Dwarkesh Patel
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
ARK Robotics Research
Automation and robotics, particularly with the integration of AI, are transforming industries and poised to significantly impact the workforce, but are likely to lead to a reduction in work hours and increased productivity rather than total job destruction.
## Questions to inspire discussion.
Investment & Market Opportunity.
🤖 Q: What is the revenue potential for robotics by 2025? A: ARK Invest projects a $26 trillion global revenue opportunity across household and manufacturing robotics by 2025, driven by convergence of humanoid robots, AI, and computer vision technologies.
💰 Q: How should companies evaluate robot ROI for deployment? A: Robots are worth paying for based on task-specific capabilities delivering 2–10% productivity gains, unlike autonomous vehicles requiring full job performance—Roomba succeeded despite early limitations by being novel and time-saving for specific tasks.
Implementation Strategy.
Most sensitive radio observations to date find no evidence of technosignature from 3I/ATLAS
Since the interstellar object (ISO) 3I/ATLAS was first discovered on July 1, 2025, it has garnered much attention, including speculation, hopes and fears that it may somehow contain evidence of technologically advanced civilizations outside of our solar system.
Now, a new paper published on the arXiv preprint server details the findings from radio observations made at the 100-meter Green Bank Telescope as a part of the Breakthrough Listen program, designed to look for signs of alien life. The data were taken on December 18, 2025—the day before the object’s closest approach to Earth, and those hoping for evidence of advanced alien civilizations may not like the results.
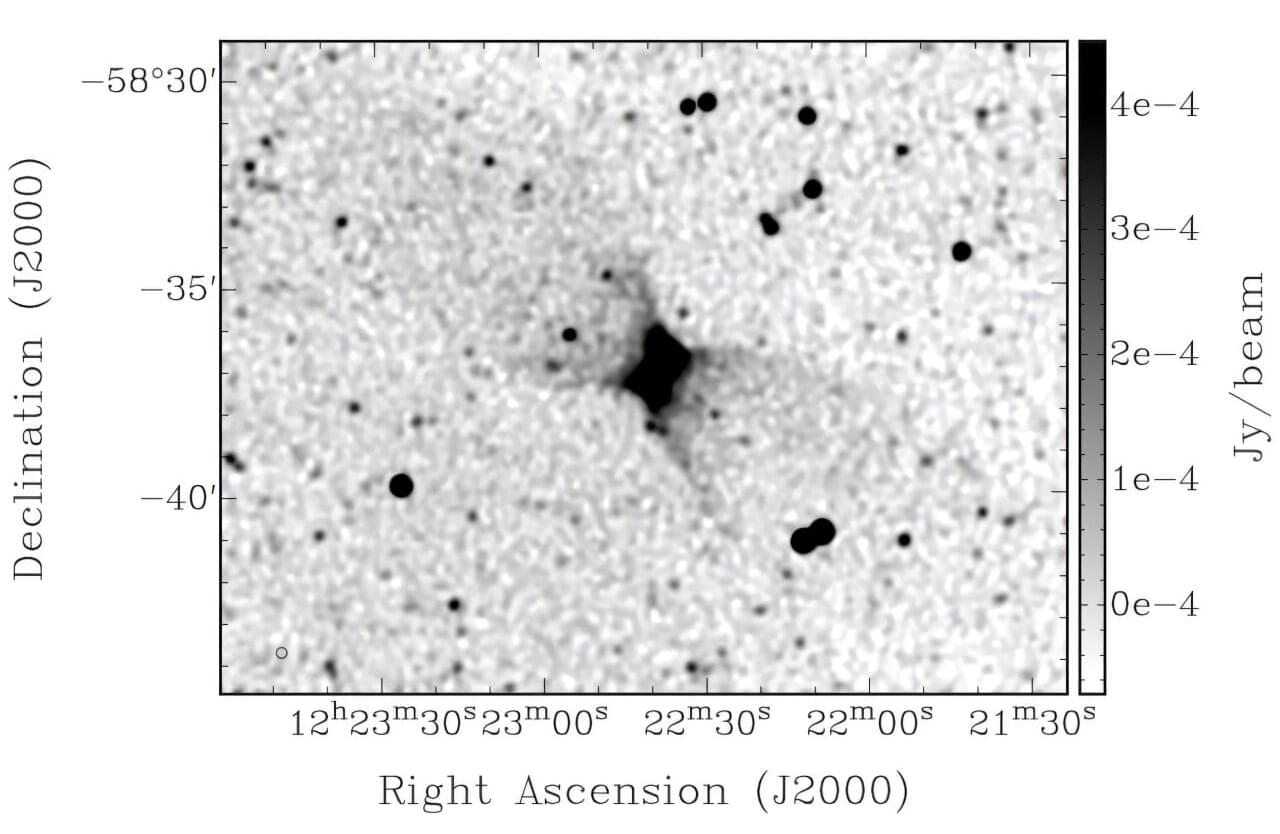
ASKAP discovers a spectacular outflow in a nearby galaxy
Using the Australian Square Kilometer Array Pathfinder (ASKAP), an international team of astronomers has discovered a spectacular bipolar outflow from the disk of a nearby galaxy known as ESO 130-G012. The finding was reported in a paper published December 17 on the pre-print server arXiv.
