Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg might be getting excited about the metaverse, but the idea is nothing new.



But with such a rapid expansion into this new virtual world, will it be safe, regulated and, is it something we should fear or accept with open arms?
We talk to David Reid, a Professor of AI and spatial computing at Liverpool Hope University to see what to expect from the future of the metaverse.
There’s a few definitions. You can think of it from a technological viewpoint, where it’s simply the successor of the internet. Computers once took up big rooms, but they’ve shrunk until we got things like pocket-sized smartphones that you constantly interact with. The metaverse takes this a step further, making the actual environment you interact with virtual, removing the interface of computers completely.

The promising results led to improved not only cognitive function but also brain connectivity.
An Inserm team at the Lille Neuroscience & Cognition laboratory is working with scientists at Lausanne University Hospital to evaluate the effectiveness of GnRH injection therapy in enhancing cognitive functions in a small group of Down syndrome patients, according to a press release published on Eurekalert.
Down syndrome is the most common chromosomal condition in the United States. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about one in every 6,000 babies born in the U.S. has Down syndrome. It causes various symptoms, such as deterioration in cognitive capacity.

Negative symptoms are complex psychopathology. Although evidence generally supported the NIMH five consensus domains, research seldom examined measurement invariance of this model, and domain-specific correspondence across multiple scales. This study aimed to examine the interrelationship between negative symptom domains captured by different rating scales, and to examine the domain-specific correspondence across multiple scales. We administered the Brief Negative Symptom Scale (BNSS), the Self-evaluation of Negative Symptoms (SNS), and the Scale for Assessment of Negative Symptoms (SANS) to 204 individuals with schizophrenia. We used network analysis to examine the interrelationship between negative symptom domains.
Summary: Fentanyl exposure produces specific EEG signatures in the brain. The findings also revealed the drug impairs people’s breathing four minutes before noticeable changes in alertness.
Source: Mass General.
Fentanyl is used to supplement sedation and to relieve severe pain during and after surgery, but it’s also one of the deadliest drugs of the opioid epidemic.

Summary: A new study reveals a genetic link between Alzheimer’s disease and several gut-related disorders. Researchers report Alzheimer’s patients and those with intestinal disorders have specific genes in common. The findings add to the evidence the gut-brain axis may play a role in the development of neurodegenerative disorders.
Source: Edith Cowan University.
People with gut disorders may be at greater risk of developing Alzheimer’s Disease (AD).
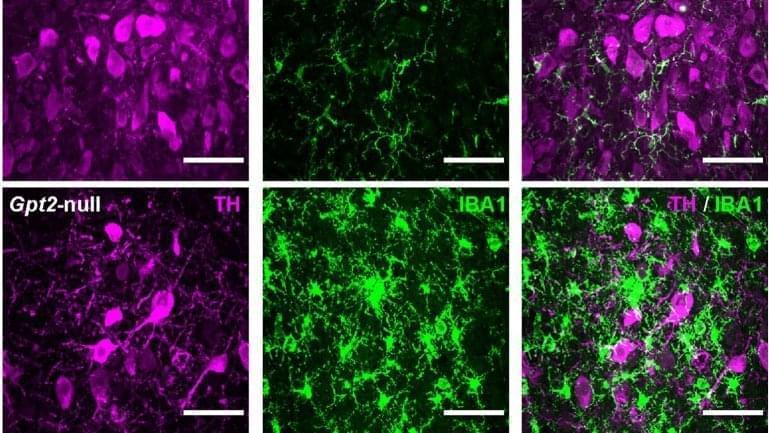
Summary: Study reveals a novel mechanism in locus coeruleus neurons caused by the loss of the GPT2 mitochondrial enzyme that is implicated in the development and progression of neurodegenerative diseases.
Source: Brown University.
The locus coeruleus is among the first brain regions to degenerate in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, physicians and scientists have known. But why this area is so vulnerable is less understood.
Summary: Researchers created a form of artificial vision for a blind woman with the aid of a brain implant position in the visual cortex. The results pave the way for the creation of visual brain prosthetics to help the blind to regain sight.
Source: KNAW
Newly published research details how a team of scientists from the University Miguel Hernández (Spain), the Netherlands Institute of Neuroscience (Netherlands) and the John A. Moran Eye Center at the University of Utah (USA) successfully created a form of artificial vision for a blind woman using a brain implant.

Summary: Those who are prone to motion sickness have a harder time adapting to cybersickness and different virtual reality environments. However, people can adapt to the effects of VR-associated cybersickness by playing the same game repeatedly.
Source: Iowa State University
While virtual reality has been around for decades, a combination of higher-resolution graphics, smoother tracking of the user’s movements and cheaper, sleeker headsets has propelled the immersive technology into arenas beyond gaming and military training.
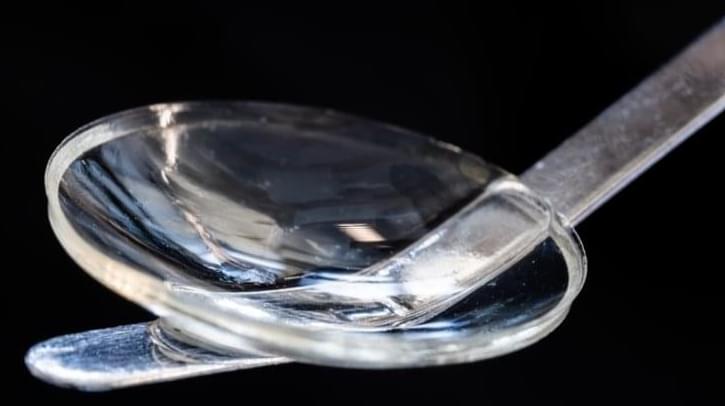

Summary: Researchers have developed a cornea implant from the collagen protein of pig skin. The implant restored the vision of 20 people with diseased corneas. The new implant could be a viable alternative to human cornea transplantation.
Source: Linkoping University.
Researchers and entrepreneurs have developed an implant made of collagen protein from pig’s skin, which resembles the human cornea. In a pilot study, the implant restored vision to 20 people with diseased corneas, most of whom were blind prior to receiving the implant.