A Nature analysis reveals the 25 highest-cited papers published this century and explores why they are breaking records.



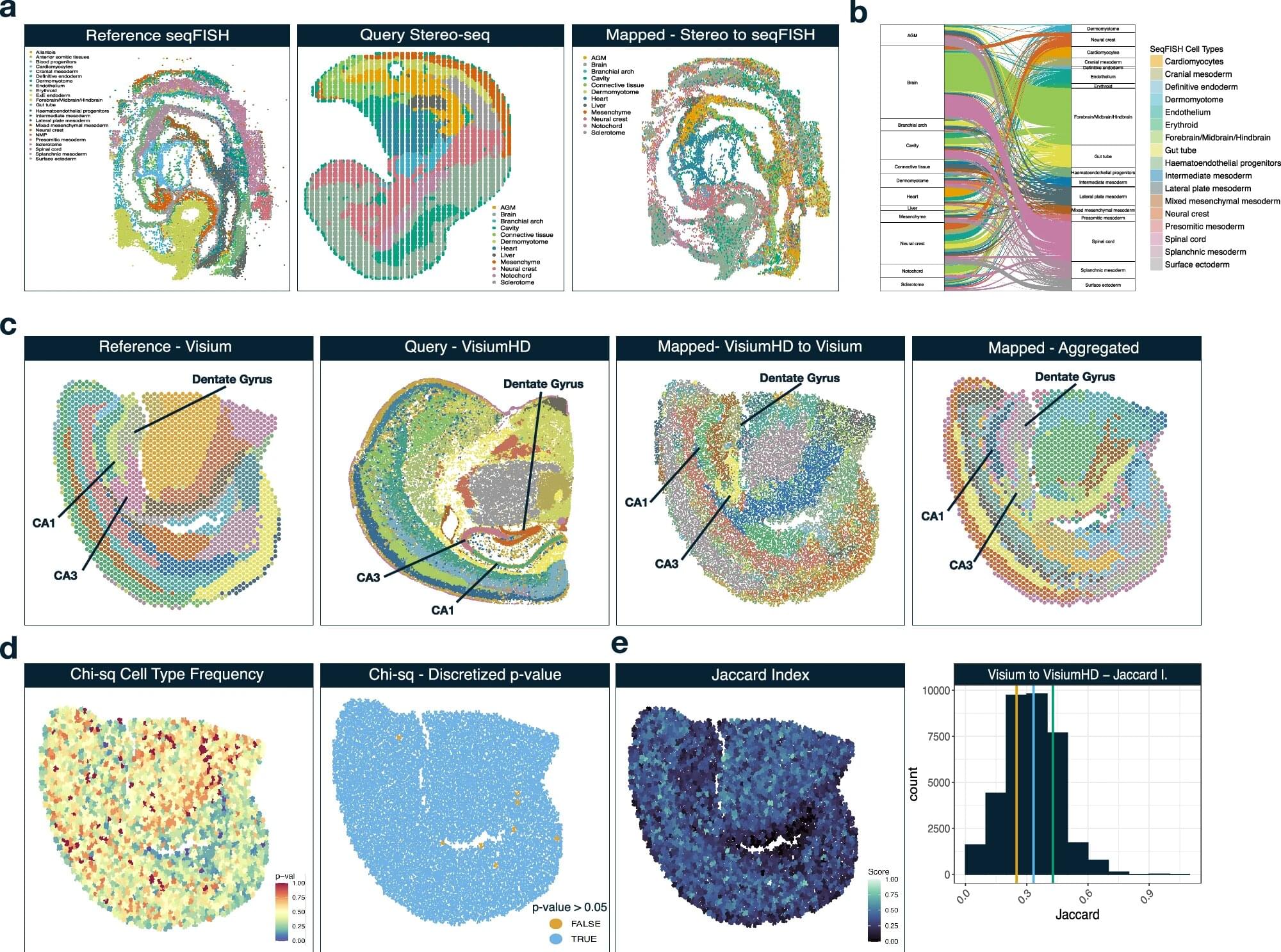
Researchers at VCU Massey Comprehensive Cancer Center have developed a new computational tool called Vesalius, which could help clinicians understand the complex relationships between cancer cells and their surrounding cells, leading to potential discoveries regarding the development of hard-to-treat cancers.
Findings from a new study, published in Nature Communications, could help guide the identification of predictive biomarkers for multiple cancers and better inform the effectiveness of different treatment options based on individuals’ specific type of disease.
Rajan Gogna, Ph.D., member of the Developmental Therapeutics research program at Massey and assistant professor in the VCU School of Medicine’s Department of Human and Molecular Genetics, and a team of collaborators were driven by the goal of interpreting extensive amounts of data in a meaningful way.