ESO 130-G012 is an edge-on galaxy at a distance of some 55 million light years, with an estimated stellar mass of about 11 billion solar masses. The galaxy has a star-formation rate at a level of 0.2 solar masses per year and hosts a black hole approximately 50 million times more massive than the sun.
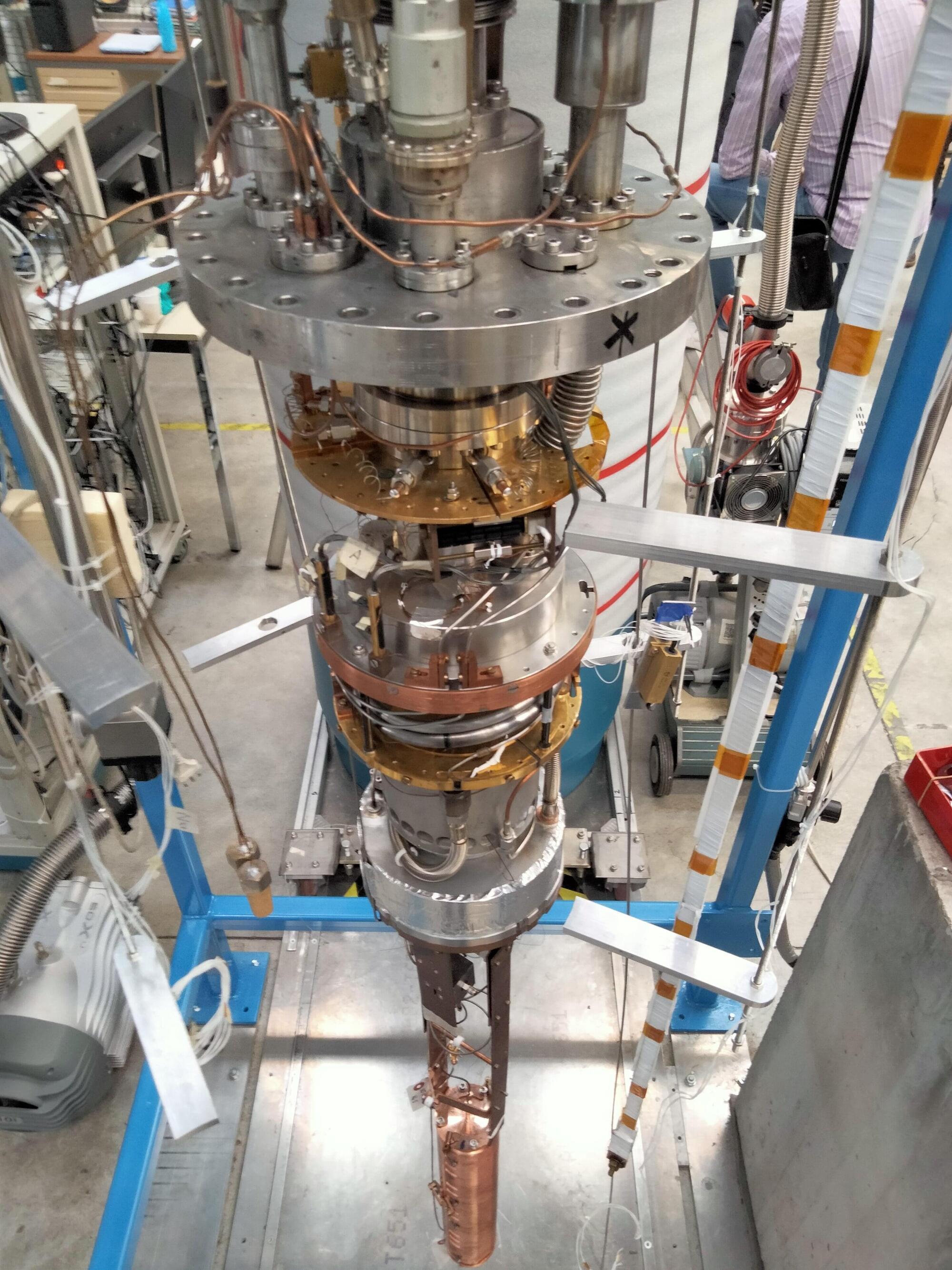

Hunting for dark matter axions with a quantum-powered haloscope
Axions are hypothetical light particles that could solve two different physics problems, as they could explain why some nuclear interactions don’t violate time symmetry and are also promising dark matter candidates. Dark matter is a type of matter that does not emit, reflect or absorb light, and has never been directly observed before.
