Millennium will deliver the ground and on-orbit segments of the program and Firefly will provide the responsive launch service.
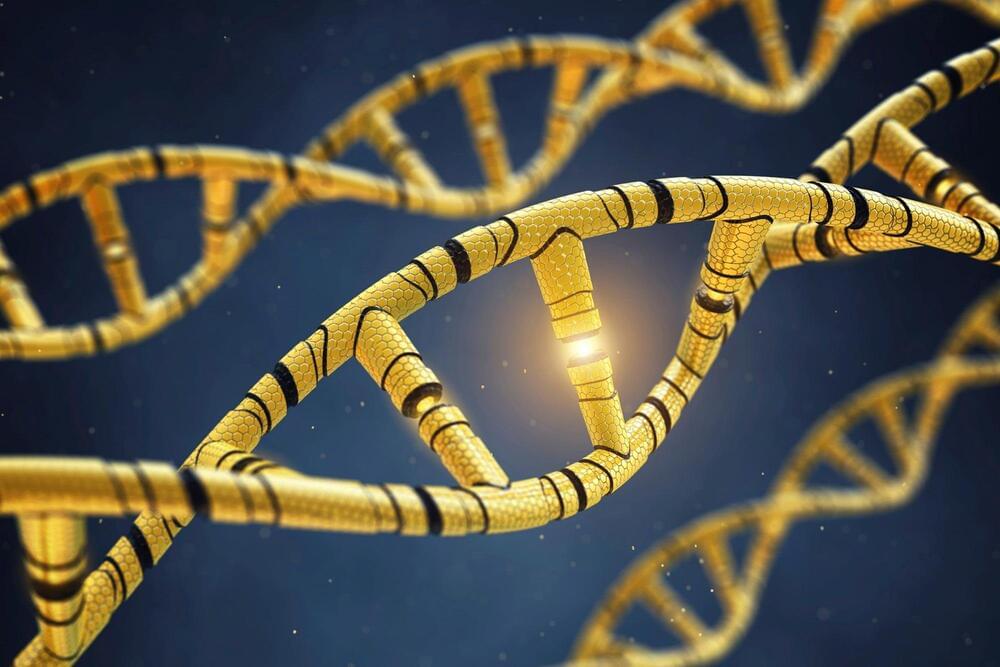




Changing the epigenetic marks on chromosomes results in altered gene expression in offspring and in grandoffspring, demonstrating ‘transgenerational epigenetic inheritance.’
Without changing the genetic code in the DNA
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule composed of two long strands of nucleotides that coil around each other to form a double helix. It is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms that carries genetic instructions for development, functioning, growth, and reproduction. Nearly every cell in a person’s body has the same DNA. Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus (where it is called nuclear DNA), but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria (where it is called mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA).
Please Support The Channel:
YouTube Super Thanks (click below)
YouTube Membership (click below)
https://www.buymeacoffee.com/JoeBlogs.
https://www.patreon.com/joeblogsYT
Amazon Shopping USA — https://amzn.to/3qwnwHB
Amazon Shopping UK — https://amzn.to/3LbHjFL
Amazon Shopping Canada — https://amzn.to/3BIyXlS
Amazon Shopping Australia — https://amzn.to/3eHQZvy.
Click thro the link, buy your items as normal and Amazon will pay me a small commission.
Russia is LOSING the War against Ukraine and has RETREATED from the Key Town of LYMAN which it has held since May and was used as a Supply & Transport HUB for the North of Ukraine. In Direct Response one of President Putin’s RIGHT HAND MEN has Urged Russia to Launch LOW YIELD NUCLEAR STRIKES on Ukraine. In this video I provide full details of the latest situation, as well as providing on update on the NORD STREAM Pipelines, European Gas SUPPLY and details of what a Low Yield Nuclear Bomb is. Finally I provide my view on the implications of the current situation for both Russia & the GLOBAL ECONOMY.
For specific details please check out the CHAPTER list below.
Thanks for watching and please LIKE and SUBSCRIBE.
If you like this video and are would like to buy me a coffee please click the link below. THANK YOU it is very much appreciated.
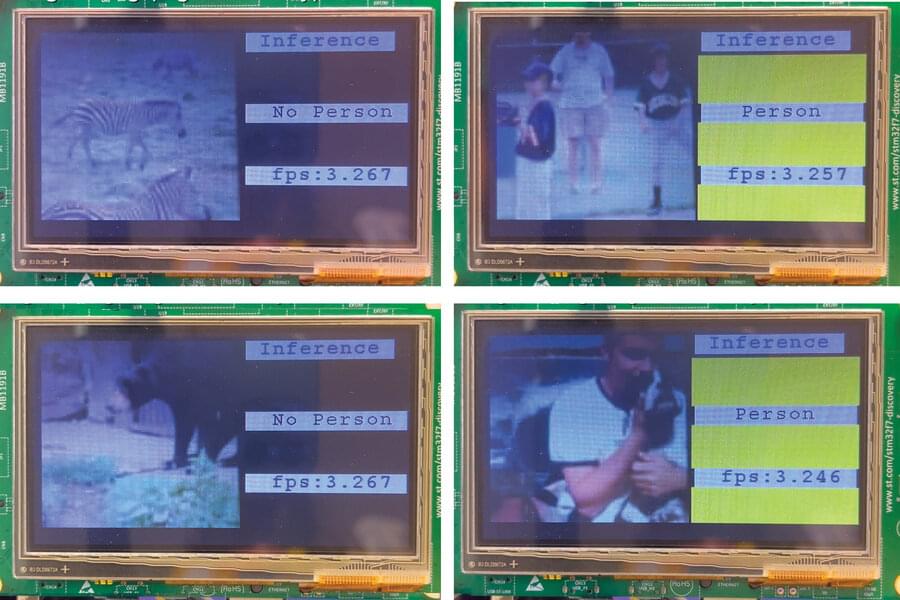

