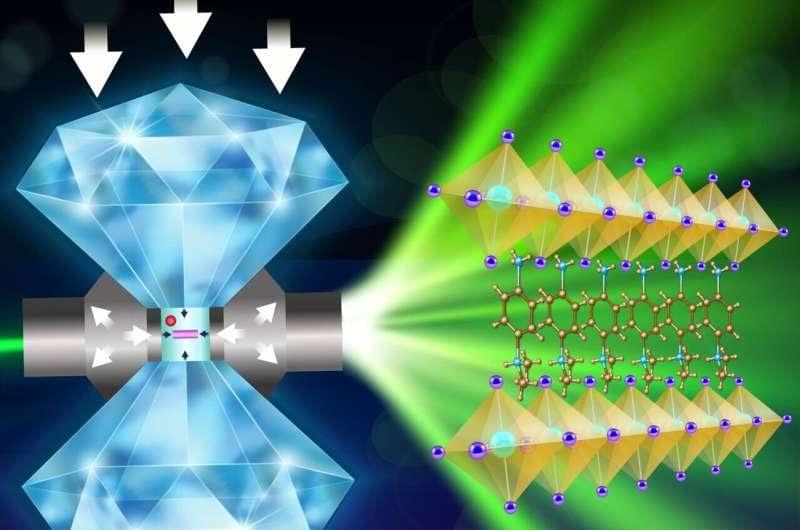
Perovskites have long captivated the interest of materials scientists and engineers for their remarkable potential in next-generation solar cells, LEDs, and optoelectronic devices. Now, a newly published study pushes the envelope even further by showing how carefully applied pressure can finely tune the light-handling properties of a 2D hybrid perovskite, marking a significant leap toward real-time structural control in photonic technologies.
The research, carried out using the Canadian Light Source (CLS) at the University of Saskatchewan and the Advanced Photon Source (APS) in Chicago, utilized ultrabright synchrotron radiation to observe how perovskite layers respond under pressure. The focus was a 2D Dion–Jacobson hybrid lead iodide perovskite with alternating organic and inorganic sheets—structures whose interaction defines how the material absorbs, emits, or modulates light.