Rejuveron increases to near-majority stake in Endogena to progress treatments for degenerative diseases of the eye.
Boston-based biotech Vincere Biosciences is on a mission to combat neurodegenerative disease by improving the quality of the mitochondria in our cells. The company was spun out from AI drug discovery company NeuroInitiative in 2018 after its platform identified that modulation of certain enzymes to repair mitochondrial health “may slow or stop the progression of Parkinson’s disease and other age-related disorders.”
In addition to seed funding, Vincere has received grants from the National Institutes of Health and Michael J Fox Foundation, and the company is now gearing up for a Series A funding round in early 2022.
Longevity. Technology: Mitochondria’s role in longevity is a hot topic. Often referred to as the “powerhouse of the cell”, these miniature organs within our cells play a key role in providing the energy needed for growth, repair and rejuvenation. As we age, our mitochondria begin to decline in function, and this decline is linked to a range of age-related diseases. We caught up with Vincere’s co-founder and CEO Dr Spring Behrouz to find out how her company aims to tap into the potential of these small but mighty biological players.
Visit our sponsor, Brilliant: https://brilliant.org/IsaacArthur/
When the largest of stars dies, the supernova they produce can outshine a whole galaxy, and potentially sterilize vast swathes of space. Future civilizations will need to be able to prevent or mitigate such events, though some might seek to artificially ignite a nova.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Support us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/IsaacArthur.
Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/1583992725237264/
Reddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/IsaacArthur/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Isaac_A_Arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: https://discord.gg/53GAShE
Listen or Download the audio of this episode from Soundcloud:
Episode’s Audio-only version: https://soundcloud.com/isaac-arthur-148927746/killing-stars.
Episode’s Narration-only version: https://soundcloud.com/isaac-arthur-148927746/killing-stars-narration-only.
Credits:
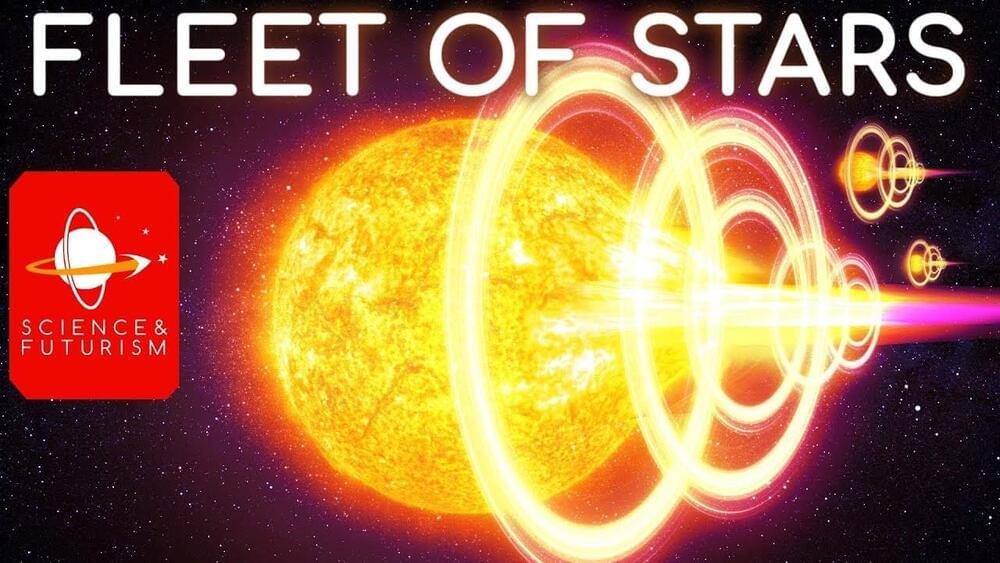
Fleet of Stars
Posted in cosmology, space travel
Start listening with a 30-day Audible trial and your first audiobook plus two Audible Originals are free. Visit.
http://www.audible.com/isaac or text “ISAAC” to 500–500.