Microcontrollers, miniature computers that can run simple commands, are the basis for billions of connected devices, from internet-of-things (IoT) devices to sensors in automobiles. But cheap, low-power microcontrollers have extremely limited memory and no operating system, making it challenging to train artificial intelligence models on “edge devices” that work independently from central computing resources.
Training a machine-learning model on an intelligent edge device allows it to adapt to new data and make better predictions. For instance, training a model on a smart keyboard could enable the keyboard to continually learn from the user’s writing. However, the training process requires so much memory that it is typically done using powerful computers at a data center, before the model is deployed on a device. This is more costly and raises privacy issues since user data must be sent to a central server.
To address this problem, researchers at MIT and the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab have developed a new technique that enables on-device training using less than a quarter of a megabyte of memory. Other training solutions designed for connected devices can use more than 500 megabytes of memory, greatly exceeding the 256-kilobyte capacity of most microcontrollers (there are 1,024 kilobytes in one megabyte).
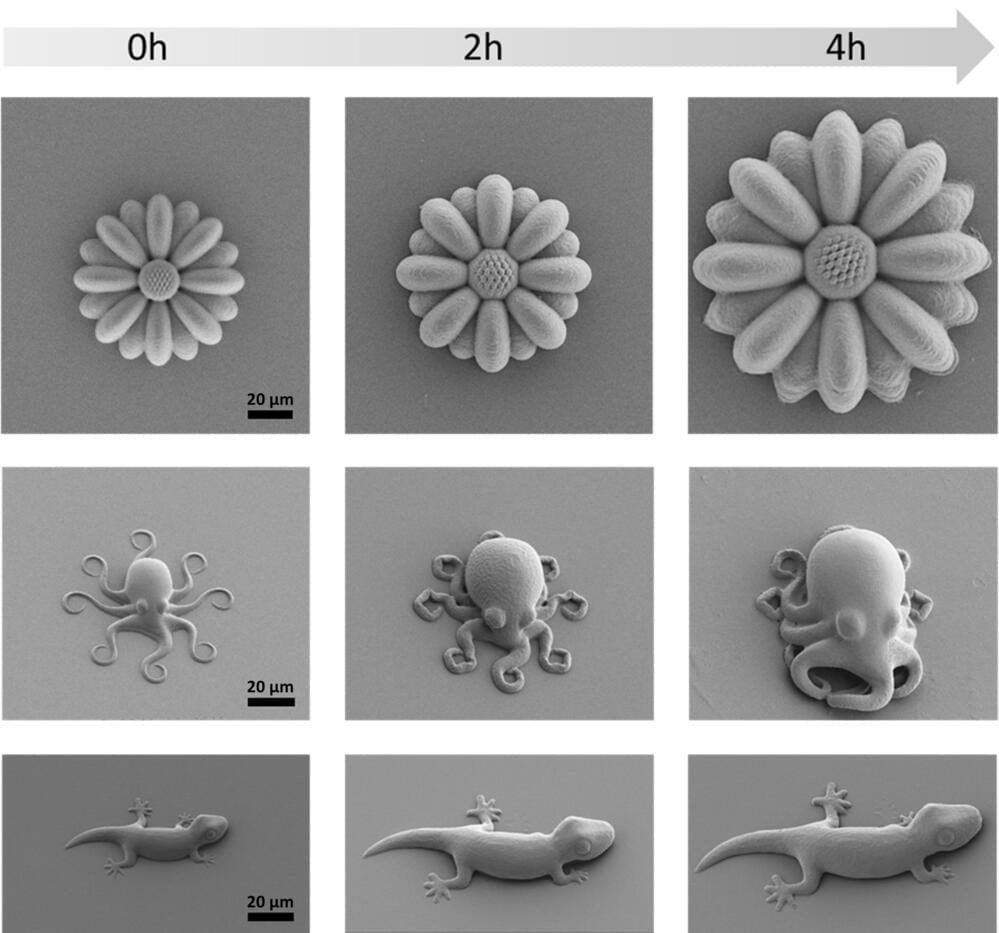
Although just cute little creatures at first glance, the microscopic geckos and octopuses fabricated by 3D laser printing in the molecular engineering labs at Heidelberg University could open up new opportunities in fields such as microrobotics or biomedicine.
The printed microstructures are made from novel materials —known as smart polymers—whose size and mechanical properties can be tuned on demand and with high precision. These “life-like” 3D microstructures were developed in the framework of the “3D Matter Made to Order” (3DMM2O) Cluster of Excellence, a collaboration between Ruperto Carola and the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT).
“Manufacturing programmable materials whose mechanical properties can be adapted on demand is highly desired for many applications,” states Junior Professor Dr. Eva Blasco, group leader at the Institute of Organic Chemistry and the Institute for Molecular Systems Engineering and Advanced Materials of Heidelberg University.



This article was originally published at The Conversation. The publication contributed the article to Space.com’s Expert Voices: Op-Ed & Insights. Have you ever made a mistake…