Axions are very light particles theorized to have been produced in the early universe but that would still be present today. These particles are expected to interact very weakly with ordinary matter and sometimes convert into photons (i.e., light particles), particularly in the presence of a strong magnetic field.
The QUAX (Quest for Axions/QUaerere AXion) collaboration is a large group of researchers based at different institutes in Italy, which was established to search for axions using two haloscopes located in Italy at Laboratori Nazionali di Legnaro (LNL) and Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati (LNF), respectively.

AI model uses social media posts to predict unemployment rates ahead of official data
Social media posts about unemployment can predict official jobless claims up to two weeks before government data is released, according to a study. Unemployment can be tough, and people often post about it online.
Researcher Sam Fraiberger and colleagues recently developed an artificial intelligence model that identifies unemployment disclosures on social media. The work is published in the journal PNAS Nexus.
Data from 31.5 million Twitter users posting between 2020 and 2022 was used to train a transformer-based classifier called JoblessBERT to detect unemployment-related posts, even those that featured slang or misspellings, such as “I needa job!” The authors used demographic adjustments to account for Twitter’s non-representative user base, then forecast US unemployment insurance claims at national, state, and city levels.
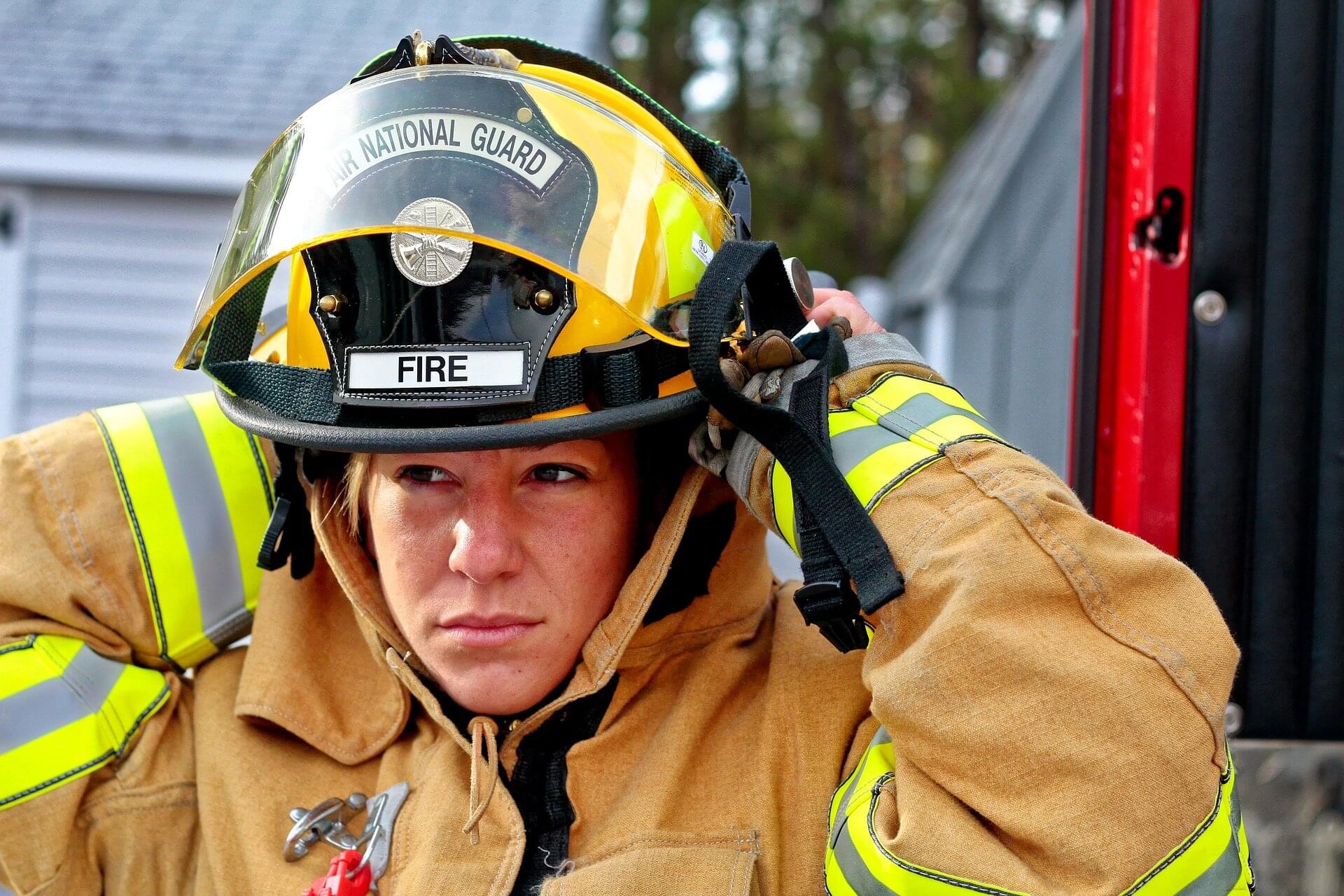

Simple wipe test reveals hidden PFAS contamination on firefighter protective gear
The flames die down. The sirens fade. Firefighters peel off their gear, thinking the danger has passed. But in the quiet aftermath, another enemy lingers, an invisible film of “forever chemicals” clinging to jackets, pants and masks.
Researchers at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, part of the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, have developed a way to see what the eye cannot.
