Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a common virus that causes mononucleosis, or mono for short, and is associated with some types of cancer and autoimmune diseases. Despite EBV’s known effects and potential to cause disease, there are few therapeutic options and no licensed vaccines targeting the virus. Looking for ways to counter EBV, NIAID researchers are examining how the virus recognizes and interacts with cells at the molecular level. New research published in Immunity reveals the high-resolution crystal structure of a protein on the surface of EBV in complex with the receptor it binds to on the surface of human immune cells, called B cells. The researchers also discovered antibodies that potently neutralize EBV and found that they recognize the viral surface protein using interactions similar to those between EBV and its receptor on host cells. This research identifies a vulnerable site on EBV that could lead to the design of much-needed interventions against the virus.
EBV, also known as human herpesvirus 4, is one of the most common human viruses—nine out of ten people have or will have EBV in their lifetime. After being infected with EBV, many people experience no symptoms, but some experience symptoms of mononucleosis, such as fever, sore throat and fatigue. These symptoms are often mild but can be more severe in teens or adults. After the early stages of infection, the virus hides in the body and can emerge later in life or when the immune system is weakened. Recent studies have also found that EBV is linked to several types of cancer, autoimmune diseases including lupus, and other disorders.
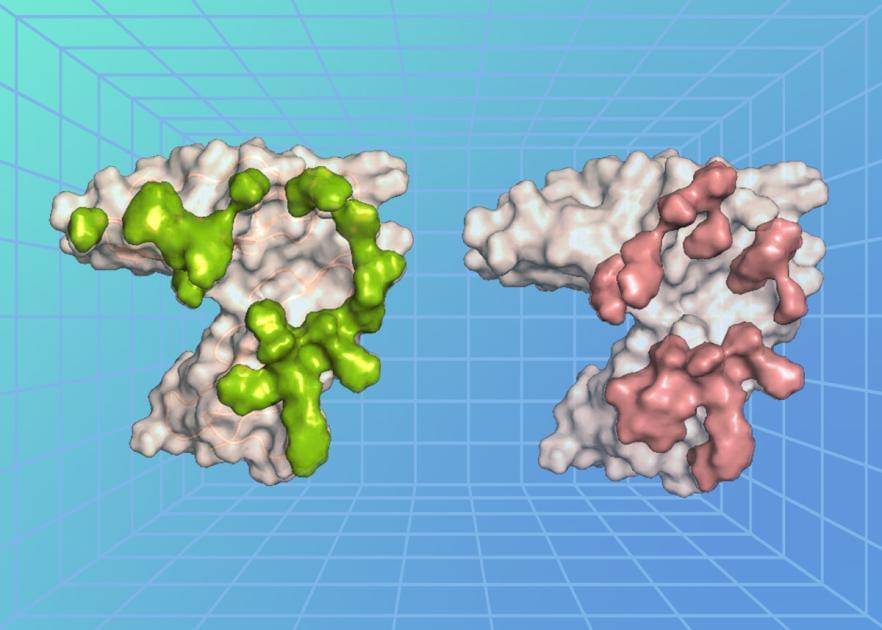
A key step in EBV infection is for the virus to enter a cell in the body, which begins with the virus binding to a protein on the cell’s surface. The researchers, led by Dr. Masaru Kanekiyo, chief of the Molecular Immunoengineering Section at NIAID’s Vaccine Research Center, examined the atomic-level structure of an EBV surface protein called gp350 when bound to a protein on the surface of B cells called complement receptor type 2 (CR2). Usually, CR2 binds to a protein fragment, or ligand, called complement component C3d as a part of the immune response following a viral infection. The researchers found that the EBV protein precisely bound to the cell surface protein CR2 at the region where its natural ligand C3d binds, revealing that there is structural similarity between EBV and C3d in recognizing CR2 and how the virus exploits this interaction to enter and infect a cell.