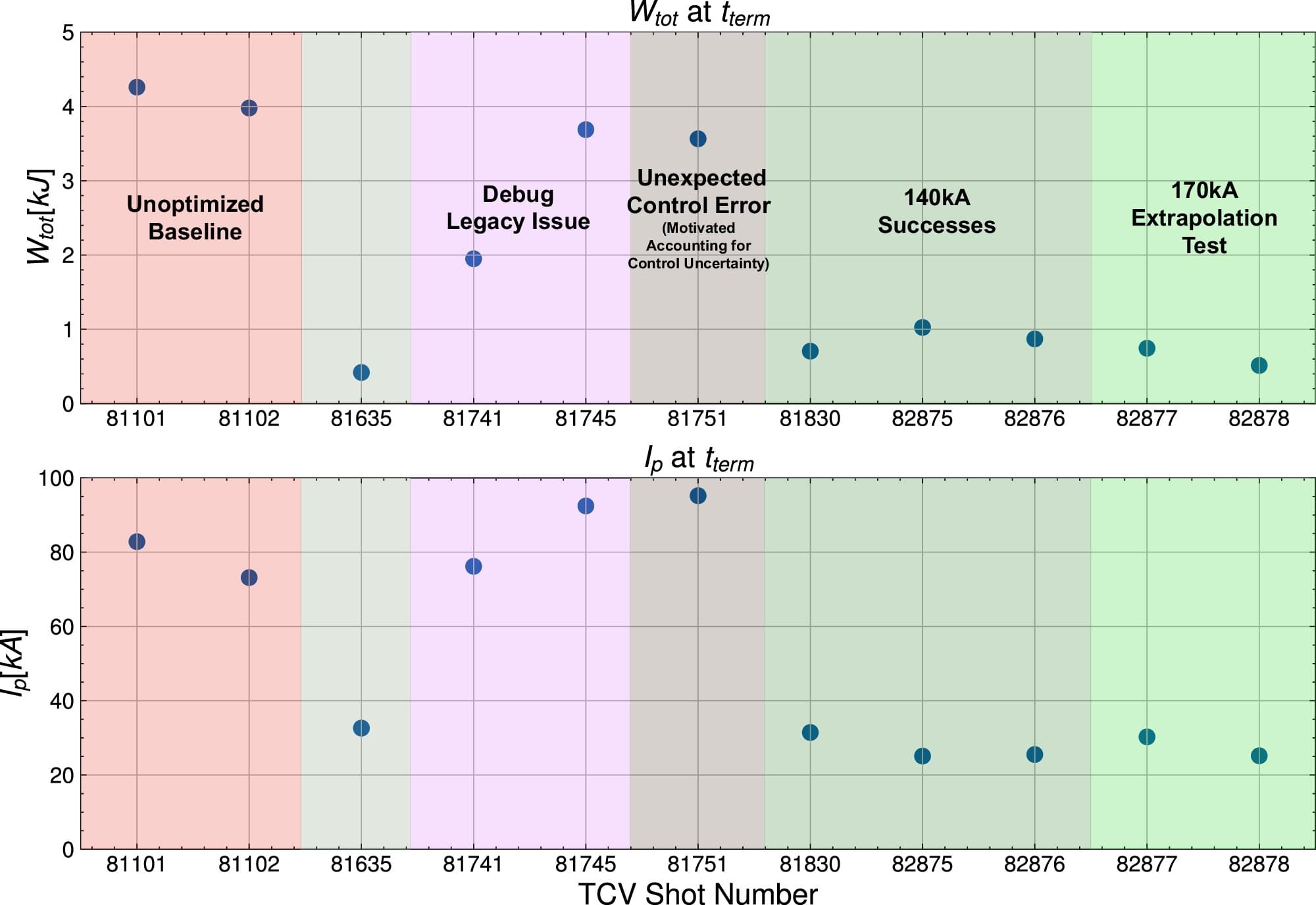
Most studies of sleep focus on a single aspect, such as duration, and examine how it relates to a single outcome, like poor mental health. However, trying to understand and predict outcomes by combining the results of many different single-association studies invariably fails. The new study by Perrault and team takes a different approach. Using a sample of 770 people from the Human Connectome Project dataset, they conducted a multivariate, data-driven analysis.