A simple wipe test detected invisible cancer-linked “forever chemicals” on every set of firefighter gear examined, including breathing masks, according to new research from Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, part of the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine. The non-destructive method offers fire departments a practical way to identify and reduce exposure to per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), chemicals tied to increased cancer risk that can linger on gear long after a fire is out.

High risk of sleep apnea linked to poorer mental health in adults over 45
Researchers at Ottawa Hospital Research Institute and University of Ottawa found that high risk of obstructive sleep apnea was associated with approximately 40% higher odds of a composite poor mental health outcome at baseline and follow-up among adults aged 45–85 years in the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging.
Identifying factors associated with mental health outcomes is an important goal on several fronts. Mental health conditions rank among the leading contributors to global disease burden, with anxiety and depressive disorders described as most common. Individuals living with mental health conditions face higher risks of cardiometabolic diseases, unemployment, homelessness, disability, and hospitalizations. Economically, mental disorders carry an estimated $1 trillion annual global cost in lost productivity.
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) involves repeated upper airway narrowing during sleep. Disturbed breathing can break up sleep (sleep fragmentation), trigger a stress response in the nervous system (sympathetic activation), and cause episodes of low oxygen in the blood (intermittent hypoxemia).

Too much screen time too soon? Study links infant screen exposure to brain changes and teen anxiety
Children exposed to high levels of screen time before age 2 showed changes in brain development that were linked to slower decision-making and increased anxiety by their teenage years, according to new research by Asst. Prof. Tan Ai Peng and her team from A*STAR Institute for Human Development and Potential (A*STAR IHDP) and National University of Singapore (NUS) Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, using data from the Growing Up in Singapore Towards Healthy Outcomes (GUSTO) cohort.
