Convolutional neural networks used to be the typical network architecture in modern computer vision systems. Transformers with attention mechanisms were recently presented for visual tasks, and they performed well. Convolutions and self-attention aren’t required for MLP-based (multi-layer perceptron) vision models to perform properly. As a result of these advancements, vision models are reaching new heights.
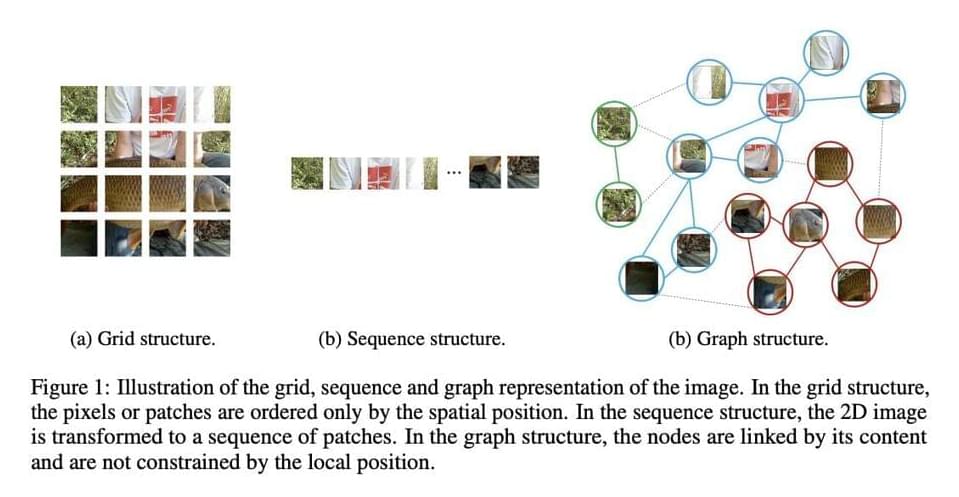
The input image is handled differently by different networks. In Euclidean space, image data is commonly represented as a regular grid of pixels. On the image, CNNs apply a sliding window and introduce shift-invariance and locality. The MLP vision transformer, which was released recently, treats the image as a series of patches.
Recognizing the items in an image is one of the most basic tasks of computer vision. The typically utilized grid or sequence structures in prior networks like ResNet and ViT are redundant and inflexible to process because the objects are usually not quadrate whose shape is irregular. An item can be thought of as a collection of parts, such as a human’s head, upper torso, arms, and legs. These sections are organically connected by joints, forming a graph structure. Furthermore, a graph is a generic data structure, with grids and sequences being special cases of graphs. Visual perception is more flexible and effective when an image is viewed as a graph.