JMP offers a 30-day free trial for anyone, anywhere. Go to https://www.jmp.com/scishow to see the benefits of visual statistics for yourself.
Rocky bodies like moons, asteroids, and comets are chock full of resources, from water, to helium-3, to rare earth elements. But how can we access them? Some scientists have proposed using microbes to aid in the mining of certain metals.
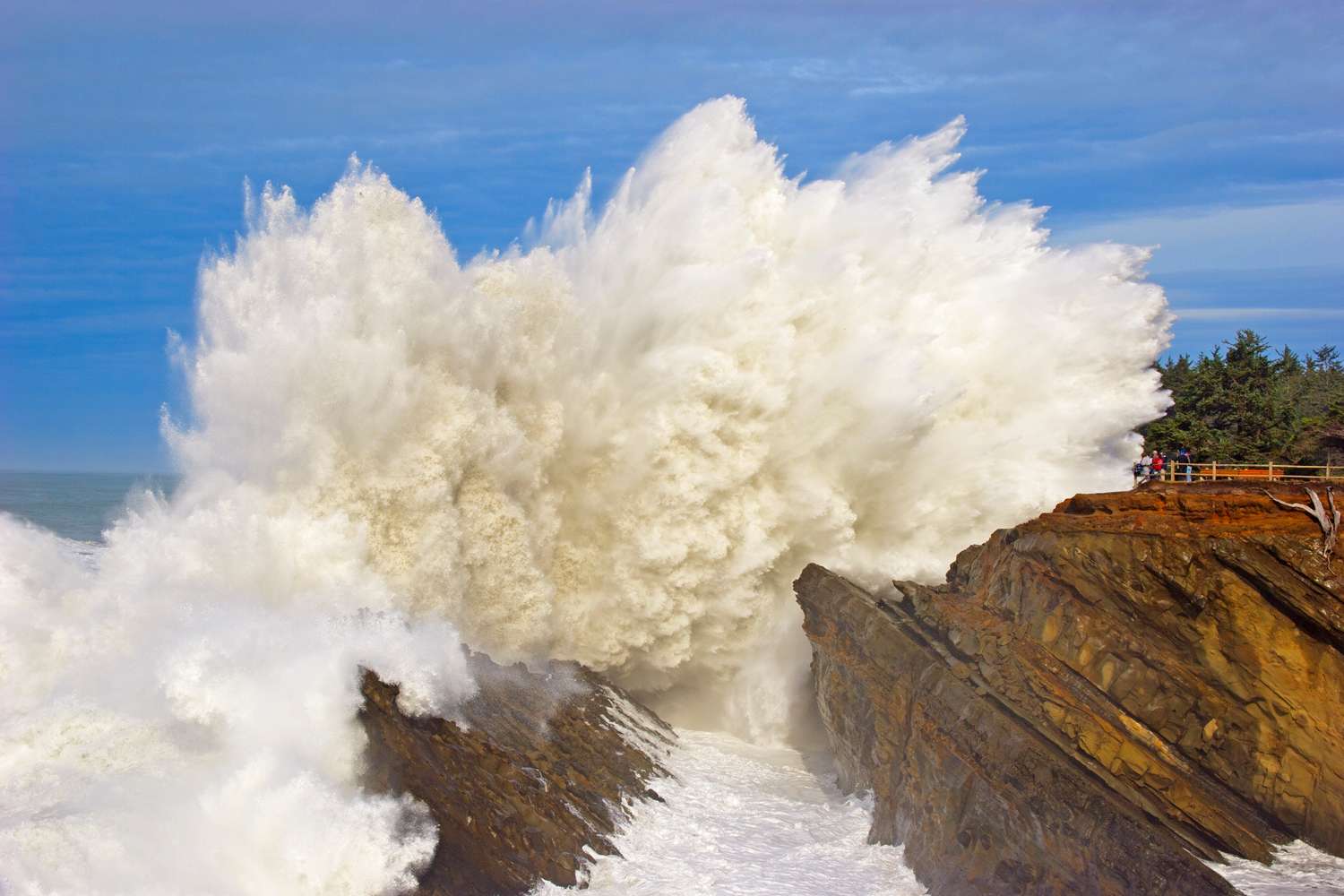



An underwater volcano off the Pacific northwest coast is projected to erupt soon.
Researchers at Oregon State University (OSU) have been recording activity at the Axial Seamount, located roughly 300 miles off the coast of Oregon and 4,900 feet under the surface, per ABC News and Axios. The underwater volcano’s recent behavior has signaled to OSU researchers that it’s tending toward an eruption in the near future.
