Background and ObjectivesVascular dysfunction contributes to Alzheimer disease (AD) and related dementias (ADRDs), but the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. Previous studies link midlife hemostasis and platelet aggregation measures to late-life…






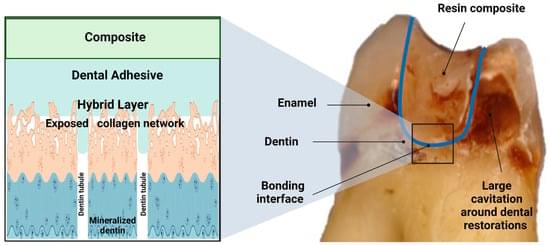
Damage in the bonding interface is a significant factor that leads to premature failure of dental bonded restorations. The imperfectly bonded dentin-adhesive interface is susceptible to hydrolytic degradation and bacterial and enzyme attack, severely jeopardizing restorations’ longevity. Developing caries around previously made restorations, also called “recurrent or secondary caries,” is a significant health problem. The replacement of restorations is the most prevailing treatment in dental clinics, leading to the so-called “tooth death spiral”. In other words, every time a restoration is replaced, more tooth tissue is removed, increasing the size of the restorations until the tooth is eventually lost. This process leads to high financial costs and detriment to patients’ quality of life.
A new study reveals a surprising mechanism that might be behind the beneficial effects of NAD+ in preclinical models of Alzheimer’s [1].
Which way to splice it?
Not every part of a DNA sequence gets translated into a protein. Each sequence consists of exons, which are included in the final RNA transcript, and introns, which are thrown away.