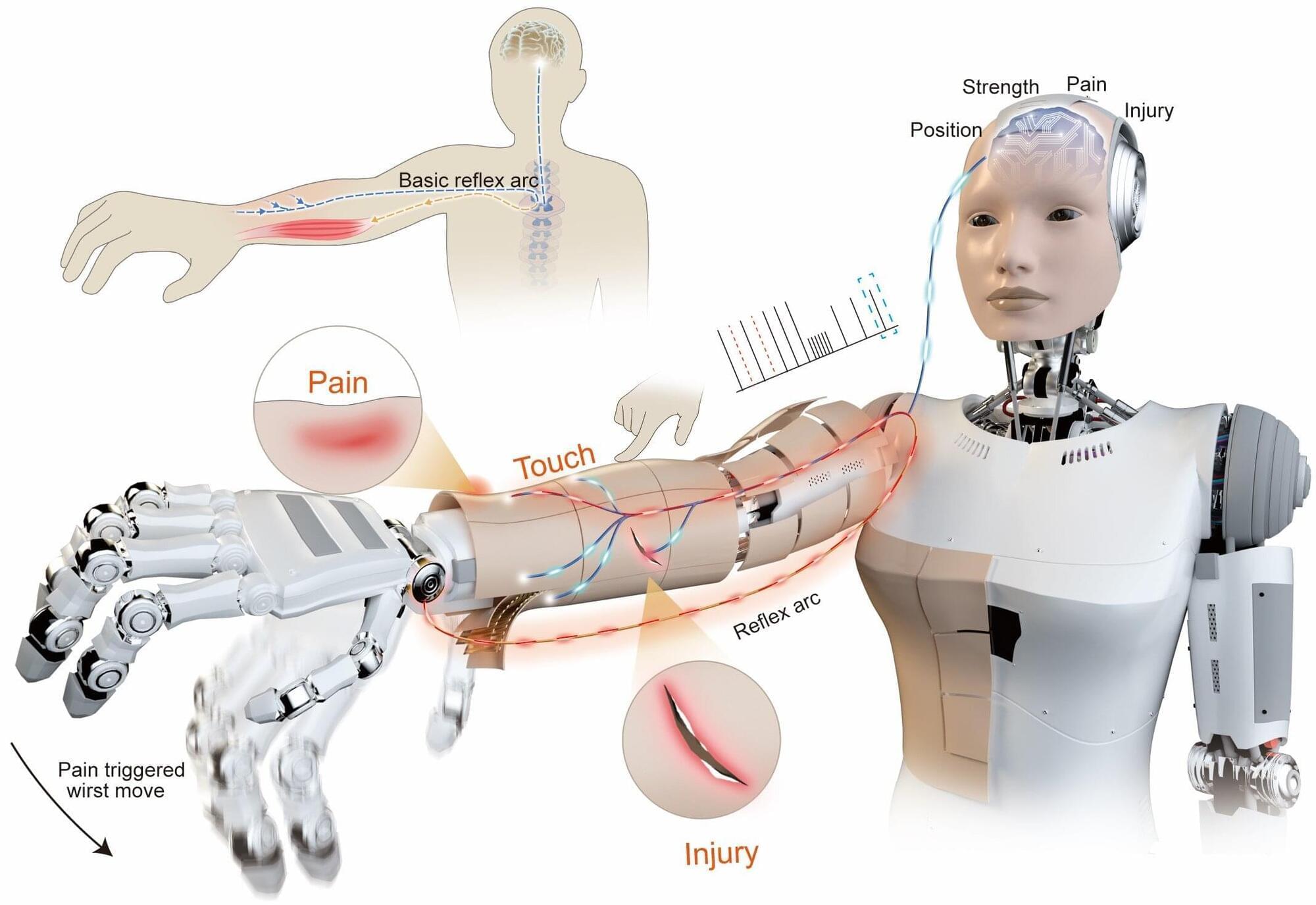
New robotic skin lets humanoid robots sense pain and react instantly
If you accidentally put your hand on a hot object, you’ll naturally pull it away fast, before you have to think about it. This happens thanks to sensory nerves in your skin that send a lightning-fast signal to your spinal cord, which immediately activates your muscles. The speed at which this happens helps prevent serious burns. Your brain is only informed once the movement has already started.
If something similar happens to a humanoid robot, it typically has to send sensor data to a central processing unit (CPU), wait for the system to process it, and then send a command to the arm’s actuators to move. Even a brief delay can increase the risk of serious damage.
But as humanoid robots move out of labs and factories and into our homes, hospitals and workplaces, they will need to be more than just pre-programmed machines if they are to live up to their potential. Ideally, they should be able to interact with the environment instinctively. To help make that happen, scientists in China have developed a neuromorphic robotic e-skin (NRE-skin) that gives robots a sense of touch and even an ability to feel pain.