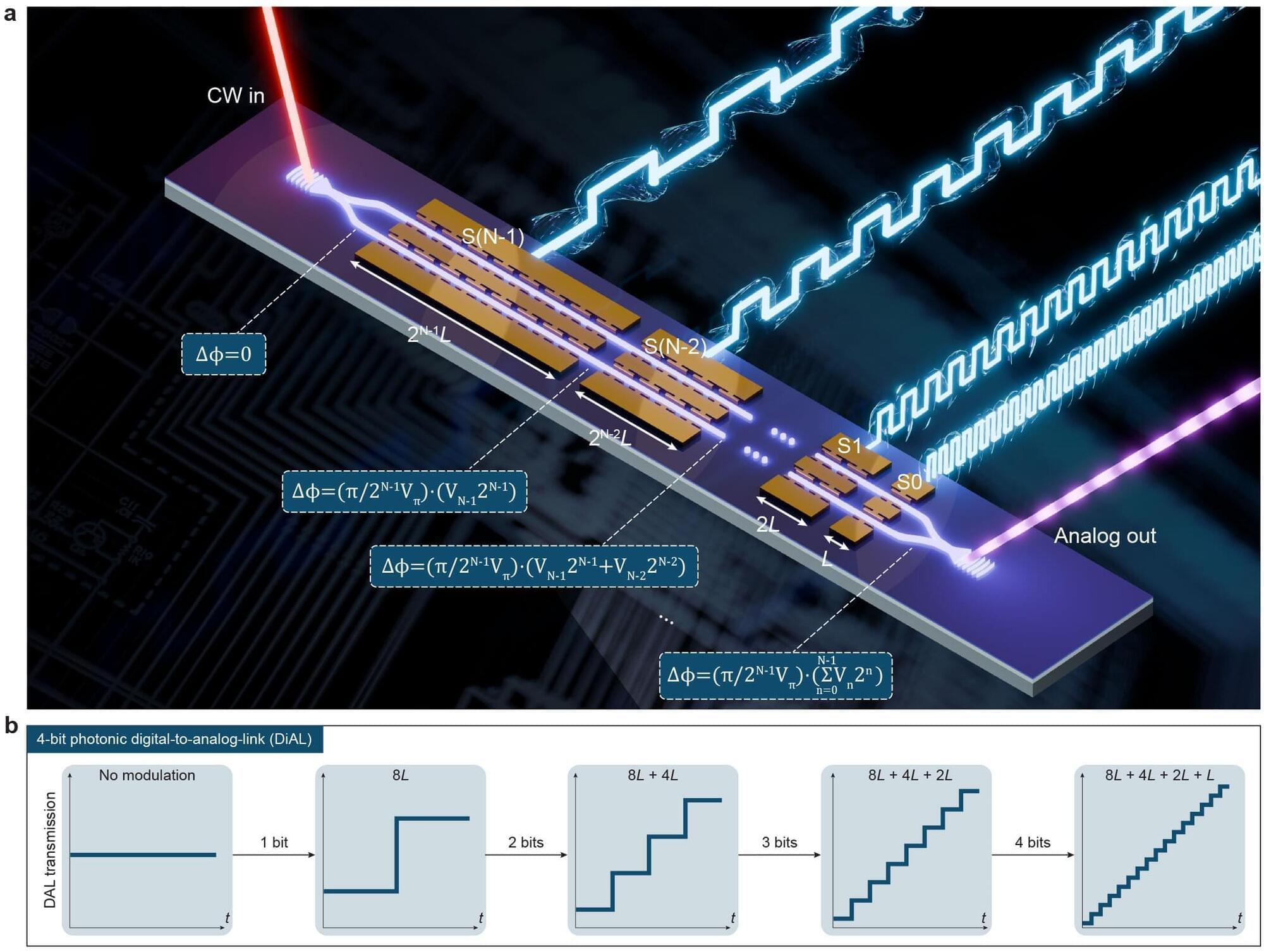
Addressing a major roadblock in next-generation photonic computing and signal processing systems, researchers at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have created a device that can bridge digital electronic signals and analog light signals in one fluid step.
Built on chips made out of lithium niobate, the workhorse material of optoelectronics, the new device offers a potential replacement for the ubiquitous but energy-intensive digital-to-analog conversion and electro-optic modulation systems used all over today’s high-speed data networks.
“Optical communication and high-performance computing, including large language models, relies on conversion of massive amounts of data between the electrical domain—used for storage and computation—and the optical domain used for data transfer,” said senior author Marko Lončar, the Tiantsai Lin Professor of Electrical Engineering at SEAS.