Interstellar travel is very time consuming, moving from star to star, but perhaps we could use stars themselves as spaceships, and move whole solar systems or even galaxies.
Today we’ll look at how to use Shkadov Thrusters, novas, supernovae, black holes and quasars to move through space, literal starships.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Support us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/IsaacArthur.
SFIA Merchandise available: https://www.signil.com/sfia/
Social Media:
Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/1583992725237264/
Reddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/IsaacArthur/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Isaac_A_Arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: https://discord.gg/53GAShE
Listen or Download the audio of this episode from Soundcloud: Episode’s Audio-only version: https://soundcloud.com/isaac-arthur-148927746/fleet-of-stars.
O,.o! Omg o.o
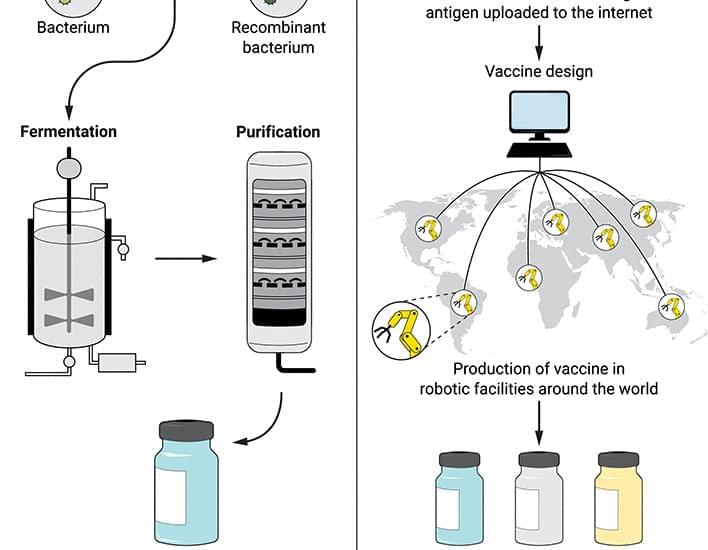
The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic has generated a renaissance in vaccinology, with COVID-19 mRNA vaccines delivering a “digital code” of the viral antigen with no need to purify proteins or inactivate pathogens.
A small community of mathematicians is using a software program called Lean to build a new digital repository. They hope it represents the future of their field.
At this point, the paper mingles cosmology, or the study of the universe and its origins, with biology. “We ask whether there might be a mechanism woven into the fabric of the natural world, by means of which the universe could learn its laws,” the authors write. In other words, a universal law might transcend all scientific fields. That means that the laws of physics, as we know them, could be subject to higher-order laws of the universe that control them—and that we can’t even comprehend.
“Exploring links between fields is crucial because knowledge is not fundamentally compartmentalized,” says Bruce Bassett, professor at the University of Cape Town’s Department of Mathematics and head of the Cosmology Group at the African Institute of Mathematical Sciences in South Africa. We humans are simply narrow-minded. “We segment and compress knowledge into biology, and physics, and sociology because of our limited brains, and the cost of that segmentation and compression is that we easily miss the commonalities and hidden universality between branches of human knowledge.”
It’s simple enough for AI to seem to comprehend data, but devising a true test of a machine’s knowledge has proved difficult.
This article is part of our reviews of AI research papers, a series of posts that explore the latest findings in artificial intelligence.
With their millions and billions of numerical parameters, deep learning models can do many things: detect objects in photos, recognize speech, generate text—and hide malware. Neural networks can embed malicious payloads without triggering anti-malware software, researchers at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of Illinois have found.
Their malware-hiding technique, EvilModel, sheds light on the security concerns of deep learning, which has become a hot topic of discussion in machine learning and cybersecurity conferences. As deep learning becomes ingrained in applications we use every day, the security community needs to think about new ways to protect users against their emerging threats.